Cybersecurity Continuous Control Monitoring: A Checklist for CISOs





Join thousands of professionals and get the latest insight on Compliance & Cybersecurity.
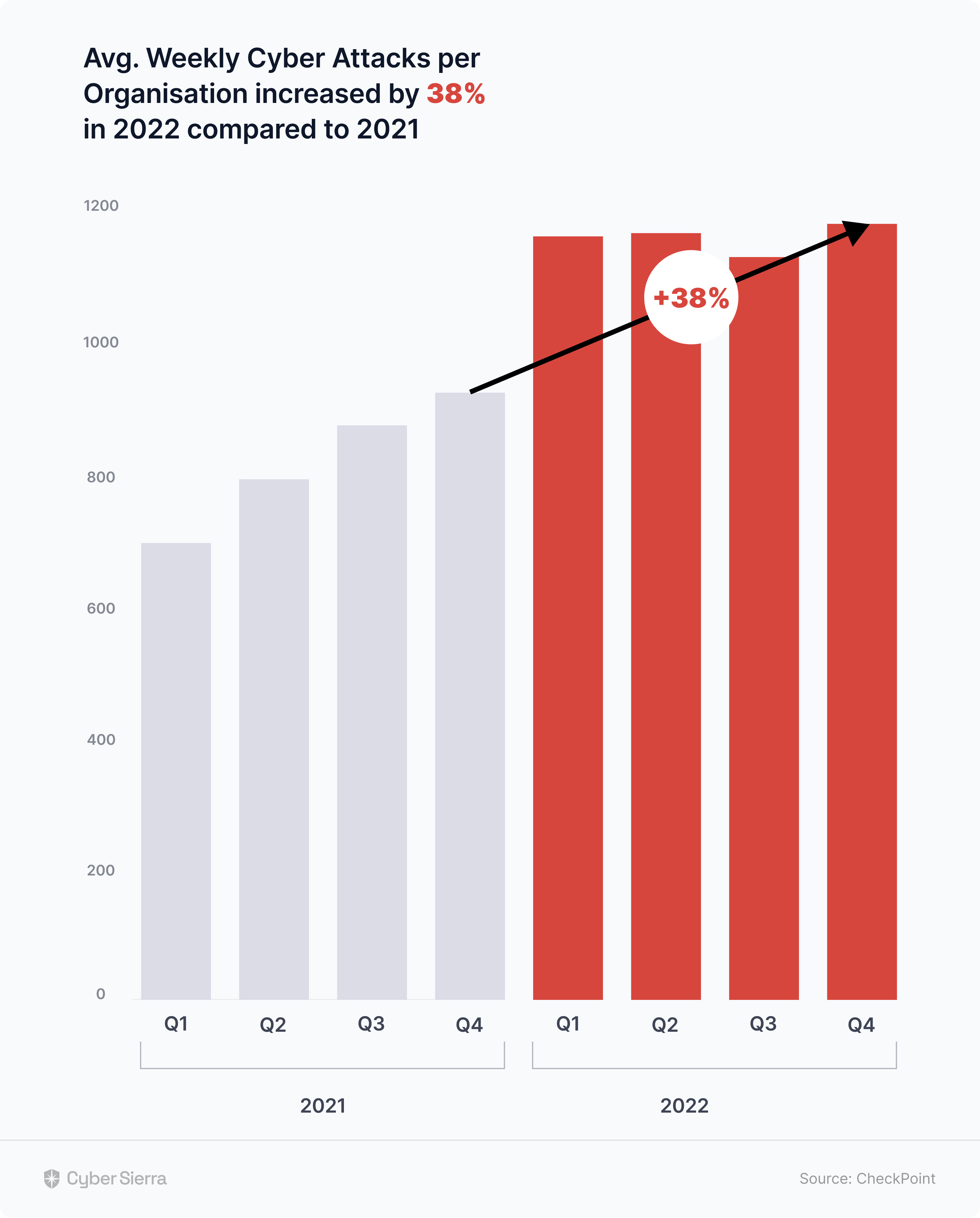
Cybercriminals are becoming more sophisticated. And their growing sophistication is expanding the cyberattack landscape every quarter:

To outsmart them and secure enterprise organizations, security teams must adopt measures that proactively identify and mitigate vulnerabilities and attacks beforehand. Narendra Sahoo, CISA, reiterated how enterprise security teams can do this.
He wrote:


Gartner calls this recommended proactive measure cybersecurity continuous control monitoring (CCM). Being a relatively new approach, it’s best for CISOs and enterprise security executives to begin by knowing what to include as they plan its implementation.
We’ll cover that in this guide and explore an actionable checklist to help your security team get it right. But let’s start with the often-asked question…
What Should a Continuous Cybersecurity Monitoring Plan Include?


Based on this definition, an effective continuous cybersecurity monitoring plan should, through technology and automation:
- Map and maintain awareness of all systems and IT assets across your company and third-party vendor ecosystem.
- Understand all emerging external threats and internal threat-related activities relative to established security controls.
- Collect, analyze, and provide actionable security-related info across all mapped IT assets, security frameworks, and compliance regulations.
- Integrate risk management and information security frameworks, and enable your security team to proactively manage risks.
Automating the areas outlined above in your CCM plan ensures coverage for all steps of the typical CCM lifecycle phases:
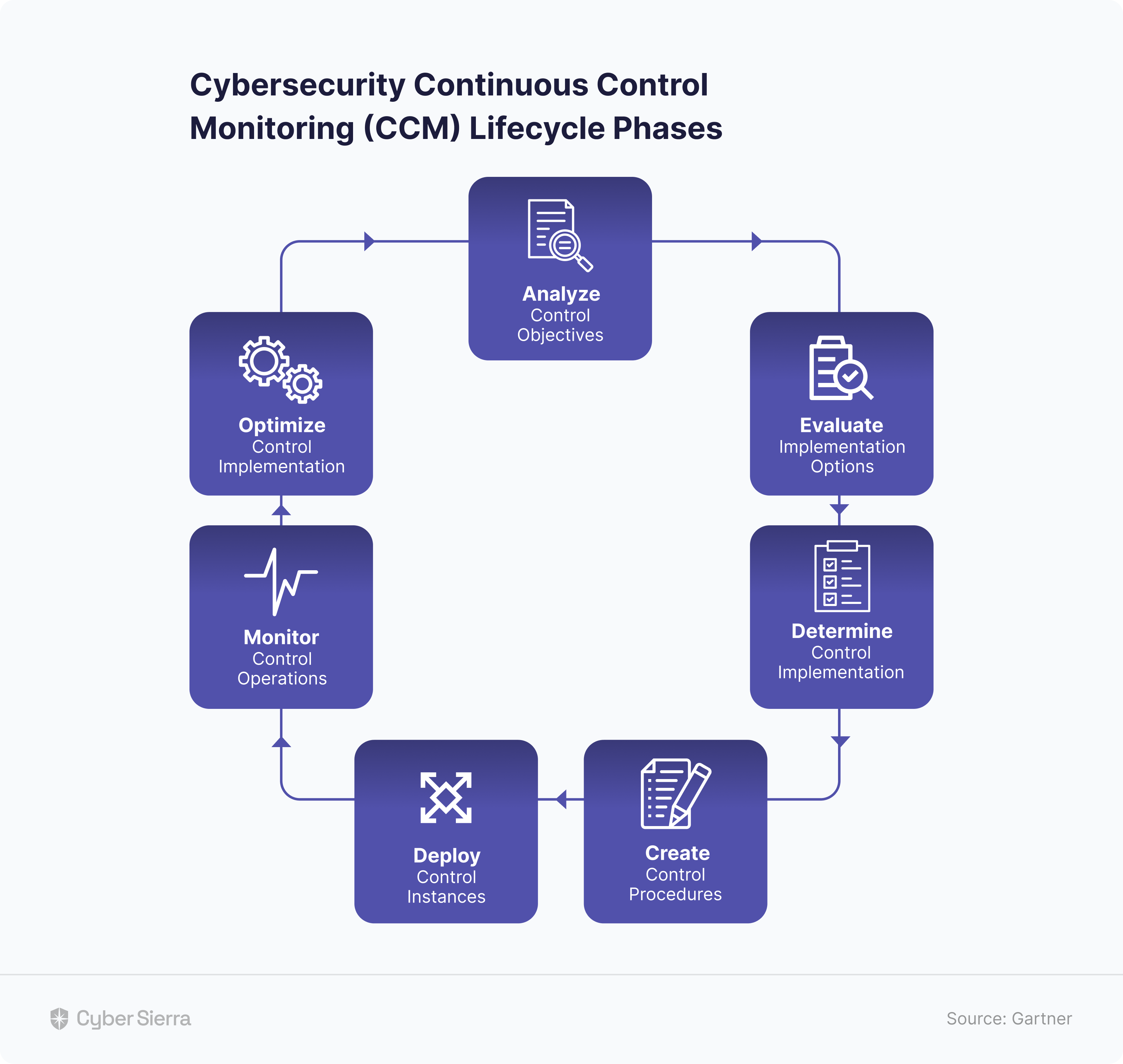

But each phase of the CCM lifecycle above has many steps and, in some cases, substeps. This, in turn, makes their implementation something security teams need to meticulously follow, step-by-step.
In the cybersecurity continuous control monitoring (CCM) checklist below, we explore the steps in each phase. You’ll also see how Cyber Sierra, our interoperable cybersecurity and compliance automation platform, streamlines their implementation.
Download the checklist to follow along:
Why should we implement the CCM process?
By implementing a CCM process, enterprises can proactively manage risks, maintain regulatory compliance, improve operational efficiency, and foster a culture of continuous improvement, ultimately contributing to long-term success and sustainability.
Regulatory compliance:
CCM facilitates regulatory conformity and adherence to industry benchmarks pertaining to internal control oversight, such as the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX), COSO framework, and other governance, risk, and compliance (GRC) directives.
Risk mitigation:
It offers near real-time visibility into control vulnerabilities, empowering organizations to promptly identify and mitigate risks, thereby reducing the potential for fraud, errors, or operational disruptions.
Operational efficiency:
CCM automates the monitoring of controls, diminishing the need for periodic manual testing and audits, which can be time-consuming and resource-intensive endeavors.
Continuous enhancement:
By continuously monitoring controls, organizations can pinpoint areas for improvement and implement necessary adjustments to bolster the efficacy of their control environment.
Cost optimization:
An effective CCM can aid organizations in avoiding the costs associated with control failures, such as fines, legal fees, and reputational damage.
Informed decision-making:
CCM furnishes management with up-to-date information on the state of internal controls, enabling them to make more informed decisions regarding risk management and resource allocation.
Competitive Advantage:
Implementing a robust CCM process demonstrates an enterprise’s commitment to strong internal controls, risk management, and good governance practices, which can enhance its reputation and provide a competitive advantage in the market.
Enterprise Cybersecurity Continuous Control Monitoring (CCM) Checklist
Renowned Security Architect, Matthew Pascucci, advised:


Matthew’s advice is spot on.
In short, it is the expected outcome of the first step of our CCM checklist. So let’s dive in.
1. Analyze Continuous Control Objectives
Enterprises with any form of existing compliance and risk management process already have some form of security controls in place. If that’s your case, as it is with most enterprise organizations, achieving continuous monitoring of those security controls starts with analyzing your controls’ objectives.
You achieve this by initiating an extensive assessment of your organization’s compliance and cybersecurity controls. In other words, assess existing risks, cyber threats and vulnerabilities with a CCM platform.
The platform you choose should be able to:
- Connect and map all the IT assets in your cloud and network environments, and those of third-party vendors.
- Outline and categorize all technical and non-technical security controls across mapped assets and environments.
- Integrate existing risk management, compliance, and information security frameworks to match outlined controls.
- Identify vulnerabilities and gaps in existing security controls relative to mapped assets across cloud environments.
You can automate these tasks with Cyber Sierra. First, connect and map IT assets used across your company and third-party vendor ecosystem by integrating them with Cyber Sierra:
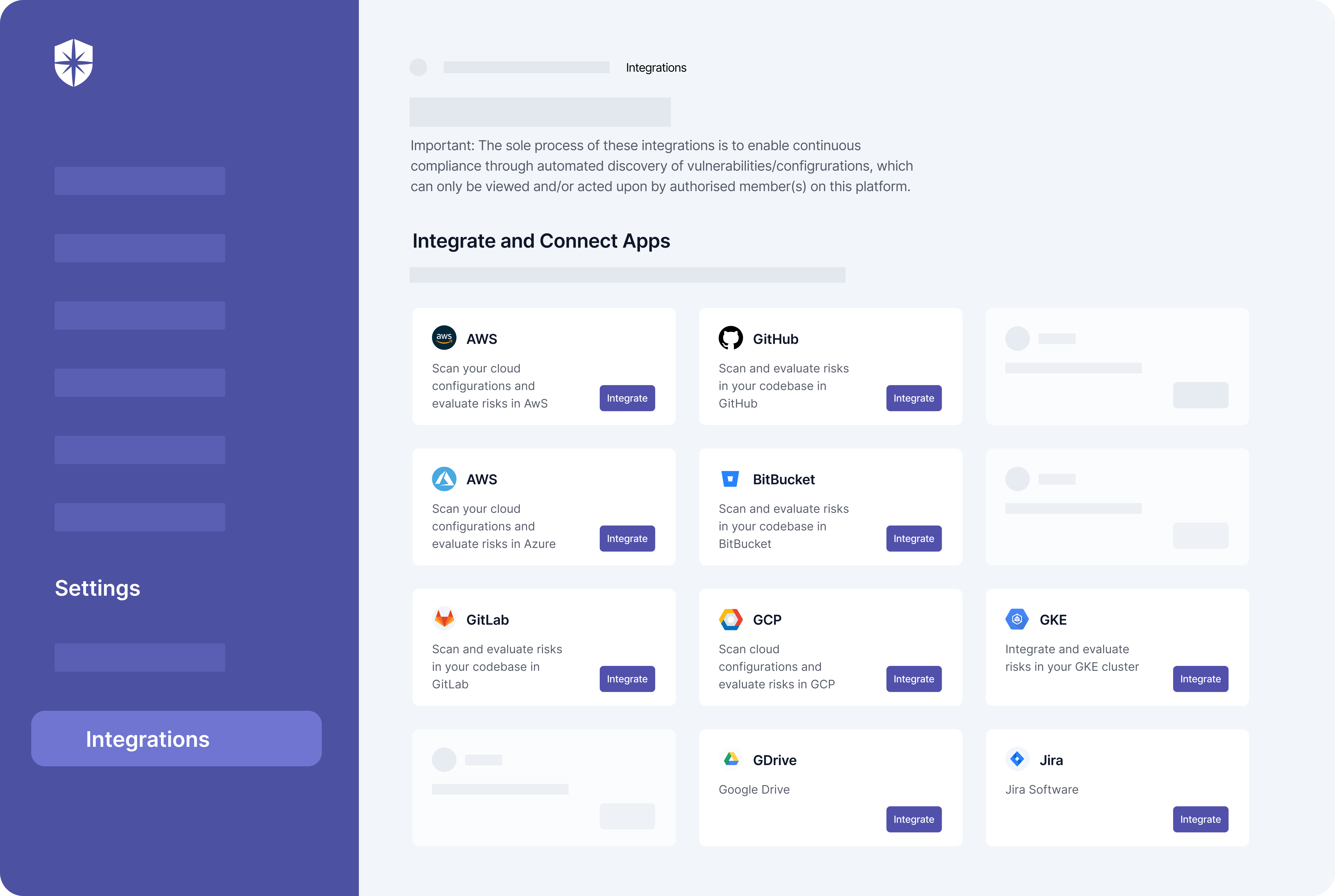

After integrating, scan one, some, or all apps and systems used across your organization in a few clicks. Each time your team initiates a scan with Cyber Sierra, it not only performs a scan, but also performs a comprehensive risk assessment of the integrated IT assets.
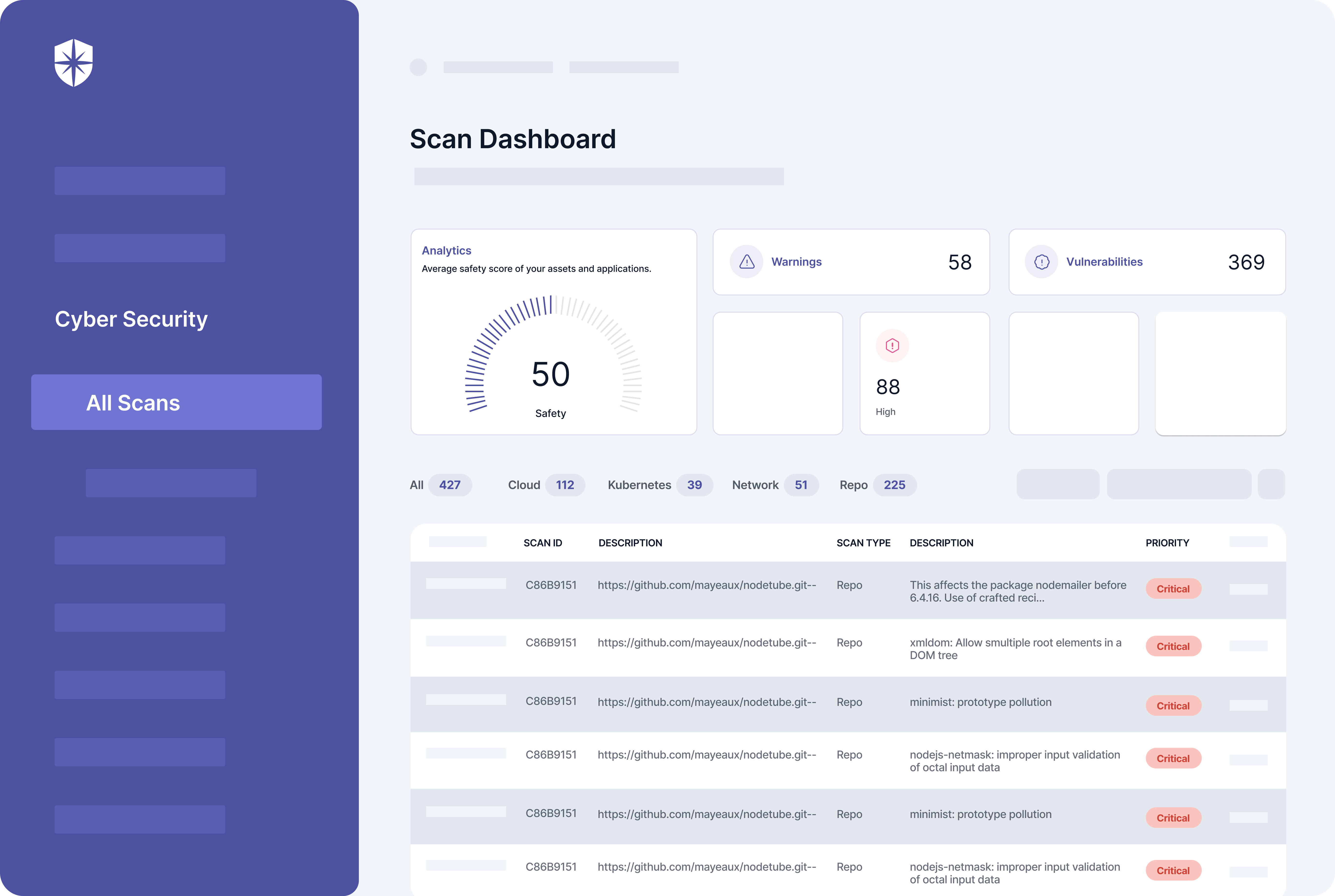
This is because our interoperable cybersecurity platform analyzes all integrated assets against standardized risk management, compliance, and information security frameworks in the background. This helps to detect and push vulnerabilities, cyber threats, and risks into your dashboard.
Here’s a peek:

2. Evaluate Controls’ Implementation Options
What implementation options are feasible after analyzing the objectives of your controls through a comprehensive risk assessment? That’s the question your team must answer here.
To do this:
- Review your company’s service portfolio to identify and determine what security controls are mission-critical.
- Identify areas where additional resources (i.e., expertise, capital, training, etc.) are required for implementing continuous monitoring of mission-critical security controls, based on gaps found during the analysis and risk assessment phase.
- Examine existing risk management, compliance, and information security procedures and processes to uncover what needs an upgrade to achieve continuous control monitoring.
3. Determine Continuous Control Implementation
According to Steve Durbin, CEO of the Information Security Forum:


Continuous control monitoring is a fast-paced process, where your security team must stay one step ahead of cybercriminals. So as observed by Steve, having a cohesive security architecture is essential for effective, consistent, and safe implementation.
You can do this by:
- Developing a common language by creating standard terms and principles for implementing continuous control monitoring in your organization. This makes it clear for your security team and new members to understand what they should and should not do.
- Establishing the objective and priority of each implemented or should-be implemented security control relative to your business goal(s). This helps everyone in your security team working on specific security controls to give it necessary priority.
- Determining and documenting acceptable approaches for implementing CCM. This helps your team know where to start, how to proceed, and the possible, acceptable outcome of each implemented or should-be implemented security control.
- Outlining the conditions and steps for adapting all mission-critical security controls being monitored.
4. Create Continuous Control Procedures
This step involves creating continuous security control procedures based on stardardard or customized cybersecurity policy frameworks. Examples of standard cybersecurity policy frameworks to create continuous control procedures from are NIST, ISO, SOC, etc.
So for this step:
- Examine standard cybersecurity policy frameworks to identify security controls critical to your business.
- Create procedures for implementing controls identified from standard policy frameworks.
- Identify necessary security controls not available in the standard cybersecurity policy frameworks examined; then, create custom policies and procedures for implementing them.
For the third sub-step, you’ll need a platform like Cyber Sierra that allows the upload of custom cybersecurity policies. Our compliance automation suite allows the creation of customized risk governance programs and uploading of custom control policies for them:
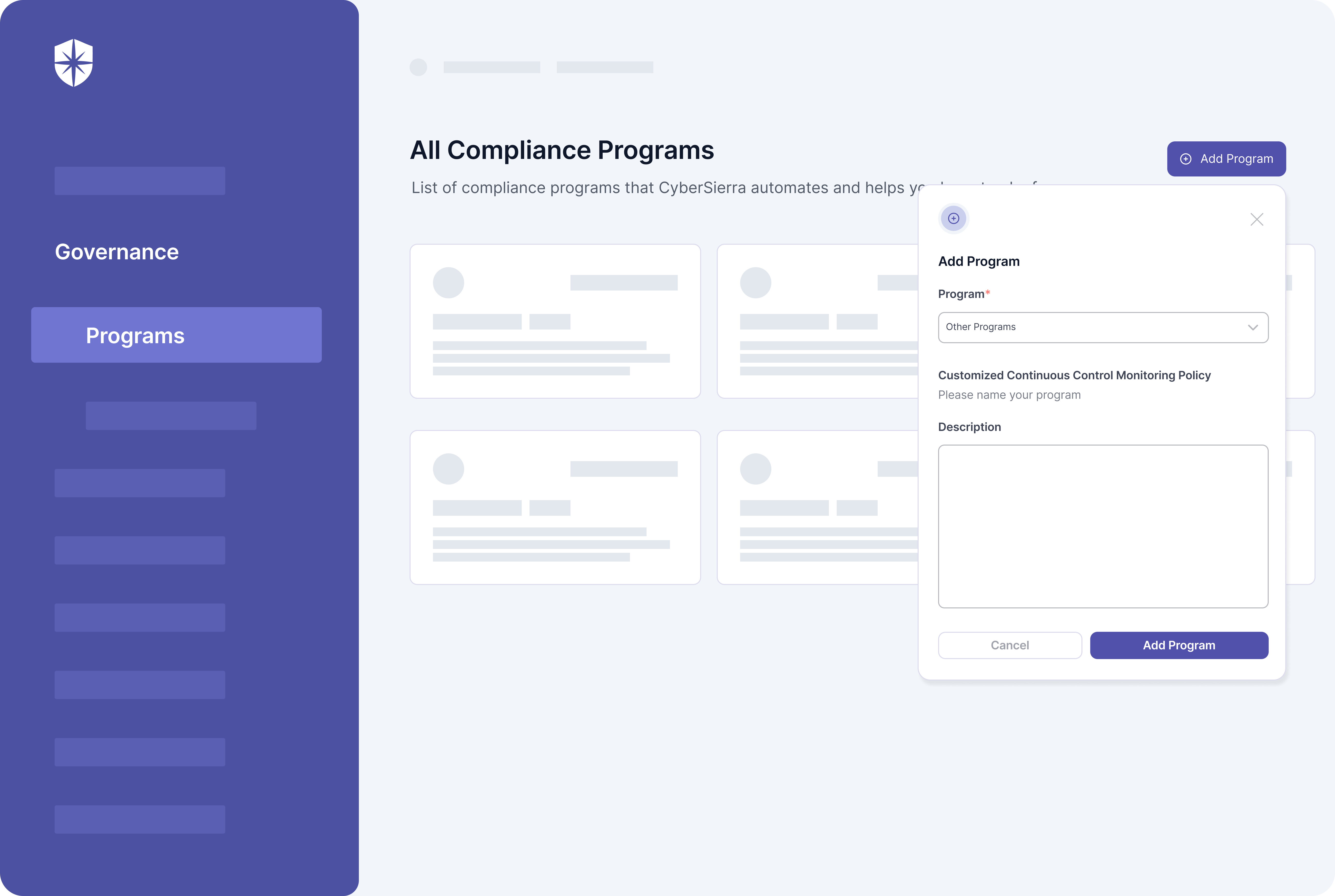

5. Deploy Continuous Control Instances
Implementing control instances operationalizes the cybersecurity controls established within the policy frameworks developed in the previous phase.
This involves:
- Collaborating with your security operations team to implement continuous cybersecurity controls instances.
- Implementing the security services needed to enforce and make defined control instances work.
- Providing evidence for evaluating adherence to established security controls, policies, and procedures.
You may need to hire external expertise or launch employee security awareness training on deploying continuous control instances. Cyber Sierra can help with the latter:
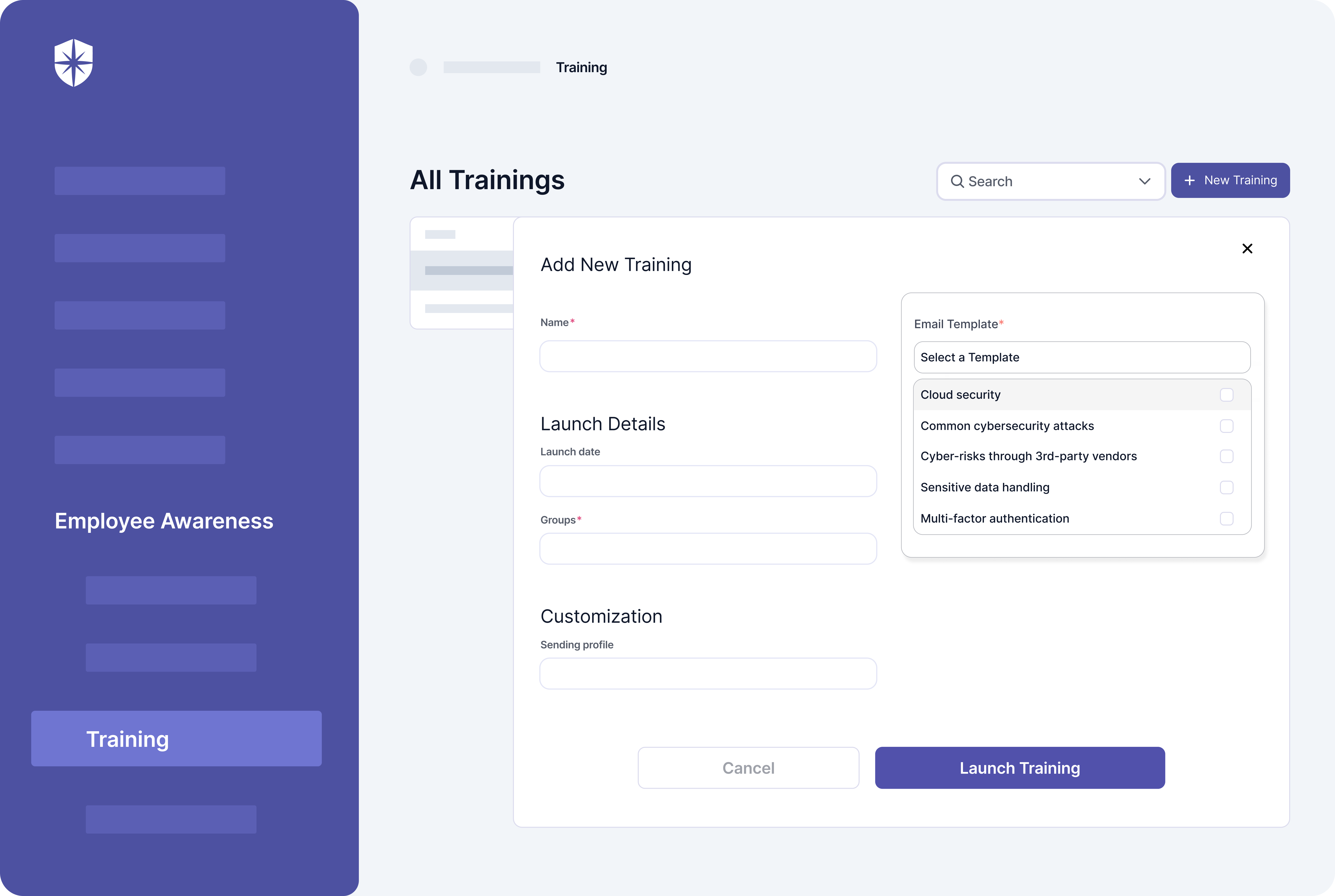

As shown, you can launch and track the completion of cybersecurity training programs relevant to implementing CCM with our employee Security Awareness module.
6. Automate Security Controls’ Monitoring
This step is where the main functions of a cybersecurity continuous control monitoring (CCM) platform come to bare. So choose one that enables your security team to automatically:
- Monitor and test security controls based on defined procedures and implemented risk management and compliance policies.
- Identify and score emerging threats according to their likely impact on your organization’s security program.
- Provides actionable information for your DevSecOps team to remediate threats and vulnerabilities in near-real-time.
For a CCM platform to tick the boxes above, it must ingest data from your mapped IT assets against established security policies. It must also refresh this ingested data in real-time automatically, ensuring continuous monitoring of security controls. Finally, it must alert security teams of risks that could lead to a breach.
The Risk Register on Cyber Sierra meets those requirements.
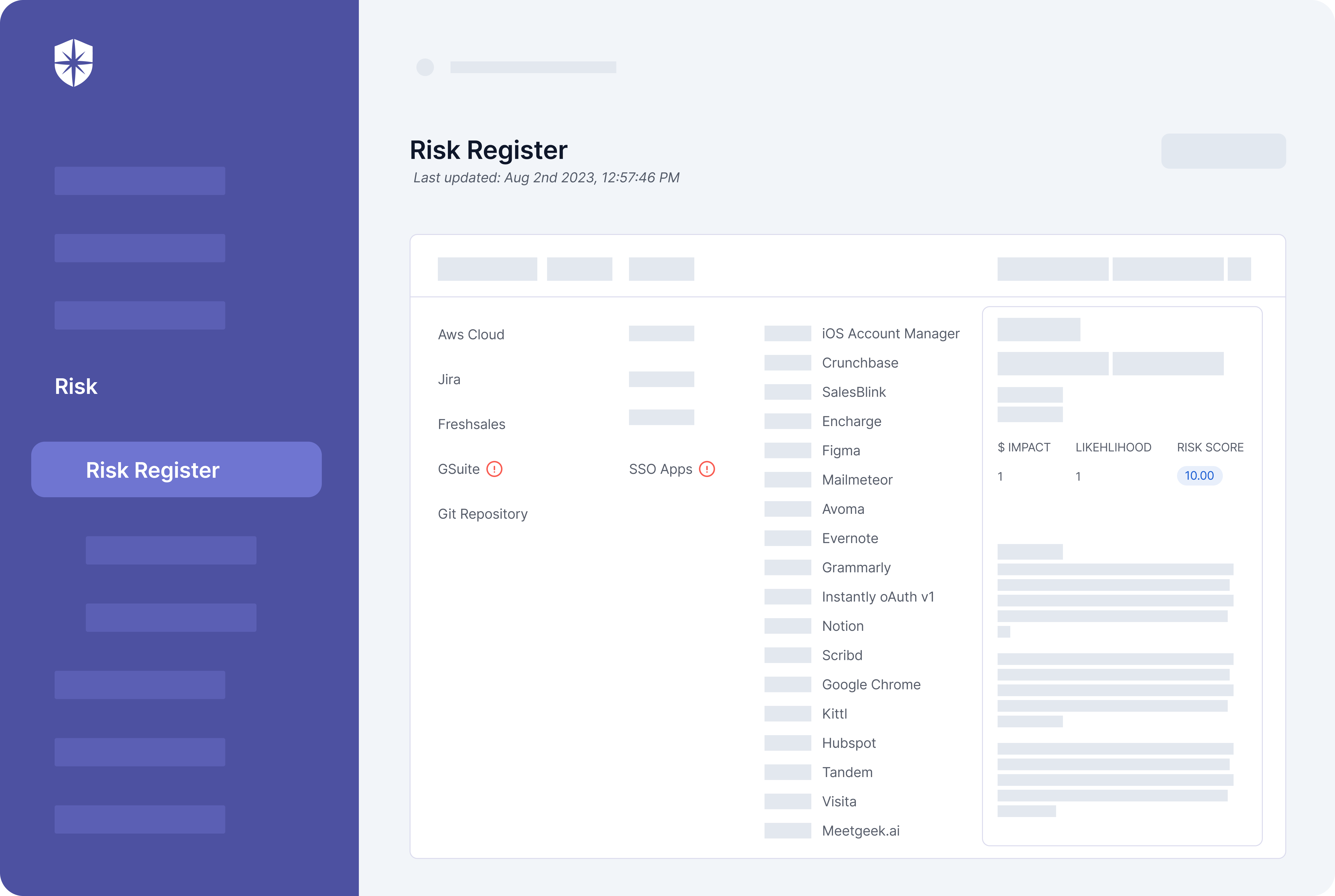

As shown, it detected threats in a GSuite asset category down to individual users. In this case, it refreshes ingested data in real-time, creating a threat alert and risk score whenever a user connects an unapproved external app with SSO to their GSuite.
7. Optimize Continuous Control Implementation
Continuous control monitoring is a never-ending process.
As the threat landscape, risk management trends, and compliance regulation requirements evolve, so should your continuous control implementation. Also, as your organization grows or collaborates with new third-party vendors, your continuous security control requirements will must adjust, too.
So choose an interval that makes sense for your organization, say weekly or monthly; and optimize CCM implementation by:
- Enhancing ongoing data ingestion by uncovering new or disconnected apps and systems in your IT asset inventory.
- Detecting control gaps and threats not accounted for as your DevSecOps team remediates identified risks.
- Informing overall threat intelligence management across your organization based on risks and vulnerabilities detected throughout the CCM process.
What Tool is Used in Continuous Control Monitoring?
Due to its growing popularity, pure-play continuous control monitoring (CCM) platforms are emerging. At the same time, some niche governance, risk, and compliance (GRC) vendors are incorporating CCM capabilities into their solutions.
While the latter can do some of the job, it’s best to use a CCM tool built to support implementation across all phases of the CCM lifecycle. As the checklist explored above showed, that includes a long list of steps all related to each other in one way or another.
Based on this, Gartner recommends the use of a CCM tool that automates four core things:


Cyber Sierra has these capabilities built into its platform.
In short, ours is an interoperable cybersecurity and compliance automation software. This means the capabilities outlined above work well together, making the automation of CCM procedures and processes seamless.
Automate Continuous Cybersecurity Control Monitoring
As shown throughout various steps of the CCM lifecycle phases, automation is at the core of implementing CCM. And it is more feasible with an interoperable cybersecurity and compliance automation platform.
This is where Cyber Sierra comes in.
Why not book a free demo of Cyber Sierra to get a sneak peek into how our platform automates the ongoing implementation of CCM?



A weekly newsletter sharing actionable tips for CTOs & CISOs to secure their software.
Thank you for subscribing!
Please check your email to confirm your email address.
Find out how we can assist you in
completing your compliance journey.