Data Sharing and Third Parties - Risks and Benefits Unveiled





Join thousands of professionals and get the latest insight on Compliance & Cybersecurity.
Have you ever wondered about the risks your business could face whenever data is shared with a third party?
As businesses operate in an ever more interconnected landscape, third-party data sharing has become a common facet of routine operations. Despite the numerous benefits it brings, sharing data with external entities is not without its risks.
And you need a robust strategy to manage those risks.
This guide will help you understand everything about data sharing and offer strategies to mitigate them.
Let’s dive in.
What is a Third-Party Data Sharing Vendor?
A third-party data-sharing vendor is a business entity that functions as a bridge between your company and disparate sources of information that are otherwise disconnected from your direct operations. These vendors do not have a direct relationship with your customers, unlike your company, which is considered the first party in this context.
They harvest data from many web platforms—information that may not be directly accessible or usable by your company. This raw data can have varying degrees of complexity and is often unstructured or semi-structured.

The vendors then clean this data, removing any inaccuracies or redundancies that might compromise its reliability. This cleaned data is then consolidated and structured to align with your business’s specific data analytical needs.
What is an example of a Third Party?
Generally, a third party refers to any person, entity, or organization indirectly involved in dealings or interactions that primarily involve two other parties. Third parties often enable or facilitate specific processes or transactions between the two primary parties in business contexts.
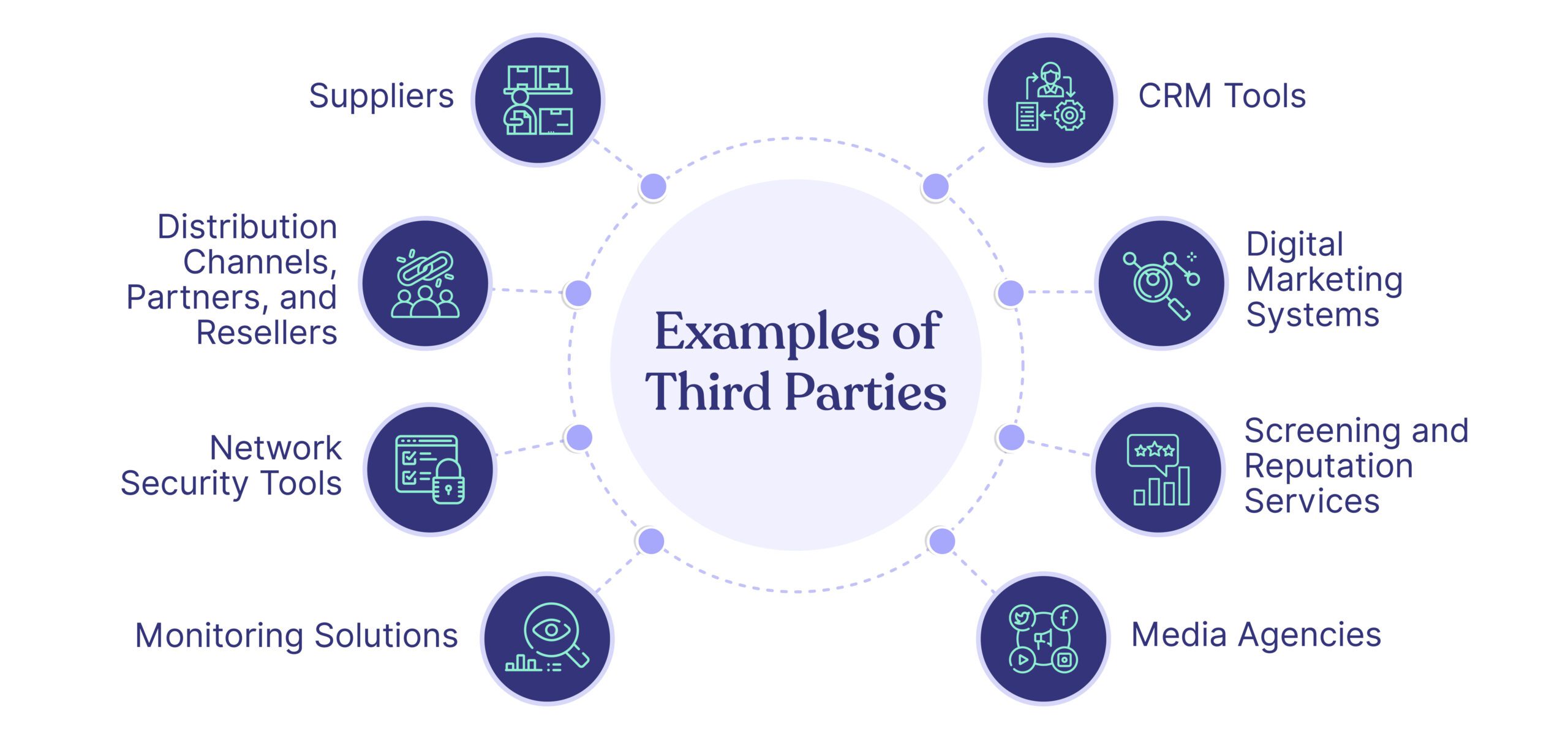

Here are some examples:
- Suppliers: Provide necessary goods or raw materials for smooth business operations.
- Distribution Channels, Partners, and Resellers: Aid in sales, extend the company’s reach, and contribute to revenue generation.
- Network Security Tools: Strengthen the company’s cybersecurity measures, safeguarding sensitive data.
- Monitoring Solutions: Provide real-time analytics, improving decision-making and overall efficiency.
- CRM Tools: Streamline customer data management and personally tailored marketing, leading to better retention.
- Digital Marketing Systems: Enhance marketing efforts with automation and tracking to improve outreach and revenue growth.
- Screening and Reputation Services: Assist with background checks and reputation management, maintaining a safe business environment.
- Media Agencies: Oversee a company’s branding, ads, and public relations, influencing perception and success
What is Third-Party Data Sharing?
Third-party data sharing is a process where data about individuals, typically collected through various platforms and websites, is procured, compiled, and exchanged by entities distinct from the original users and data collectors. An example could be a Data Management Platform (DMP) aggregating this information.
This exchange process provides companies with rich, diverse data sets yielding valuable insights about consumer habits, behaviors, and preferences. It is broadly used in targeted advertising, social media marketing, and predictive analytics.
DMPs, as intermediaries, accumulate vast amounts of structured and unstructured data from disparate sources, sort it into usable segments, and make this data available so businesses can make data-informed decisions.
Despite its benefits, third-party data sharing raises potential issues concerning data privacy and security. As such, companies involved with third-party data sharing must remain compliant with all relevant data protection regulations (like GDPR) and focus on safeguarding user information.
What is a Data Sharing Agreement?
A Data Sharing Agreement (DSA) is a legally binding document established between parties to define the terms for sharing data. The main components of a DSA often include:
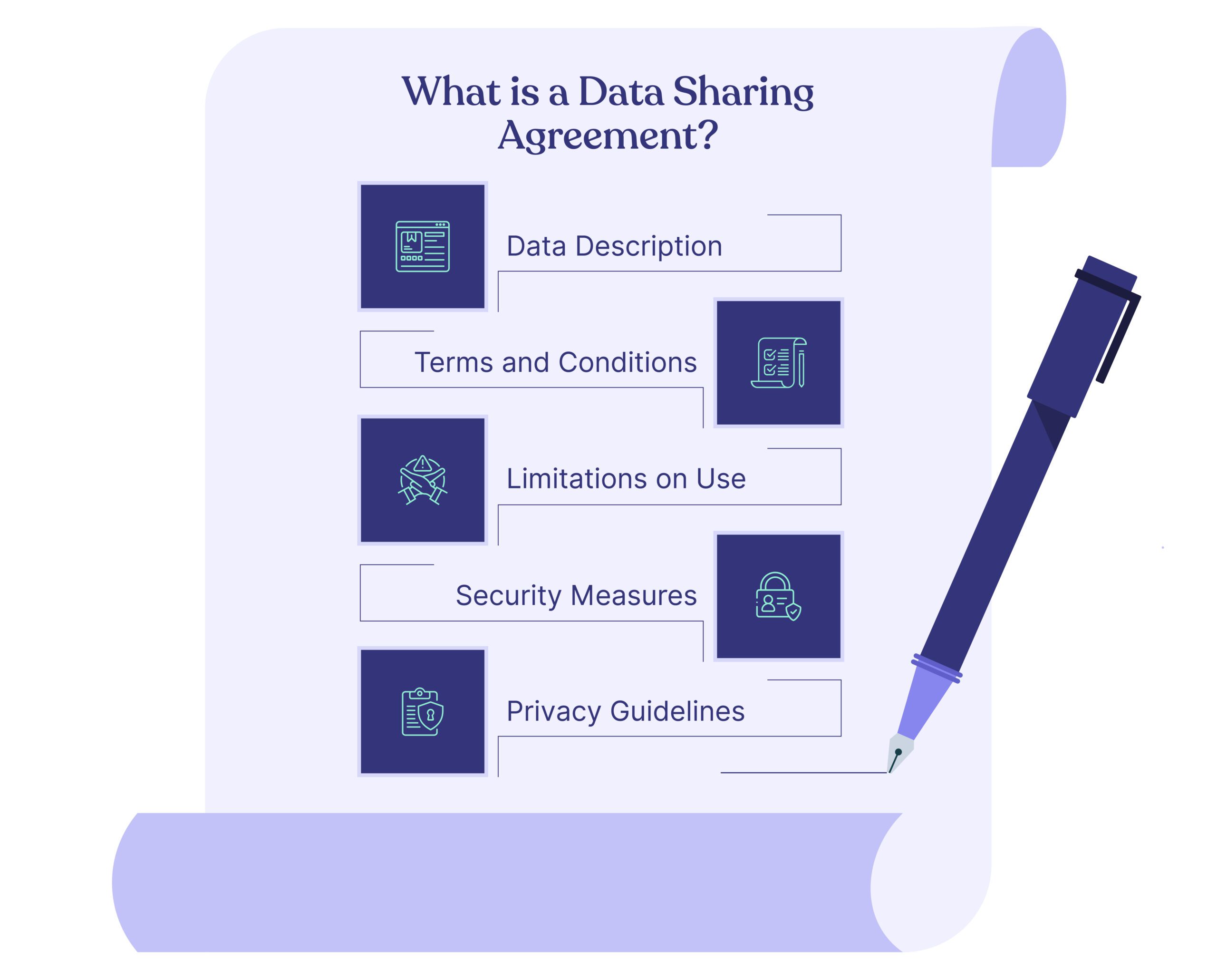

- Data Description: Specifics about the shared data, such as data type, source, and purpose of sharing.
- Terms and Conditions: Defines each party’s usage rights, confidentiality requirements, and responsibilities.
- Limitations on Use: Stipulates the scope of data usage, forbidding misuse or overuse.
- Security Measures: Outlines necessary protection measures to prevent unauthorized access, breaches, or data loss.
- Privacy Guidelines: Specifies how shared data should comply with relevant privacy regulations to safeguard user identity and personal information.
DSAs are critical to ensure accountability, maintain data integrity, protect sensitive information, and legitimize data exchange between parties. They help mitigate legal risks and provide a framework for resolving disputes, facilitating safe and responsible data sharing.
The Pros and Cons of Data Sharing
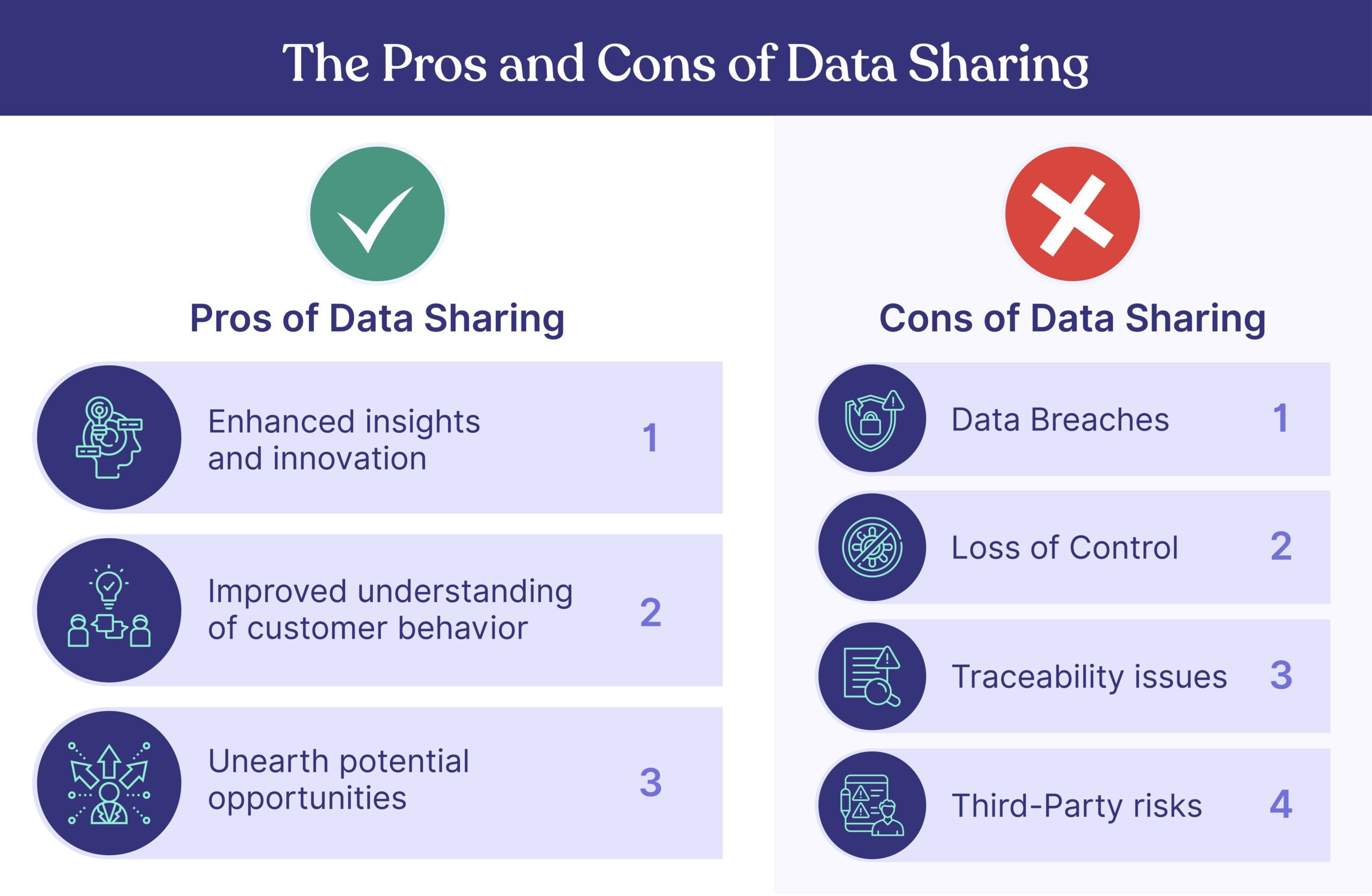
Pros of Data Sharing
- Enhanced insights and innovation: Sharing data between different organizations can help generate valuable insights. Pooling data can lead to collaborative problem-solving, innovation, and better decision-making.
- Improved understanding of customer behavior: Businesses can gain a competitive advantage by understanding their customers better through external data.
- Unearth potential opportunities: Shared data can potentially reveal new market trends, business opportunities, and unexplored customer segments.
Cons of Data Sharing
- Data Breaches: Sharing data increases the chances of data breaches. Cybersecurity measures must be in place to safeguard sensitive information during transfer or storage. However, companies like Cyber Sierra offer solutions that integrate all aspects of governance, cybersecurity, and compliance into interoperable modules, reducing this risk.
- Loss of Control: Once data is shared, control over who has access and how the data is used can be lost, potentially leading to misuse.
- Traceability issues: It can be challenging to track who has accessed shared data, when, and for what purpose – particularly crucial for sensitive information.
- Third-Party risks: Sharing data with third parties entails risk, as their security protocols and handling practices may not align with the original data owner’s standards.
When a company thinks about sharing data, they should carefully weigh the benefits of doing so, like gaining valuable insights, against the need to make sure the data is kept safe from unauthorized access or misuse.
What is Third-Party Risk?
Third-party risk refers to the potential hazards of third parties, such as service providers or vendors, who can indirectly impact an organization’s stability or security. This risk broadly falls into operational, cyber-security, legal, financial, or reputational threats.
One significant aspect of third-party risk is data breaches. As a company shares data with third parties, vulnerabilities may emerge if the external entity doesn’t take sufficient precautions, exposing sensitive data to unauthorized access.
Rapid response complications represent another facet of third-party risk. An organization may struggle to respond promptly in crises due to limited control over third-party operations.
Additionally, businesses may experience risks when collaborating with third parties that have weak data governance practices. This could potentially endanger data security, compromise its quality, or lead to misuse.
What Is Third-Party Risk Management?
Third-party risk management involves identifying, evaluating, and mitigating risks associated with working with third-party vendors. It often involves conducting due diligence, establishing data-sharing agreements, monitoring vendor performance, and implementing data privacy and security controls.
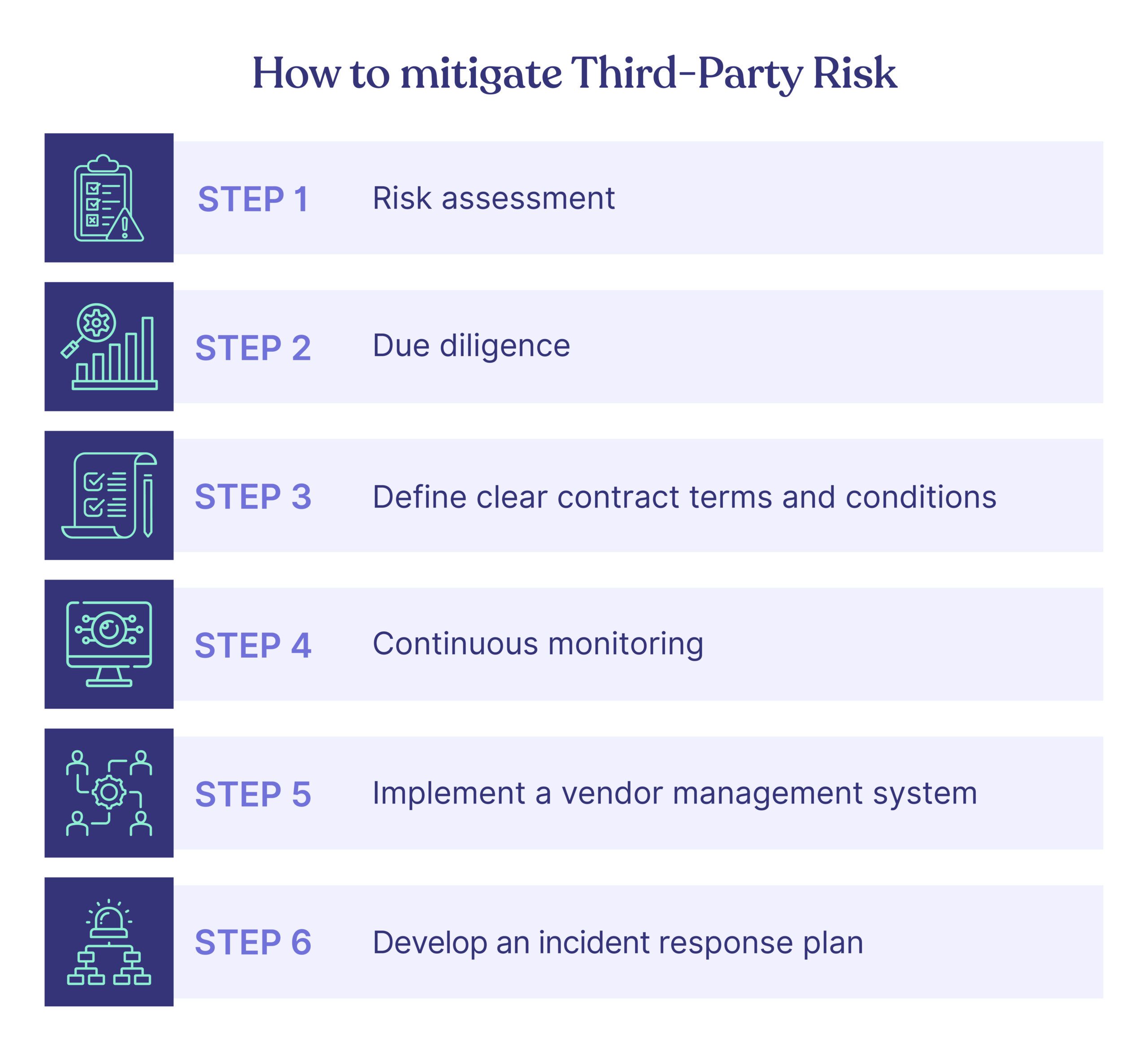
How to mitigate Third-Party Risk and why it is important
You can mitigate third-party risk by establishing a robust third-party risk management program. This includes:

Let’s take a look at each of these steps in more detail.
1. Risk assessment
Start by conducting a comprehensive risk assessment of any potential third-party vendor. Explore every dimension of their business operation, from financial stability and ability to comply with agreed terms and conditions to reputation and history related to any security incidents.
You should also consider your degree of outsourcing to the third party, their geographic location, and whether tumultuous political or economic landscapes impact their business operations.
2. Due diligence
A due diligence process helps ensure that the third parties you engage with have stringent procedural, technical, and administrative safeguards. Take your time to thoroughly evaluate their policies, certifications, and service level agreements (SLAs).
Do they have the necessary certifications that pertain to their industry and yours, such as ISO 27001 or SOC 2? Do they conduct regular security audits and make the results available? Do the terms of their SLAs align with your expectations?
Thoroughly scrutinize their contracts for any hidden liabilities or responsibilities.
Cyber Sierra automates the entire process and gives you one-stop access for managing and mitigating your third party risks.
3. Define clear contract terms and conditions
When drafting contracts, be explicit about your expectations from the third party. This includes your data protection standards, penalties applicable for non-compliance, and the milestones they are expected to meet.
Your contracts should also outline any regulatory standards you must comply with, like GDPR, CCPA, or HIPAA, and reinforce the third party’s obligation to uphold these standards.
4. Continuous monitoring
Once a third party is onboarded, the job doesn’t end there. Monitoring their operational performance, adherence to the contract terms, and key performance indicators (KPIs) is necessary.
You should regularly conduct audits and assessments to ensure third parties stay compliant and their performance is congruent with your expectations. Don’t be afraid to revise your business strategies as the market changes.
Again, Cyber Sierra can be your ally, providing seamless monitoring and timely recommendations to address potential threats and risks.
5. Implement a vendor management system
To effectively manage multiple third-party vendors, consider investing in a robust vendor management system (VMS). A good VMS will allow you to keep a detailed record of all third-party relationships, track their performance, and monitor any potential risks.
Technological advancements, such as AI and Big Data, have enabled more automated, efficient systems that can offer real-time risk monitoring and send alerts when a deviation is from the normal pattern.
Cyber Sierra’s TPRM program allows you to monitor the security posture of all your vendors and helps you score them based on their risk potential.
6. Develop an incident response plan
In the unfortunate scenario that a third party causes a security incident, you must have a well-prepared incident response plan. This plan should include the steps to contain and remediate the situation, how you would notify any affected parties, and address any related regulatory obligations.
Predefine communication protocols educate all stakeholders about their responsibilities and detail the steps for escalation to minimize damage caused by the incident.
Wrapping Up
The above six steps will help you to create a solid cybersecurity program and reduce the risks associated with third-party vendors. However, it’s important to remember that this is an ongoing process; you’ll need to continue monitoring your vendor relationships, ensuring they’re up-to-date on security best practices and keeping them accountable for their compliance.
Given the complexity of third-party data sharing, a well-rounded, professional solution is crucial. That’s where Cyber Sierra comes in. With a suite of tools to help you keep your data secure and up-to-date on the latest security standards, we provide the resources to make decisions that will keep your business safe.
If you’re interested in learning more about how Cyber Sierra can help you manage your third-party data sharing, book a free demo today.



A weekly newsletter sharing actionable tips for CTOs & CISOs to secure their software.
Thank you for subscribing!
Please check your email to confirm your email address.
Find out how we can assist you in
completing your compliance journey.