A Guide to Hong Kong Monetary Authority Outsourcing Regulations




Join thousands of professionals and get the latest insight on Compliance & Cybersecurity.
It’s no longer news.
The Hong Kong Monetary Authority (HKMA) updated its outsourcing regulations in December 2023. For enterprise security executives like you seeking to become compliant, a crucial first step is asking: Why did the regulatory body update it again?
Reviewing the recent documentation extensively, I sensed why this update and compliance to it became a necessity. The first reason is the increasing adoption of technologies by financial institutions (FIs). The second is the ever-growing reliance on third-party vendors.
Albert Yuen also echoed these:


Yuen isn’t just the Head of Technology at Hong Kong-based Linklaters. He’s a Counsel with over 20 years of experience, specializing in privacy and cybersecurity. As he pointed out, this update is the HKMA’s reminder to re-evaluate your governance systems and security controls for identifying and mitigating all third-party vendor risks.
To help you do that, let’s begin by dissecting…
The New Hong Kong Monetary Authority Outsourcing Letter
The letter’s title, ‘Managing Cyber Risks Associated with Third-party Service Providers,’ stressed the need to facilitate becoming compliant. A section of the letter’s introduction reiterates:


Imagine that as you read this, threat actors are busy targeting weak links in your organization’s supply chain. The HKMA observed this trend when it conducted thematic examinations. They found that cybercriminals are becoming more rampant and sophisticated in their attacks. To help security teams at financial institutions fight back, they updated their outsourcing regulations, outlining critical areas companies now need to prioritize when outsourcing to 3rd parties.
What the HKMA Outsourcing Regulations Entail
Sound cybersecurity practices.
Those three words sum up what the HKMA’s recent Outsourcing Regulations entail. Specifically, they expect security teams at all Authorized Institutions (AIs) to bolster resilience against cyber threat actors by putting effective cyber defense in place. An excerpt from the HKMA’s Outsourcing ‘Sound Practises’ section confirms this.
It reads:


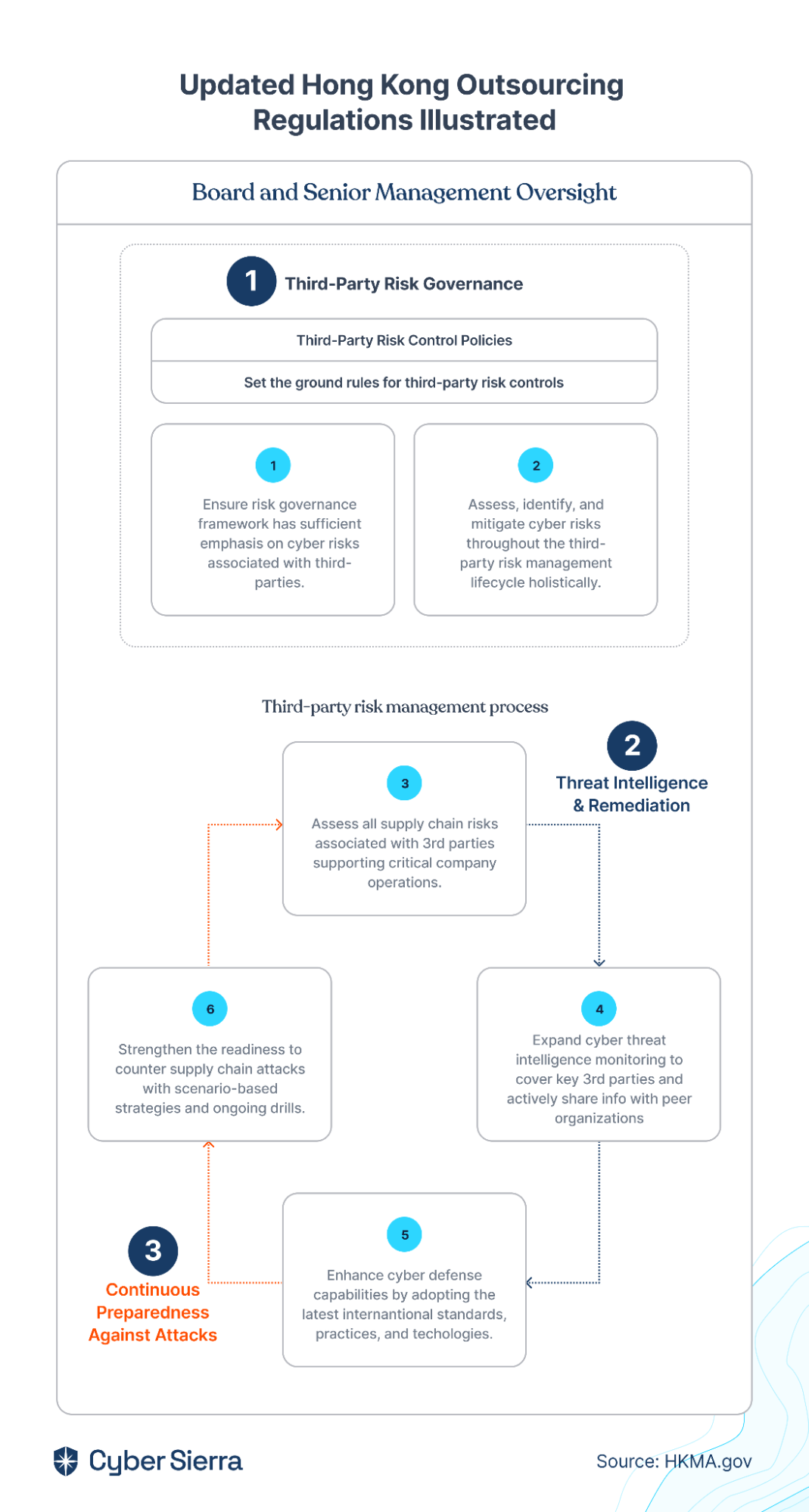
To comply with the requirement of putting effective cyber defense covering in place, the HKMA outlined six areas that must be addressed. They are as follows:
- Ensure risk governance framework has sufficient emphasis on cyber risks associated with third-parties
- Assess, identify, and mitigate cyber risks throughout the third-party management lifecycle holistically
- Assess all supply chain risks associated with 3rd parties supporting critical company operations
- Expand cyber threat intelligence monitoring to cover key 3rd parties and actively share information with peer institutions
- Strengthen the readiness to counter supply chain attacks with scenario-based response strategies and ongoing drills
- Enhance cyber defense capabilities by adopting the latest international standards, practices, and technologies.
Out of these six areas outlined, the HKMA made a crucial recommendation when summarizing the sixth requirement.
It noted:


By encouraging organizations to adopt the technology that can automate and streamline processes, the HKMA clearly stated its importance in becoming compliant. For instance, with Cyber Sierra’s vendor risk management suite, you can automate critical third-party risk management processes and become compliant with the HKMA Outsourcing Regulations.
Before I show you how:


Becoming Compliant with the Updated HKMA Outsourcing Regulations
Three critical third-party risk management stages can be deduced from the HKMA’s six updated outsourcing requirements. Although the regulatory body didn’t spell this out, our team did this grouping to outline parts of becoming compliant that can be automated.
- Third-party risk governance
- Threat intelligence and remediation
- Continuous preparedness against attacks:
As illustrated below:

1. Third-Party Risk Governance
The 1st and 2nd requirements of the updated HKMA Outsourcing Regulations go hand-in-hand. First, all Authorized Institutions (AIs) are mandated to involve relevant stakeholders when implementing a third-party risk governance framework:


Second, and this is more important. The implemented governance framework should enable your security team to identify all third-party risks.
According to the HKMA:



Two things we took from here:
- You need a single pane where all stakeholders can collaborate on the third-party risk governance framework to be implemented.
- You need a selection of third-party risk frameworks trusted for identifying all risks involved in working with third-parties.
You can achieve both with an enterprise governance, risk management, and compliance (GRC) platform (like Cyber Sierra).
Specifically, the platform should be pre-built with templates of globally-accepted, third-party risk management governance frameworks such as ISO and NIST. You should also be able to invite your leadership team to jointly review, customize, and add custom questions to each. Finally, the platform should enable your organization to automate the many steps involved in implementing a holistic third-party risk management governance framework.
2. Threat Intelligence and Remediation
The HKMA now requires organizations to prioritize third parties and threats likely to pose the most risk. This is emphasized in the 3rd and 4th requirements of the updated HKMA Outsourcing Regulations.
According to the regulatory body:



A good way to do this is to segment the third-parties working with your organizations based on relevant criteria. For instance, when assessing third-party vendors, you can segment by:
- Critical vendors sent custom security questionnaires
- Assessee types (i.e., software, services, and so on)
- Operating locations
Using these, your security team can easily filter and know what 3rd parties they need to conduct additional threat intelligence on. Also, by prioritizing risks from these critical vendors, they’ll know what threats and risks to prioritize when remediating.
A smart GRC platform helps your team automate parts of this process in two ways. First, you can enforce segmenting third-parties when sending initial security assessments. Second, your security team can easily filter and track 3rd parties that need more scrutiny based on the segmentation criteria outlined above.
3. Continuous Preparedness Against Attacks
The threat landscape is always evolving. As such, it has become difficult, if not impossible, to know all new ways threat actors will attack your organization through third-parties.
Even the HKMA knows this:


One way to strengthen preparedness against attacks is through continuous employee security awareness training. When the push comes to shove, your people —security team, other company employees, and partners— are your last line of defense.
By continuously training employees with scenario-based response strategies and lessons from previous supply chain incidents, you equip them with the know-how for countering attacks.
To achieve that:
- Launch new third-party breach cybersecurity defense training as the need for them arises
- Continuously monitor training progress to ensure employees are completing them and equipped to counter attacks.
HKMA Outsourcing FAQs
Below are answers to some frequently asked questions.
Who does HKMA Outsourcing Regulations apply to?
- The HKMA Outsourcing Regulations, as the name goes, apply to banks and financial institutions, referred to as Authorized Institutions (AIs), operating in Hong Kong. The regulator emphasizes those digitalizing financial operations and relying on third-party vendors to facilitate service delivery. The rules also apply to those based out of Hong Kong but whose operations are used by consumers and other institutions in Hong Kong.
What is the HKMA regulatory approach?
- The HKMA’s regulatory approach provide digitalized banks and financial institutions operating in Hong Kong with a balanced and proportional risk-based approach to counter third-party risks. The regulatory body’s approach has three principles: risk differentiation, proportionality, and “zero failure” regime. These principles apply equally to all financial institutions in Hong Kong.
When was the release date and compliance deadline of the latest HKMA Outsourcing Regulations?
- The latest version of the HKMA Outsourcing Regulations was released in December 2023. Although the regulator didn’t give a deadline for becoming compliant, with the increasing onslaught of threat actors, financial institutions are advised to comply to protect themselves and avoid being breached.
How many requirements are in the updated HKMA Outsourcing Regulations?
- There are six requirements organizations must comply with in the updated HKMA Outsourcing Regulations.
How does the HKMA recommend organizations to facilitate becoming compliant with its updated outsourcing regulations?
- According to the regulatory body, “AIs are encouraged to adopt technologies to refine, automate and streamline their third-party risk management and cybersecurity controls.”
As stated, prioritize technology that enables your team to facilitate the entire process from a single pane. This will reduce the various mundane tasks involved in the initial implementation phase, as well as for staying compliant.
And that’s where Cyber Sierra’s interoperable, enterprise cybersecurity platform comes in. For instance, Cyber Sierra’s vendor risk management Assessments’ suite is pre-built with globally-accepted third-party risk management templates. So in just a few clicks, you (and your team) can customize any to your specific HKMA Outsourcing Regulations implementation needs:
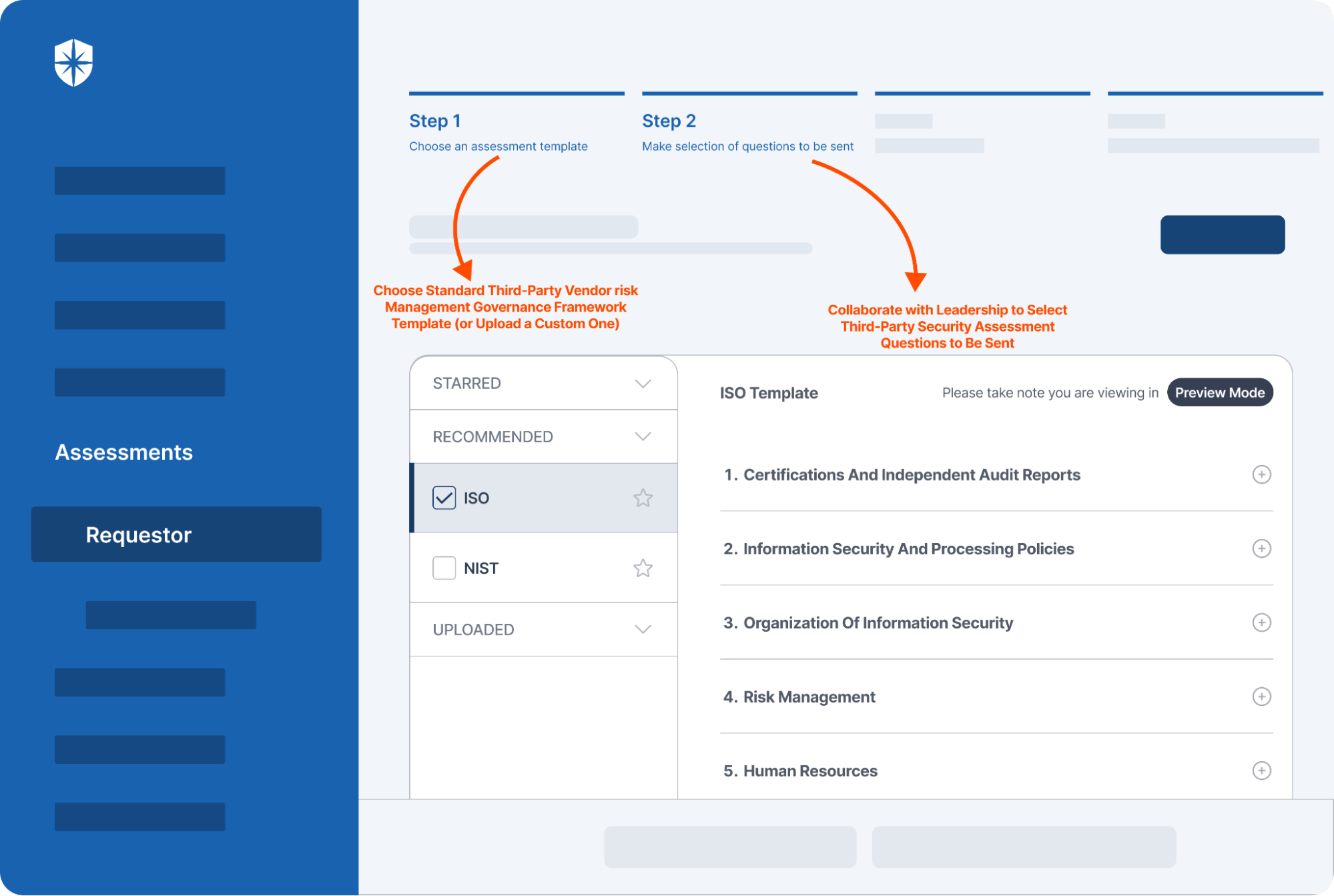

This, among others, automates many steps involved in becoming and staying compliant with the HKMA Outsourcing Regulations.
And it’s why an Asian-based global bank relies on Cyber Sierra for automating its third-party risk management processes:


Read the bank’s success story here:
Find out how we can assist you in
completing your compliance journey.