GRC Framework: What is it and Why is it Important?




Join thousands of professionals and get the latest insight on Compliance & Cybersecurity.
In the rapidly changing and ever-demanding business scenario, organizations face huge pressure to successfully navigate the complexities while simultaneously ensuring compliance with various cyber security standards and regulations. The more disorganized the structure, the higher the chance for scattered data, mismanaged human resources, lack of risk visibility, and inadequate audit trails. The solution to these issues lies in the adoption of a GRC (Governance, Risk, and Compliance) framework which aligns with your business objectives to achieve a well-managed set of functions. Let’s delve deeper and understand what the GRC framework is, how to implement it, its associated key components, and its benefits.
What is a GRC Framework?
The GRC framework, or Governance, Risk, and Compliance Framework, is a well-designed and structured model that leverages timely information on data, risks, policies, and compliance to reduce compliance risk.
It is more than a mere checklist that enables organizations to align their everyday operations with planned strategic objectives while managing risks and complying with relevant regulations. When adopted well, a GRC framework can help organizations integrate best practices and process day-to-day operations to effectively manage its IT and security risks, reduce costs, and meet compliance requirements.
Key components of GRC framework


The GRC framework comprises three important components. Each of these components has its own nature, and mastering all three is important for a rewarding GRC framework.
Governance
Governance, in simple terms, is about the set of rules, policies, and processes that help an organization plan its everyday activities and align them to support and enable its business goals.
Good governance in the GRC framework
- includes ethics, procedures, resource management, accountability, stability, and management controls.
- enables the top management to guide and take control of what happens at every level of the organization.
- helps every business unit in the organization be directed and aligned with the defined corporate goals and overall customer needs.
- makes employees feel empowered, though their behavior and resources are controlled, but not in a negative way.
- focuses more on being well-coordinated and heavily controlled.
- aims to achieve accountability for conduct and results.
- defines employee roles based on lines or sectors of the business.
- evaluates employees based on their performance and results achieved, not on their job responsibilities.
Governance in the GRC framework predominantly aims to balance the interests of multiple stakeholders in the organization. These include top management, employees, contractors, freelancers, suppliers, and investors. It also provides control over available facilities and infrastructure.
How does governance help in maintaining balance? Here’s a GRC framework example – an organization encompasses multiple internal and external stakeholders. The contracts between these stakeholders need to be intact so that there is a proper sharing of responsibilities, rights, and rewards. It also includes well-defined procedures for reconciliation in cases of conflicting interests among stakeholders. Also, structured policies aid in supervision, control, and data flow functions, including a system of checks and balances.
Risk Management
Right on cue comes risk management. The ignored middle child of the GRC framework turns out to be a headache later. Risk management is the process of identifying, evaluating, analyzing, and mitigating or transferring different risks. These risks can be financial, legal, process-oriented, strategic, and security-related and threaten an organization’s operations.
Risk management
- reduces the risks faced by an organization through an effective IT governance and compliance framework.
- effectively monitors, controls, and reduces the impact of negative incidents on the organization.
- focuses on maximizing the impact of positive events.
- creates objectives that are in line with an organization’s values. Based on this, it builds a system of people, processes, and technology.
- aims to achieve the objectives of an organization while refining its risk profile and securing value.
- works on identifying threats and risks related to cybersecurity and information security.
For example, a risk management program within the GRC framework will include an assessment of the technology used and the identification of operational and technological failures, as these will impact the core business. It will also monitor the risks involved with infrastructure and the potential failure of networks and find ways to control them.
A risk assessment program needs to adhere to internal, contractual, legal, ethical, and societal objectives and keep track of any new rules pertaining to technology and cybersecurity. A company can safeguard itself from uncertainty, cut expenses, and raise the possibility of success and business continuity by concentrating on risk and allocating the resources required to control and mitigate risk.
An effective risk assessment program
- should be in line with the different objectives of an organization, such as legal, contractual, internal, social, and ethical.
- stay on top of the new technology-related regulations, and government regulations and monitor them to ensure compliance.
- will allocate resources accordingly and help businesses safeguard themselves against uncertainty.
- helps in effective risk control that results in cost reduction and enhances the likelihood of business continuity and success.
Compliance
Here comes the last one on the cue, the most spoiled one of the lot: compliance. Compliance management deals with adherence to rules, procedures, policies, and laws laid down by an organization, government, agency, and more. Non-compliance leads to a lack of performance, hefty fines, penalties, and lawsuits.
Regulatory compliance also encompasses external laws, regulations related to jurisdiction, and industry standards that are mandatory for functioning. On the other hand, internal compliance deals with different aspects such as rules, regulations, and management internal controls decided by an individual company. Both the internal compliance management program and external compliance requirements need to be integrated for the smooth functioning of an organization.
An effective compliance program
- helps in understanding the areas of greatest risk and allocating more resources to those areas.
- focuses on developing, implementing, and communicating policies to employees to overcome those risk areas.
- offers guidance for employees and vendors. This makes the process of following compliance policies easier.
Types of GRC Framework
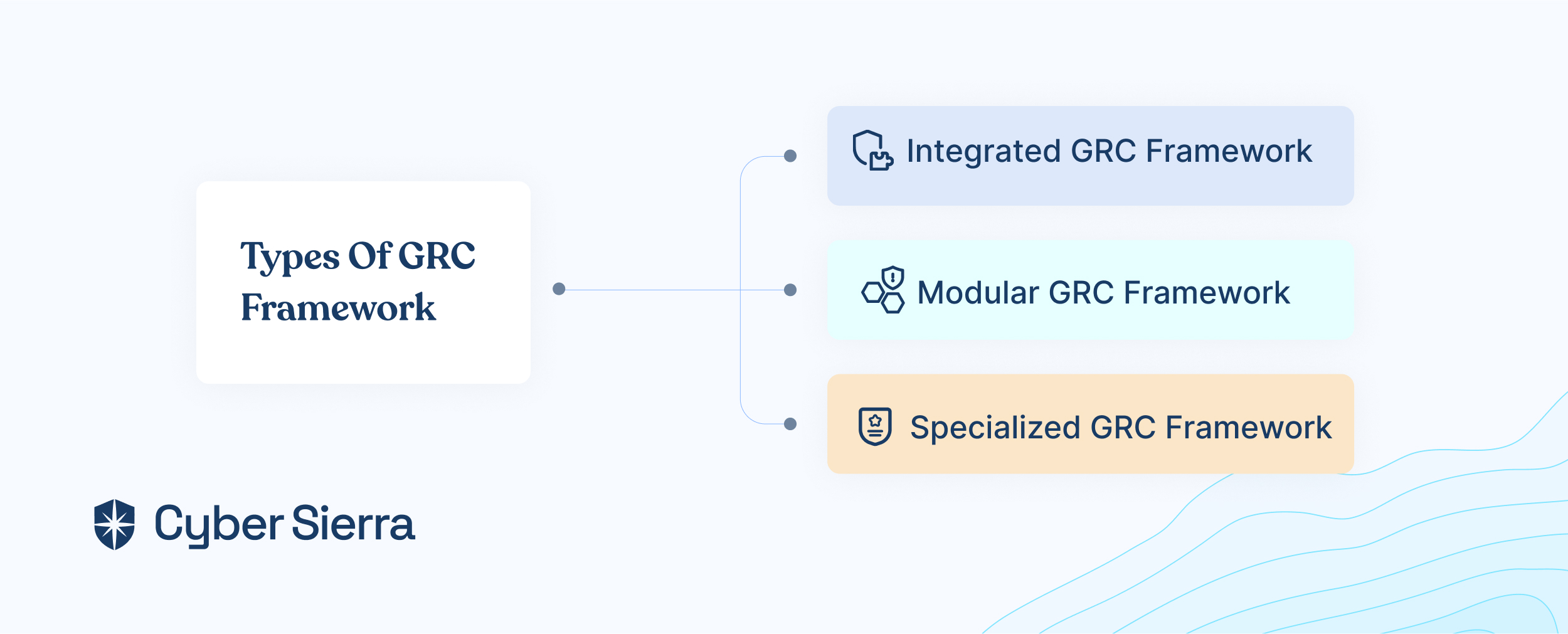

The key components of the GRC framework are clear now. Let’s learn more about the types of GRC frameworks.
Integrated GRC Framework
In an integrated GRC framework, governance, risk management, and compliance functions are unified under a single overarching structure. This approach promotes synergy and efficiency by streamlining processes and fostering a holistic view of organizational risks and compliance requirements.
Modular GRC Framework
A modular GRC framework consists of distinct but interconnected modules for governance, risk management, and compliance functions. Organizations can customize and implement individual modules based on their specific needs and priorities, allowing for greater flexibility and scalability.
Specialized GRC Framework
Specialized GRC frameworks cater to organizations operating in highly regulated industries or facing unique compliance challenges. These frameworks are tailored to address specific regulatory requirements or industry standards, offering targeted solutions for governance, risk, and compliance management.
Benefits of GRC Framework

Implementing the GRC framework makes your life easier. Period. No other way to argue about it. So, what are the benefits of the GRC framework? Read below:
Improved operational efficiency
GRC framework helps automate common mundane processes. Continuous monitoring of controls, risks involved, and KRIs leads to this. So, organizations learn better and more efficient ways to run operations.
Better quality information
The GRC framework brings an integrated approach, and now your management team can have a complete 360-degree view of every piece of data. This helps with informed decision-making.
Cost reduction
With the GRC framework, you can build a roadmap of business rules, better reviews, and consolidated controls. This leads to better use of resources and reduces the cost of implementation.
Automation
The GRC framework reduces manual efforts by eliminating the need for spreadsheets, documents, emails, and direct calls to manage everyday functions. This leads to a shift in reduced manual efforts and eliminates redundant tasks, processes, workflows, and more.
Transparency
Siloed functions come with the GRC framework, and this helps provide full visibility into processes. In this scenario, every department works independently. So, you get visibility for all involved parties.
Efficiency
GRC frameworks bring all the processes related to risks, internal audits, and compliance into a centralized system, which makes managing time-consuming, complex processes easier.
Risk and security
Businesses can manage, implement, track, monitor, and automate risks with the aid of GRC frameworks. This gives upper management the ability to decide more wisely, define objectives that match shifting market demands, and allocate resources to reduce risks.
How to Implement GRC Framework

There is no right or wrong way to build your GRC framework. But the starting point is to bring together all your business components and unify them from a bottom-up approach to implementation.
1. Determine the Benefits of Putting a GRC Platform in Place
The first step is understanding, analyzing, realizing, and accepting the value of GRC framework implementation in your business. Only this will help you identify wide range GRC strategies that can be beneficial for your organization.
- Identify existing processes that are working just fine and need not be changed. These can be retained and added to your unified system.
- Identifying irrelevant data, technologies, and assets that are redundant reduces value and can even complicate your unification process.
- Now, you have the most profitable assets in your hands, and these can be used to enhance your GRC strategy.
2. Create a GRC Project Roadmap
To understand your strategy’s scope, outline the purpose clearly and summarize the main functions of the GRC framework. This has to be accurately done with ongoing collaboration between all stakeholders. Only then will the product result align with the needs of each department without contradictions. Knowing the potential benefits of the GRC framework can help identify desired outcomes for every department here. This helps in the cybersecurity GRC framework and the IT governance risk and compliance framework.
3. Conduct a Gap Analysis
A crucial step in the compliance assessment process is gap analysis, which acts as a diagnostic tool to find differences between an organization’s current procedures and the ideal level of compliance.
During gap analysis, determine the following for each:
- Process maturity
- Data quality
- Operational gaps
Keep these factors in mind when you conduct a gap analysis:
- Finding any duplicate or missing data
- Finding any redundant or duplicate processes
- Finding ways to automate processes or reduce the manual ones
4. Establish and Match Expectations with Stakeholders
Ensure your entire organization is on board with the GRC framework and its implementation. This is often overlooked. The GRC framework involves every department, and all your key stakeholders should have their voices heard about the proposal.
The main steps in achieving organizational alignment are:
- Align executive team members with important considerations, like budget and roll-out dates. Before moving forward and making any necessary changes, you must ensure the leadership is on board with your plan before you notify the rest of the organization.
- Use a top-down strategy. After receiving executive permission, you must establish practical and well-communicated change management procedures throughout all other business divisions. For instance, it’s reasonable to anticipate that your suggested modifications will encounter some opposition. Long-standing internal policies, external policies, and procedures within departments will probably need to be phased away gradually.
- You should provide each team with frequent, educational updates explaining the pertinent changes and how they will impact their duties to facilitate a smooth transition. Establish an open channel of communication for team members to share any worries, recommendations, or other insightful comments that might change your approach.
5. Create a Solid Base for Your GRC Strategy
Get the proper groundwork done. Make sure your GRC system is practical and adaptable. This plays a significant role in the IT governance risk and compliance framework given the increased risk of cyber threats and vulnerabilities and the disastrous impact of data breaches. It is also important to pay closer attention to check if your GRC framework is adaptable to ever-changing regulatory changes.
6. Join Forces with a GRC Solution Supplier
There are a lot of moving components involved in implementing a GRC program from scratch, such as merging information silos, maintaining updates, and employing manual procedures like spreadsheets. Many of these pain points can be streamlined by a smart GRC platform, freeing up your implementation time for higher-level work.
You must exercise due diligence, just like you would with any third-party vendor, to make sure your selected GRC technology complies with regulations and doesn’t put your company at serious risk for security breaches.
Through time and money savings, the appropriate GRC technology should provide a return on investment (ROI).
When selecting GRC software, consider the following crucial inquiries:
- Is it simple to use and intuitive?
- Is it using workflows that are automated?
- Is customization possible? Custom reporting, for instance
- Is it adaptable?
- Do its features carry out actions?
7. Make Your GRC Strategy Uniform
The ability of a GRC strategy to meet the needs of the entire business is one of its key characteristics. Although every department will have unique needs, there ought to be a standard to work from.
8. Oversee and Update Your GRC Plan
Launching your GRC framework is not a one-time, set-and-forget endeavor. Once the implementation is over, it is your responsibility to ensure your strategy is adaptable and evolves with the changes in your business objectives.
Every team should keep up-to-date, precise records of its GRC requirements that are dated and include a note of any significant changes, including the introduction of new technology. A smart GRC platform can automate a good majority of this workflow.
These reports are the reference for your regular stakeholder meetings. Based on these recordings and meetings, you can ensure that your whole organization is aligned with the overall strategy. Another best practice is to conduct an audit at least annually to maintain regulatory compliance management. Any compliance issues identified should then be prioritized for remediation.
How does GRC automation work?

GRC automation software works by seamlessly integrating with your existing systems and processes, streamlining governance, risk, and compliance (GRC) procedures. This integration allows for efficient data collection, analysis, and reporting, ultimately saving time and effort.
Data Integration:
GRC automation integrates with various systems like ERP, HRIS, etc., to automatically collect data, eliminating manual entry and reducing errors.
Automated Workflows:
Predefined workflows and rules process data, aligning with policies and regulations. Automated tasks include risk assessments, control testing, issue management, and compliance monitoring.
Real-time Monitoring and Reporting:
Continuous monitoring assesses adherence to policies and regulations, enabling prompt identification and resolution of risks and violations.
Centralized Dashboard and Reporting:
Consolidated dashboards provide a comprehensive view of GRC posture. Automated reporting tailors information for stakeholders, promoting transparency and informed decision-making.
Scalability and Flexibility:
GRC automation solutions adapt to growth and evolving requirements, incorporating new data sources, workflows, and reporting needs for ongoing compliance and risk management.
What are the advantages of GRC automation?

Efficiency and Time Savings:
Automating data collection, analysis, and reporting processes streamlines GRC procedures, saving significant time and effort compared to manual methods.
Reduced Human Error:
By minimizing manual interventions, GRC automation lowers the possibility of human error, ensuring consistent and trustworthy compliance management.
Proactive Risk Identification:
Real-time monitoring capabilities enabled by automation allow organizations to quickly recognize and resolve potential business risks before they escalate.
Scalability and Adaptability:
GRC automation solutions are easily scalable and can adapt to evolving compliance requirements as businesses grow and expand, ensuring ongoing regulatory adherence.
Centralized Visibility:
Automated GRC platforms often provide centralized dashboards, offering a comprehensive view of an organization’s governance, risk, and compliance posture, promoting transparency and informed decision-making.
Consistent Application of Policies and Regulations:
Automated workflows and rules ensure that policies, regulations, and risk management frameworks are applied consistently across the organization, reducing the risk of non-compliance.
Audit Trail and Reporting:
GRC automation solutions maintain detailed audit trails and generate customized reports tailored to specific stakeholders, such as executives, auditors, and regulatory bodies, facilitating compliance demonstrations and regulatory reporting.
Resource Optimization:
By automating repetitive and time-consuming GRC tasks, organizations can reallocate human resources to more strategic and value-adding activities, optimizing resource utilization.
How can Cyber Sierra’s Smart GRC automation help?
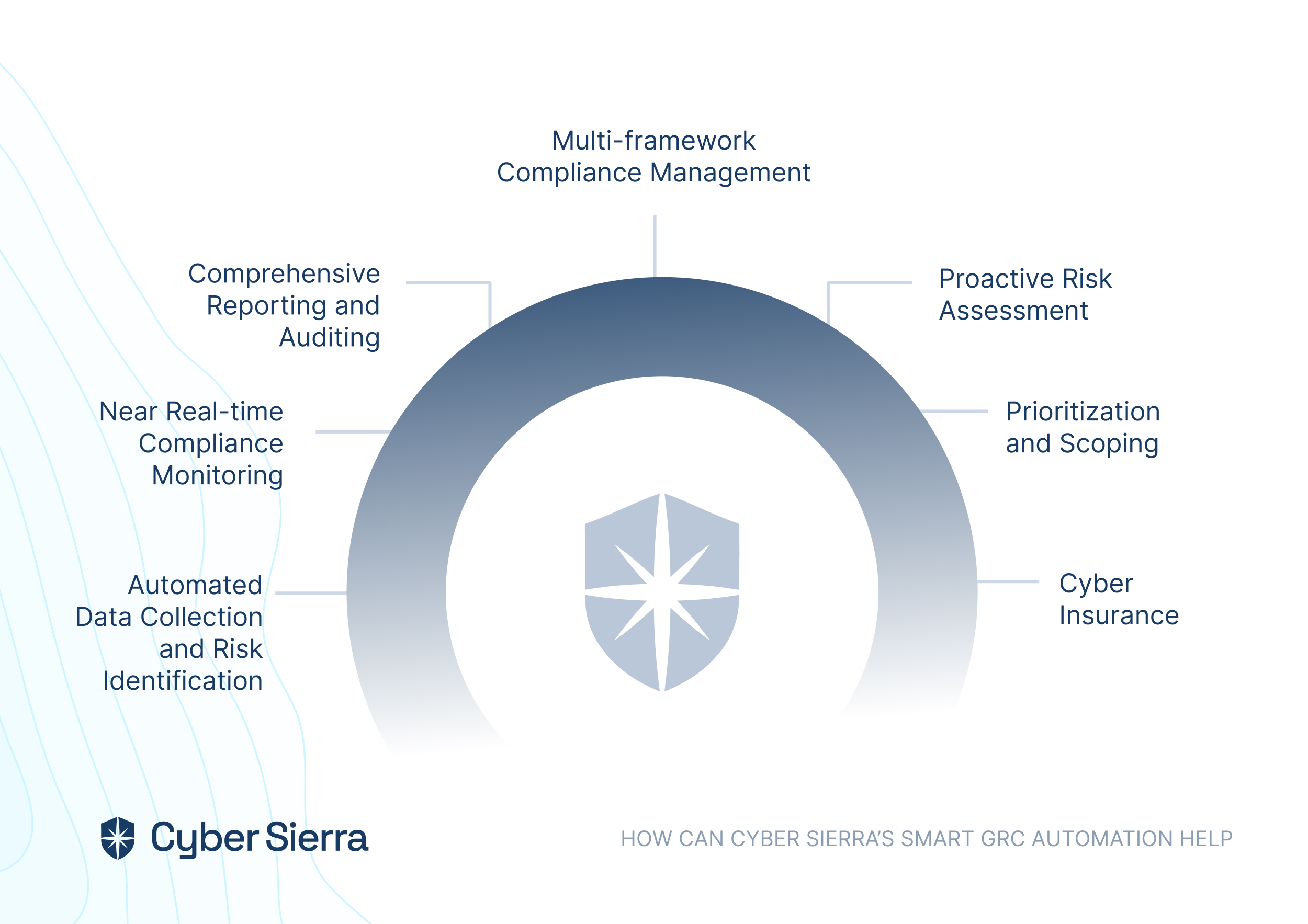

Cyber Sierra’s platform goes beyond traditional GRC frameworks by offering an all-inclusive AI-enabled platform. It encompasses features such as control mapping, automated checks, risk unification, staff training, and streamlined access control, effectively turning compliance into a seamless and integrated process.
Here’s a look at the top features:
Automated Data Collection and Risk Identification:
Cyber Sierra automates data collection and analyses from various sources for effective risk identification and mitigation.
Near Real-time Compliance Monitoring:
Cyber Sierra’s Continuous Control Monitoring (CCM) feature enables real-time monitoring of processes and activities, ensuring ongoing compliance with relevant regulations and internal policies. It proactively identifies and flags any instances of non-compliance, allowing organizations to promptly address issues before they escalate.
Comprehensive Reporting and Auditing:
The platform offers you in-depth reporting tailored to stakeholders, and detailed audit trails promote accountability and transparency.
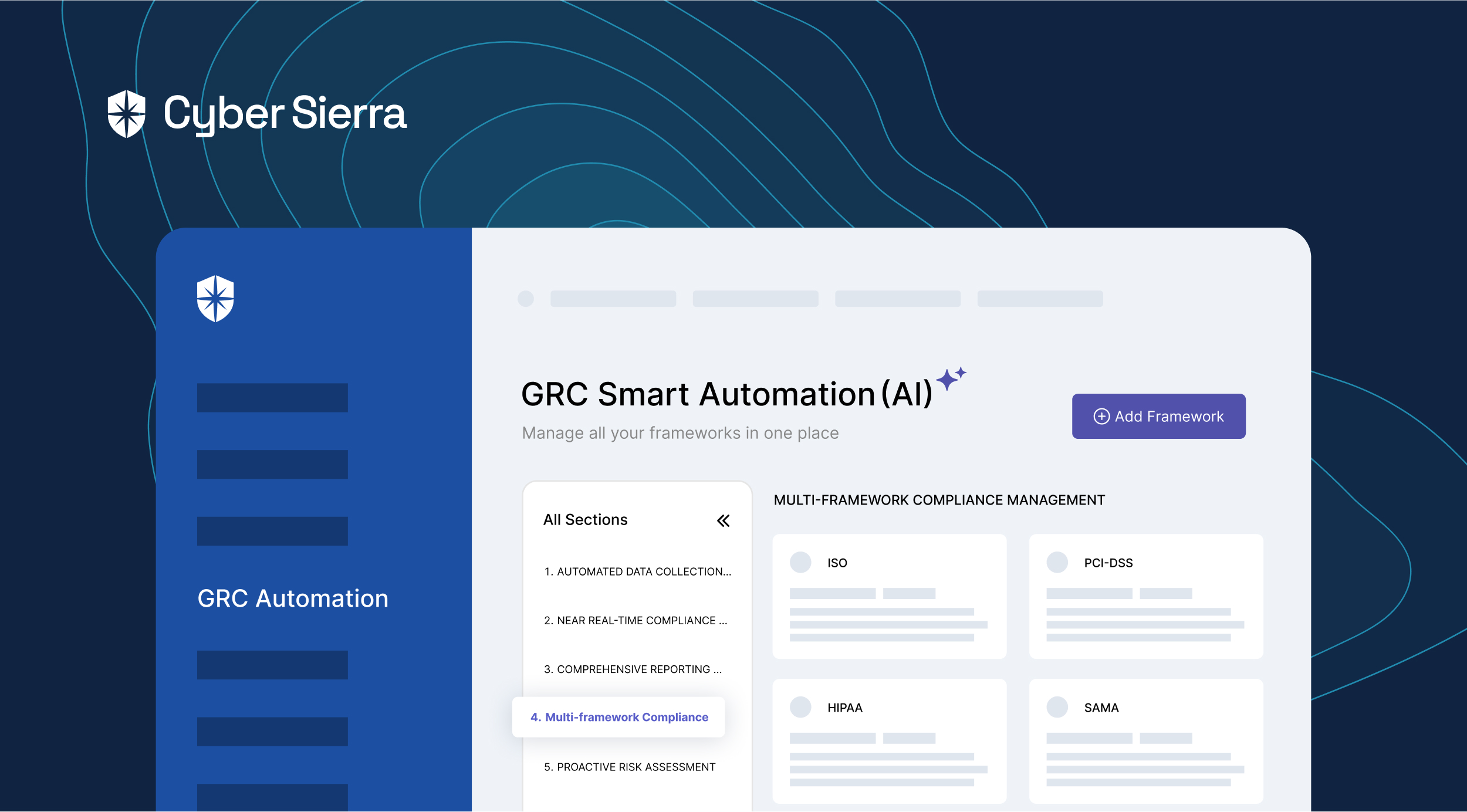
Multi-framework Compliance Management:
Cyber Sierra streamlines compliance across multiple industry regulations and standards such as ISO, PCI DSS, HIPAA, SAMA, CIRMP, MAS TRM, and HKMA, reducing non-compliance risks.
Proactive Risk Assessment:
It identifies and prioritizes potential risks based on impact and likelihood for strategic risk management.
Prioritization and Scoping
: The platform prioritizes compliance requirements, scopes risks and controls for efficient resource allocation.
Cyber Insurance:
The platform can also help you transfer risks through cyber insurance coverage.
If you are looking for a smart GRC solution, talk to our experts today to know how Cyber Sierra can help you reach your security goals.



A weekly newsletter sharing actionable tips for CTOs & CISOs to secure their software.
Thank you for subscribing!
Please check your email to confirm your email address.
Find out how we can assist you in
completing your compliance journey.