Practical Approach to Continuous Control Monitoring





Join thousands of professionals and get the latest insight on Compliance & Cybersecurity.
How confident are you in your organization’s capacity to promptly and adeptly identify and counter cybersecurity risks?
Despite your best efforts to fortify your cybersecurity approach, it’s probable that your endeavors fall short.
In the present landscape, risk factors are in a constant state of flux, demanding swift and efficient counteractions.
An avenue to tackle this predicament lies in Continuous Control Monitoring (CCM), a method that aids enterprises in upholding regulatory compliance and curtailing cyber threat vulnerabilities.
In this article, you will understand how to select the right CCM solution and how to implement the same.
Let’s get started.
Understanding continuous control monitoring
Continuous Control Monitoring (CCM) stands as an innovative risk management approach, empowering enterprises to consistently evaluate, handle, and alleviate business risks. In today’s swiftly evolving digital realm, it’s imperative for risk managers and IT administrators to possess a comprehensive grasp of CCM and skillfully integrate it within their organizations.
At its core, CCM systematically examines controls and processes to ensure that they are
- Effectively preventing or detecting risk,
- Reducing the likelihood of non-compliance, and
- Other potentially costly incidents.
CCM leverages advanced technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) to streamline and automate risk-monitoring processes. This, in turn, significantly decreases the time and resources spent on manual risk assessments and audits.
Choosing the right CCM solution
Choosing the appropriate CCM solution involves careful consideration. Here are some actionable tips to guide your selection process:


1. Identify your organization’s requirements
Start by identifying your organization’s specific needs and challenges in risk management and compliance. These could include specific industry or regulatory requirements, a shortage of risk management resources, or a need to improve operational efficiency.
Some of the challenges can include:
- Inadequate risk visibility: Limited insight into real-time risk and compliance status across different business units.
- Limited resources: Insufficient workforce or expertise to efficiently manage risks and ensure compliance.
- Inefficient processes: Current manual risk management and compliance monitoring processes may be time-consuming and prone to error.
- Data integration issues: Difficulty integrating data from disparate sources and systems for comprehensive risk assessment.
- Scalability concerns: The current risk management system may not be capable of handling increased data volume and complexity as the business grows.
- Lack of real-time reporting: Insufficient mechanism for generating real-time reports for swift decision-making.
- Security concerns: Ensuring the security of sensitive data while performing risk and compliance-related tasks.
2. Look for advanced features
Advanced features can help organizations to get the most out of their risk management systems. Some of these features include:
- Single source of truth (SSOT): The ability to view all data related to a business process from one source, including transaction details and related documentation, in a single user interface.
- Robust data modeling capabilities: Users can create and modify data models without technical knowledge or assistance from IT staff.
- Advanced data visualization capabilities: Users can create dashboards and reports with a wide range of visualizations, including charts and graphs.
- Automated workflow management: This feature automatically routes tasks to relevant stakeholders, enforces accountability, and streamlines the risk management process. It can also provide reminders for incomplete tasks or tasks nearing their due date, improving efficiency and ensuring timely action.
- Predictive analytics: Using AI and ML to access predictive analytics and foresight into potential risks or issues can help organizations anticipate risks, devise counteractive strategies, and make better informed decisions about risk mitigation.
3. Integration with existing systems
When we talk about the integration capabilities of a CCM solution, it refers to the system’s ability to work in harmony with your existing IT infrastructure. This includes linking with various business applications, databases, IT systems, and other sources of creating or storing data within your organization.
Here are a few core aspects this comprises:
- Data Collection: A powerful CCM solution should be capable of extracting data from different systems like ERP, HRM, CRM, and other bespoke applications.
- Data Consistency: Since the CCM system interacts with multiple data sources, it should ensure data consistency and resolve any potential conflicts. That way, each system using the data can have the correct and most up-to-date information.
- Tools Compatibility: The CCM solution should be compatible with your existing reporting, visualization, and data analysis tools so that you can immediately put it to use.
The primary goal of integration is to bring about efficient and consistent data management across all systems, making risk management a streamlined and automated process.
4. Consider vendor support and training
Don’t let your organization’s proficiency be constrained by your team’s capabilities to adopt a risk management solution.
The provider should furnish training and assistance throughout both the setup phase and beyond. This approach guarantees that all members within your organization grasp the tool’s mechanics, the data prerequisites for each process stage, and optimal utilization techniques.
It’s crucial to verify that the vendor offers robust customer support and comprehensive training initiatives, aiding your team during system implementation and continuous utilization.
5. Evaluate user-friendliness
Prior to procuring a CCM solution, prioritize the following checkpoints to guarantee a user-friendly experience and ease of use:
- Intuitive Interface: Clean, organized, and easily navigable layout
- Ease of use: Straightforward execution of typical activities
- Guided steps: Helpful tooltips or guides for complex tasks
- Customization: Tailored dashboards, reports, and configurable aspects
- Accessible support: Comprehensive user manuals, tutorials, and responsive customer service
- Compatibility: Availability on various devices and platforms
Step-by-Step implementation process of CCM
Implementing a new CCM system may seem daunting, but it doesn’t have to be.
We’ll walk you through the process, from planning to execution, ensuring each phase is thoroughly completed to set your CCM solution up for success.
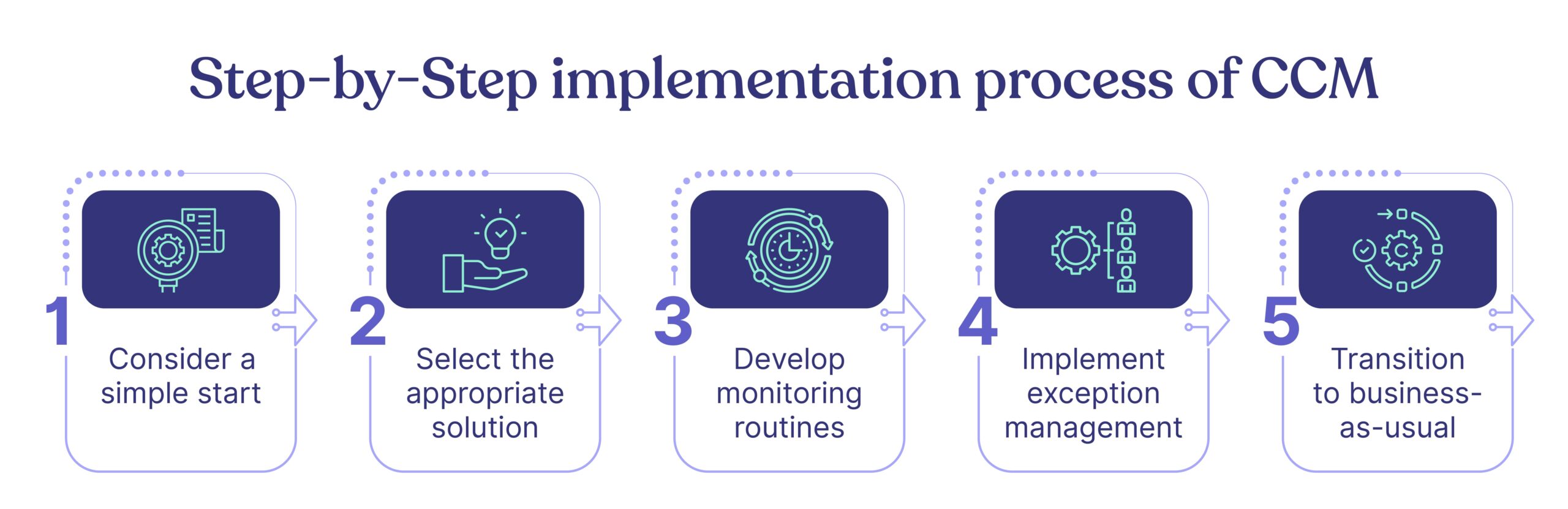

1. Consider a simple start
Every successful digital transformation starts small and builds upon early successes. Hence, when orchestrating the introduction of CCM, initiate with routine processes that stand to gain the most from sustained surveillance.
Begin by identifying vulnerable domains or those presently grappling with elevated risk levels. Internal audit findings serve as invaluable inputs, spotlighting problematic processes and controls with substantial financial implications.
Additionally, consider testing CCM on procedures previously subjected to manual audits, facilitating a comparison of efficacy and efficiency.e already been audited manually to compare the efficiency and effectiveness of both methods.
Using Cyber Sierra’s solutions can further simplify the start, as it assists with accurately mapping your business relationships and identifying potential areas of concern.
2. Select the appropriate solution
Continuous control monitoring involves complex procedures and requires a robust and reliable tool or software. While an array of off-the-shelf solutions may promise comprehensive coverage, it’s vital to recognize your organization’s distinctive needs, processes, and control environment.
The selection process demands a laser focus on locating a solution that harmonizes with your organization’s requisites and integrates seamlessly within your IT framework. Flexibility for customization to match your unique demands is equally paramount.
Cyber Sierra, for instance, provides an interoperable solution tailored to your organization’s needs governing data, risk assessments, policies, vendors, and employees in one central hub.
3. Develop monitoring routines
Developing and fine-tuning CCM routines is critical for the ongoing success of your monitoring activities.
Initially, you’ll program the system to generate high probability exceptions (HPEs), potentially indicative of control failures.
This might involve a process of iterative refinement; as the CCM system processes more data and exceptions are investigated and resolved, you’ll get a clearer picture of what indicates a likely control failure, and you can refine your routines accordingly.
This important step significantly reduces false positives and allows your team to focus more on true control issues.
4. Implement exception management
All exceptions generated by CCM need analyzing and resolution. Exceptions should be captured in a secure environment, and operational staff should be tasked with resolving them. This process must be carefully designed to avoid overwhelming staff with false positives.
5. Transition to business-as-usual
Once established, CCM should be part of the business’s standard operational procedures and processes. Regular system administration tasks, such as resolving data load issues, managing user access, or refining test logic, are essential for smooth operation.
Training your team for CCM adoption
Implementing CCM in your organization implies a technological shift and a cultural one, and involves understanding the skill set requirements, planning effective training strategies, and fostering a CCM-focused culture within your organization.
1. Skill set requirements
A successful CCM adoption demands a diverse skill set within your team, spanning comprehension of compliance intricacies, identification of cybersecurity threats, and mastery of analytics and data interpretation.
Your team must also learn to adapt to new workflows, understand the system’s outputs, reassess the risk levels of various assets, and comprehend their impacts on business operations.
2. Training strategies
Adopting a structured and gradual approach to training can be beneficial. Introduce your team to the new CCM system and train them in various aspects of CCM, such as continuous monitoring, risk assessment procedures, and control strategies.
Also, consider conducting hands-on training sessions where your team can explore and learn about the system’s features, enhancing their understanding and proficiency.
3. Fostering a CCM-focused culture
Beyond individual skills and training, nurturing a corporate culture that esteems CCM is pivotal. This culture champions transparency, risk awareness, and perpetual self-audit, necessitating a mindset shift from reactive to proactive risk management.
This transformation enhances the entire CCM implementation, fostering enthusiastic team participation in consistent control and risk evaluations. An ingrained CCM-focused culture strengthens your organization’s risk resilience and ensures an enduring commitment to effective risk management.
Identifying assertions for CCM
Assertions form a pivotal part of CCM. These are statements that management makes about certain aspects of the business, thereby validating compliance with the organization’s rules and policies.
Here’s how to identify relevant assertions for your enterprise and incorporate them into your CCM system:
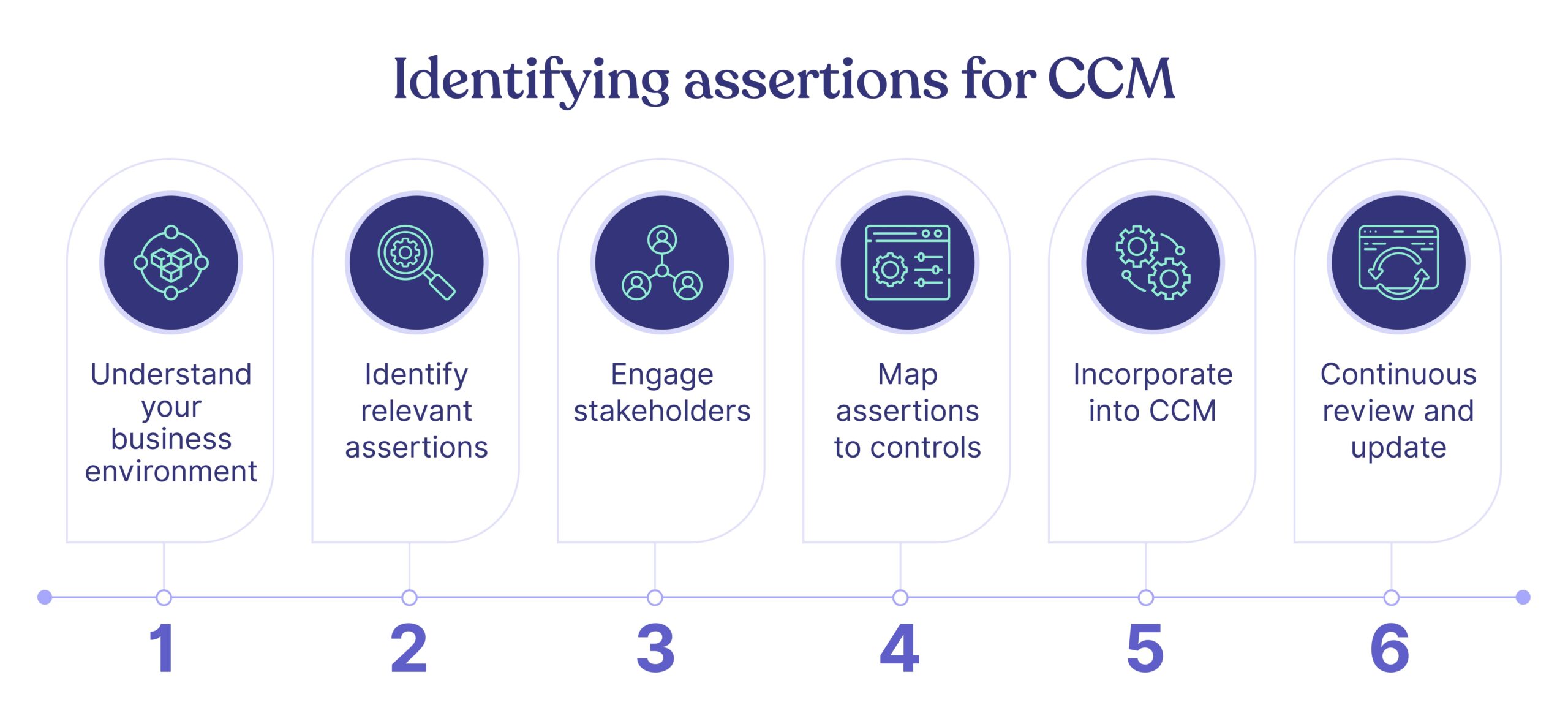

1. Understand your business environment
Start by understanding your organization’s environment, including its functions, operations, policies, and procedures. Identify the risk spots and performance indicators. Evaluate the various systems, controls, and procedures to mitigate these risks.
2. Identify relevant assertions
Different sectors and operations typically require distinct assertions. For example, a manufacturing unit might need assertions about inventory control, whereas a service-based firm could require claims about data privacy or service delivery timelines. Identifying relevant assertions depends on your organization’s specific requirements, industry standards, and regulatory mandates.
3. Engage stakeholders
Engage relevant stakeholders while identifying assertions. This includes managers from different departments and frontline staff who work directly with the systems being monitored by CCM.
4. Map assertions to controls
Once the assertions are identified, the next step is to map them to relevant controls within your organization. This mapping helps identify what control activities can validate which assertions.
5. Incorporate into CCM
After mapping, integrate these assertions into your CCM system. These become the metrics and checkpoints that continuous monitoring will track to ensure that all controls function as per required standards.
6. Continuous review and update
Business environments change and evolve. So, the assertions and their respective controls must be reviewed and updated frequently to ensure relevance and effectiveness.
Remember, assertions contribute to the reliability of your system’s compliance status. Thus, carefully identified and curated assertions can dynamically support your efforts in implementing and fine-tuning CCM in your organization.
Conclusion
CCM can be a potent tool for ensuring compliance. However, it requires careful planning and execution to be effective.
When implementing a CCM solution, it is best to do so gradually—refining processes based on practical learning and experiences. This will ensure the effective integration of CCM into business processes, leading to improved control effectiveness and risk management.
Nevertheless, CCM implementation forms only one piece of a larger puzzle. Comprehensive organizational security demands a multifaceted approach, encompassing:
- Ongoing employee cyber awareness training.
- Consistent adherence to regulatory compliance.
- Addressing cloud security issues.
- Maintaining sufficient cyber insurance coverage.

This is where Cyber Sierra comes in. Cyber Sierra’s platform enables enterprises to keep company policies in one central location and make them accessible to all employees. The platform also offers a comprehensive training regimen that addresses the risks posed by today’s most pressing cybersecurity issues.
Book a demo to learn how to use Cyber Sierra to set up your CCM program.



A weekly newsletter sharing actionable tips for CTOs & CISOs to secure their software.
Thank you for subscribing!
Please check your email to confirm your email address.
Find out how we can assist you in
completing your compliance journey.