A Guide to Managing Sensitive Data



Join thousands of professionals and get the latest insight on Compliance & Cybersecurity.
Are you taking all the necessary steps to protect your sensitive data?
In today’s fast-paced digital age, organizations, businesses, and individuals are experiencing increasing concern surrounding potential data breaches and the serious consequences they entail – from financial losses to legal troubles and reputational damage.
With the threat landscape constantly evolving and new risks emerging every day, it has become more important than ever to address this issue promptly.
Fortunately, there is a remedy at hand. Read on to know how you can adopt a comprehensive approach to managing sensitive data, encompassing the latest industry standards and recommended practices to shield your organization’s most valuable resource.
What Is Sensitive Data?
Sensitive data is any information that is considered highly confidential, requiring special protection to prevent unauthorized access, misuse, or disclosure.
It can also include other types of data that can impact the privacy of individuals or organizations—for example, credit card details, medical records, and financial information.
Examples of sensitive data include:
- Personal information (e.g., social security numbers, credit card numbers, medical records)
- Intellectual property (e.g., trade secrets, patents, copyrights)
- Financial information (e.g., bank account numbers, financial statements)
- Confidential business information (e.g., customer lists, pricing strategies)
This type of information is sensitive because there are serious consequences that could result from its improper use. Unauthorized sensitive data exposure could cause financial loss to companies, compromise an entity’s security, affect someone’s privacy or diminish a company’s competitive advantage.
Regulations on Sensitive Data
Sensitive data is information that, if lost, stolen, or accessed without authorization, could lead to severe consequences for individuals and organizations.
To protect this data, various regulations have been established globally. In this article, we will discuss five key regulations on sensitive data.
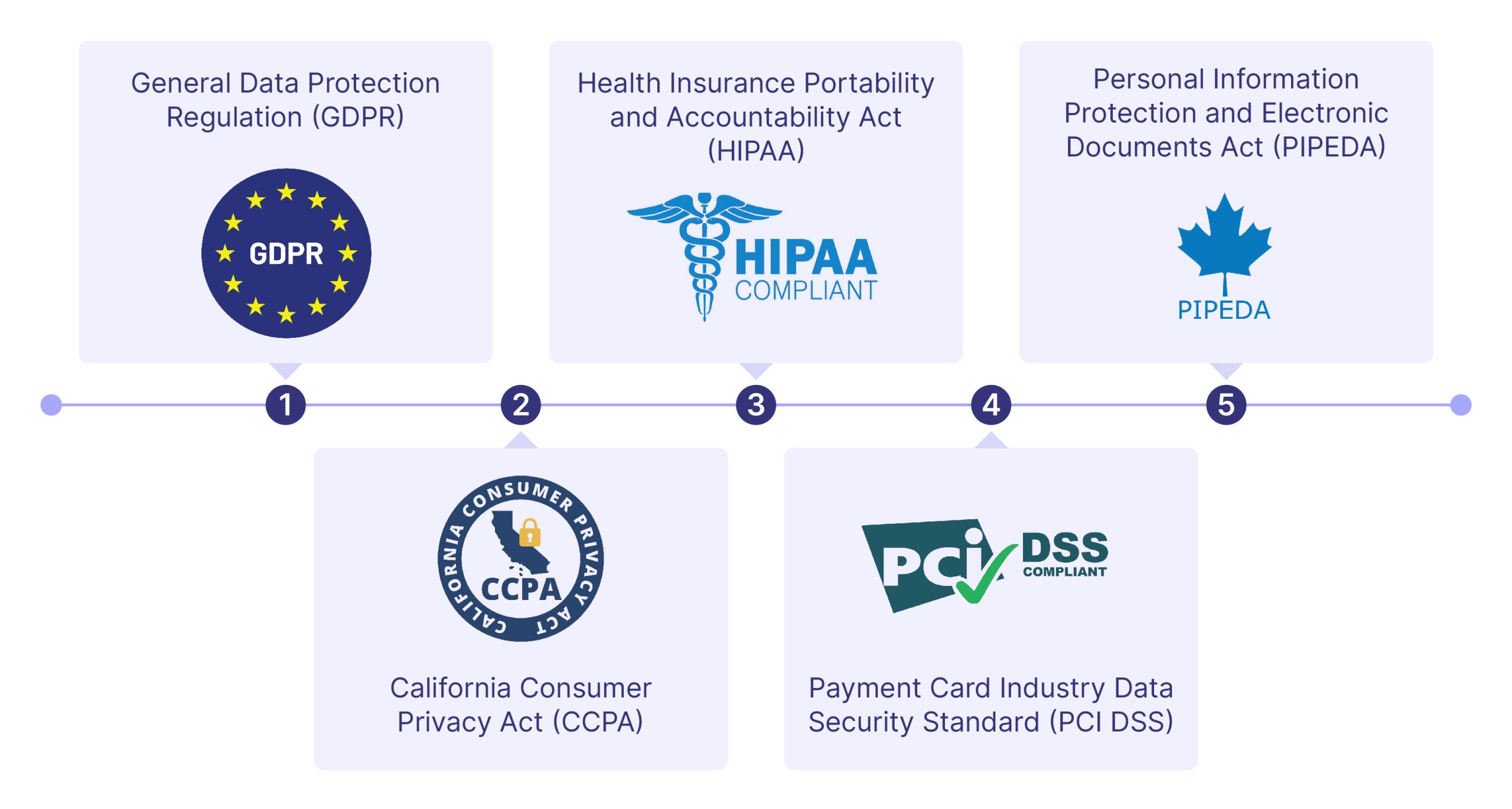

1. General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
The GDPR is a comprehensive data protection regulation the European Union (EU) implemented in 2018. It aims to protect the privacy and personal data of EU citizens. The regulation applies to all organizations that process the personal data of EU residents, regardless of where they are located. Key components of the GDPR include:
- Obtaining explicit consent from individuals before collecting and processing their data
- Providing individuals with the right to access, modify, and delete their data
- Implementing data protection measures such as pseudonymization and encryption
- Reporting data breaches to authorities within 72 hours
2. California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA)
The CCPA is a data privacy law enacted in California in 2018, granting California residents the right to control their personal information. The CCPA applies to businesses that collect, process, or sell personal data of California residents. Key provisions of the CCPA include:
- Allowing individuals to request access to and deletion of their personal information
- Providing individuals with the right to opt out of the sale of their personal data
- Implementing reasonable security measures to protect personal data
3. Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
HIPAA is a US federal law enacted in 1996 to protect the privacy and security of individuals’ health information. It applies to healthcare providers, health plans, clearinghouses, and business associates. Key aspects of HIPAA include:
- Establishing Privacy and Security Rules to protect individuals’ health information
- Limiting the use and disclosure of protected health information (PHI) without authorization
- Implementing administrative, physical, and technical safeguards to protect PHI
- Requiring notification of affected individuals and authorities in case of data breaches
4. Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS)
PCI DSS is a set of security standards designed to protect cardholder data and ensure the secure processing of credit card transactions. It applies to all organizations storing, processing, or transmitting cardholder data. Key requirements of PCI DSS include:
- Building and maintaining a secure network and systems
- Protecting cardholder data through encryption and access controls
- Implementing robust access control measures
- Regularly monitoring and testing networks and systems
- Maintaining an information security policy
5. Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA)
PIPEDA is a Canadian federal law governing private-sector organizations’ collection, use, and disclosure of personal information. It applies to businesses operating in Canada, except for those in provinces with substantially similar privacy laws. Key principles of PIPEDA include:
- Obtaining informed consent for the collection, use, and disclosure of personal information
- Limiting the collection, use, and retention of personal data to necessary purposes
- Ensuring the accuracy, confidentiality, and security of personal information
- Providing individuals with the right to access and correct their personal data
- Developing and implementing privacy policies and practices to comply with PIPEDA
How to Manage Sensitive Data?
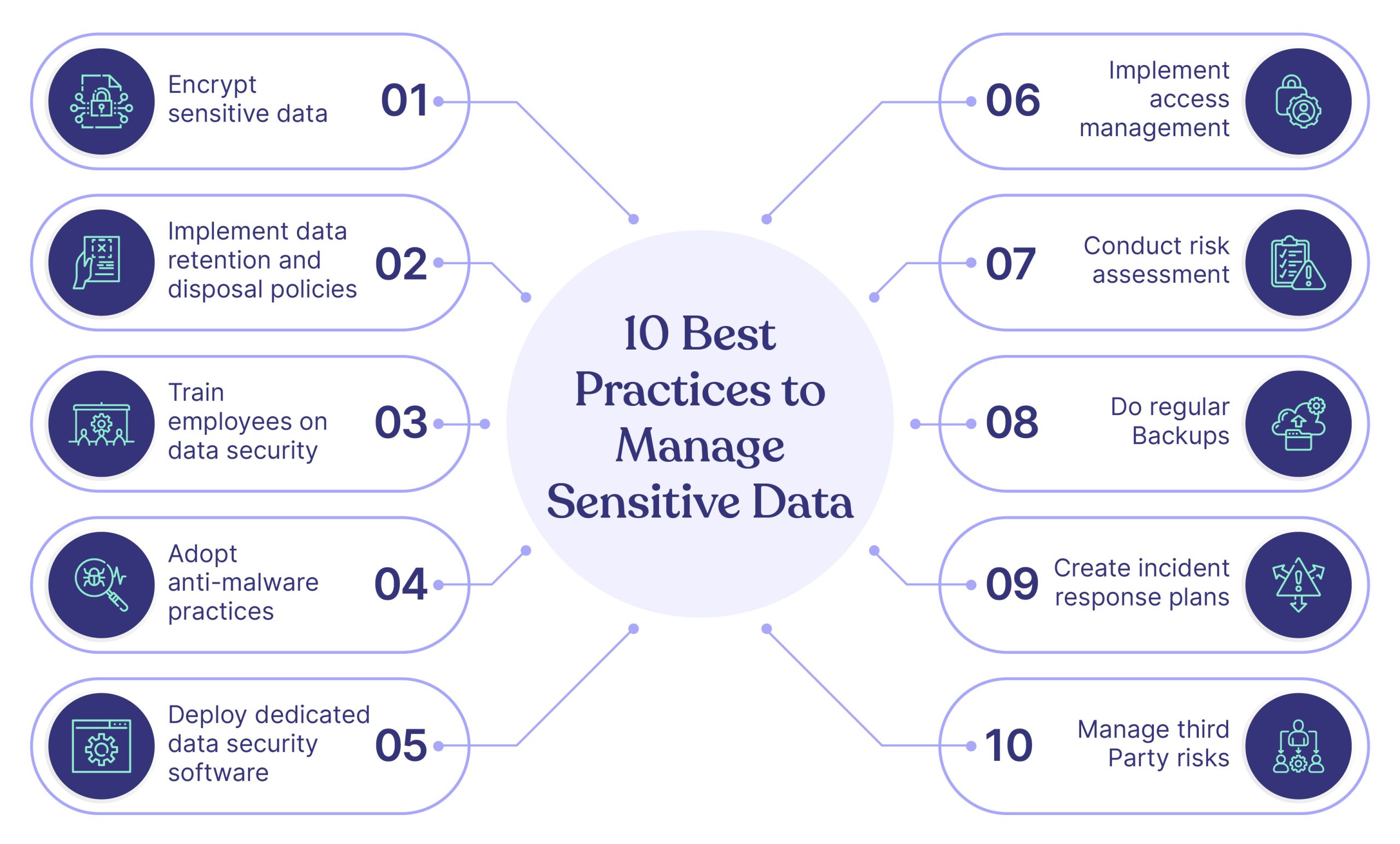

Here are five best practices to handle sensitive data properly.
- Encrypt sensitive data
- Implement data retention and disposal policies
- Train employees on data security
- Adopt anti-malware practices
- Deploy dedicated data security software
- Implement access management
- Conduct risk assessment
- Do regular backups
- Create incident response plans
- Manage third-party risks
Let’s look at them one by one.
1. Encrypt sensitive data
Encrypting data ensures that only authorized users can access it and protects against unauthorized interception of the data during transmission. A study by Ponemon Institute and Thales eSecurity found that organizations that used encryption extensively were less likely to suffer from a data breach
Use encryption to protect,
- Sensitive data at rest (e.g., stored on hard drives) and
- Data in transit (e.g., during transmission over a network).
This ensures that even if the data is intercepted, it cannot be read without the proper decryption key.
Encrypting data helps keep information safe from hackers and other intruders. This can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches and their associated costs. For instance, the GDPR mandates organizations to implement data protection measures such as pseudonymization and encryption.
2. Implement data retention and disposal policies
Establish and maintain policies that clearly state
- What data should be retained,
- How long it should remain confidential, and
- How to dispose of sensitive information once its purpose has been fulfilled.
Update these policies regularly to keep them relevant for your organization.
Proper data retention and disposal policies help minimize the risk of data breaches due to outdated or unnecessary data. They also help to ensure compliance with regulations such as GDPR and protect sensitive information.
3. Train employees on data security
A well-trained workforce is essential to maintaining the security of your company’s data. Ensure all employees are aware of the company’s data security policies and have access to any necessary training.
Provide regular training to employees on the importance of data security and best practices for handling sensitive information. In this way, the entire organization is aware of its responsibility to protect sensitive data and how best to respond in case of a security breach.
Cyber Sierra’s cybersecurity platform allows organizations to maintain a central repository of company policies that can be read and acknowledged by all employees. It also offers a comprehensive employee security training program that is tailored to the present cyber risks. Book a demo with us to know more.
4. Adopt anti-malware practices
Implement anti-malware practices to protect your organization from malware attacks.
- Install antivirus software
- Use administrator accounts only when necessary
- Keep software up-to-date
- Implement spam protection and email security
- Monitor user accounts for suspicious activity
An effective anti-malware infrastructure reduces the risk of data breaches, system downtime, and other financial costs.
5. Deploy dedicated data security software
Implement an integrated data protection system to control data security from a technological standpoint. Use a single, powerful piece of security software to monitor, automate access control, send notifications, and manage password auditing.
Deploying dedicated data security software can reduce the risk of security incidents by providing a centralized and comprehensive approach to data protection. This allows for better visibility and control over sensitive data and enables organizations to respond quickly to potential threats.
6. Implement access management
Access management involves implementing procedures and systems to ensure that only authorized individuals can access sensitive data. This can be achieved by:
- Using secure passwords and multi-factor authentication
- Limiting access to sensitive data on a “need-to-know” basis
- Monitoring access to sensitive data and logging all access attempts
When organizations implement access management measures, they can ensure that sensitive data remains secure and only accessible to those who need it.
7. Conduct risk assessments
Risk assessment involves identifying potential threats to sensitive data, ascertaining their probabilities of occurrence and taking steps to prevent them or mitigate their impact. With regular risk assessments, organizations can:
- Identify vulnerabilities in their data security infrastructure
- Develop a plan for responding to security incidents
- Ensure that data is protected against unauthorized access or theft
Regular risk assessments also help ensure compliance with data protection regulations and standards.
8. Do regular backups
Conducting and maintaining regular backups of sensitive data is critical to ensuring that it remains secure and accessible in the event of any data loss or security incident.
Regular backups allow you to restore your data quickly in the event of a breach and minimize any damage caused by it. Backups should be stored in an offsite location that is not accessible from the network where sensitive data resides.
9. Create incident response plans
Incident response plans are a critical component of managing sensitive data. By developing a plan for responding to security incidents, organizations can:
- Identify the types of security incidents that could compromise sensitive data
- Develop a clear response procedure for each type of incident
- Train employees on how to respond to security incidents
- Regularly test and update the incident response plan
Having an effective incident response plan in place ensures that your organization can respond quickly and effectively to security incidents and minimize the impact on your sensitive data.
10. Manage third-party risks
Many organizations work with third-party vendors or partners who may have access to sensitive data. It is, therefore, essential to establish clear requirements for handling and protecting data when working with third parties. Some ways to manage third-party risks include:
- Conducting due diligence before working with third parties
- Establishing clear contractual obligations for data protection
- Only sharing data with third parties on a “need-to-know” basis
- Monitoring third-party compliance with data protection regulations and standards
Proactively managing third-party risks helps organizations ensure that their sensitive data remains secure when they share it with others.
Cyber Sierra has a specialized third-party risk management feature that allows organizations to continuously monitor and manage vendor risks. Book a demo to know how to implement it in your organization.
Tips to Protect Sensitive Data

Here are some tips to help you protect your sensitive data:
- Implement strong access controls
- Perform data protection impact assessment
- Use data masking
- Use physical security of devices
Let’s take a look at each of these in more detail.
1. Implement strong access controls
Access control is a cornerstone of information security. It helps ensure that only authorized people can access your data and protects against insider threats by preventing unauthorized employees from accessing sensitive data.
Limit access to authorized individuals on a need-to-know basis and use proper identity management systems, such as biometrics, passwords, and passphrases.
Implementing strong access controls helps prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data, reducing the risk of data breaches and ensuring that only those who genuinely need access to specific information can obtain it.
2. Perform data protection impact assessment
A Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA) is a systematic process to identify and minimize the risks associated with the processing of personal data. Conducting a DPIA ensures that your organization complies with data protection laws and regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
3. Use data masking
Data masking is a technique to conceal sensitive information by replacing actual data with fictitious yet realistic data. This method is often used when the actual data is unnecessary, such as in testing and development environments, training sessions, or when sharing data with third parties.
Data masking can protect sensitive data from unauthorized access and reduce the risk of data leaks.
4. Use physical security of devices
Maintaining the physical security of devices that store or handle sensitive data is crucial in protecting your information. This includes proper locks, secure storage, and access controls for laptops, devices, and servers.
Implementing strong security measures like video surveillance, card access systems, and alarms can also help protect your physical infrastructure from unauthorized access or theft.
Wrapping Up
The most important thing to remember regarding security is that it’s an ongoing process. There is no one-size-fits-all approach, and you will need to constantly evaluate your environment, technology infrastructure, and business practices.
Managing passwords, organizing folders, and following the best security practices can sometimes seem overwhelming. But as long as you are mindful of all your responsibilities, it is completely manageable!
Find out how we can assist you in completing your compliance journey.