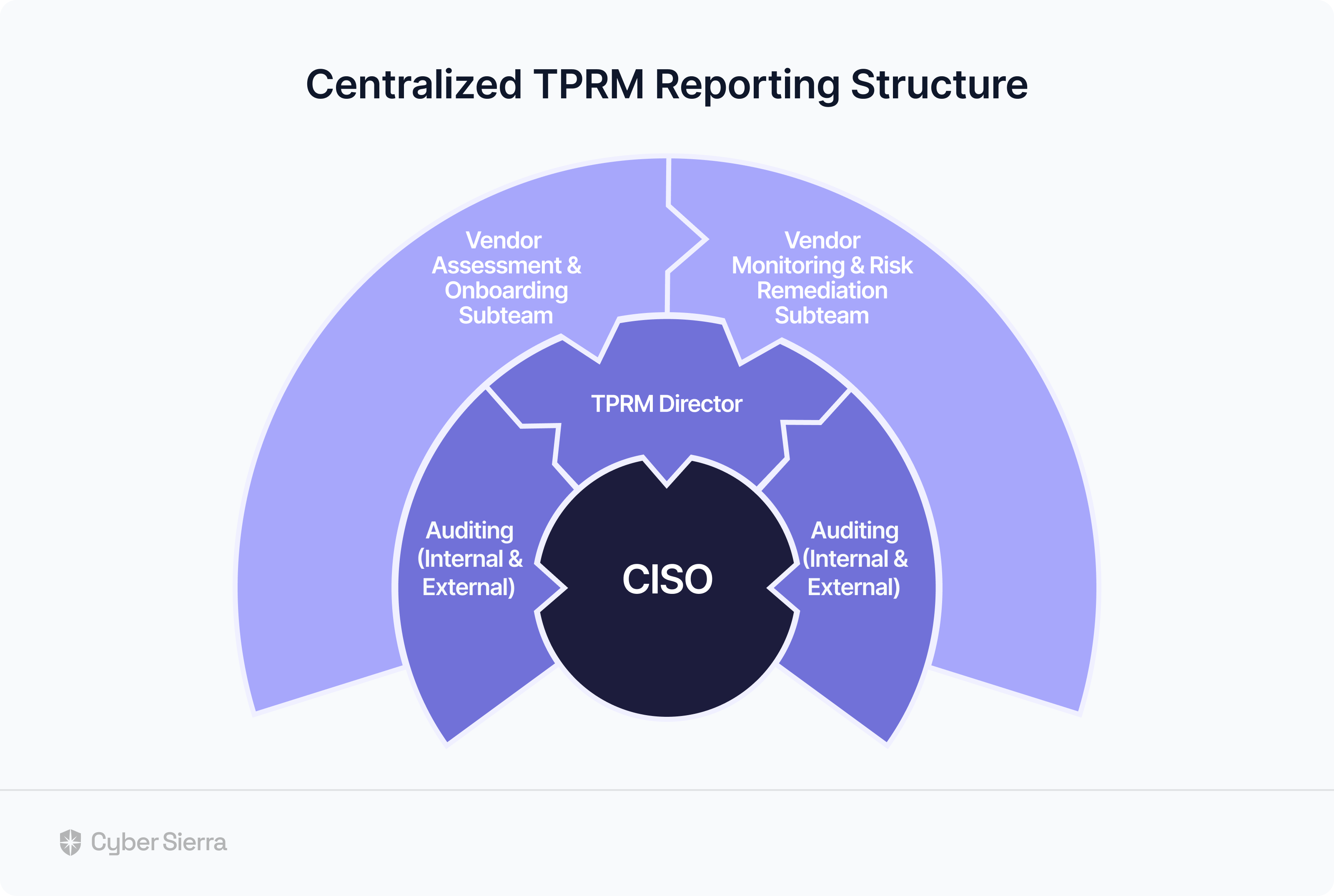
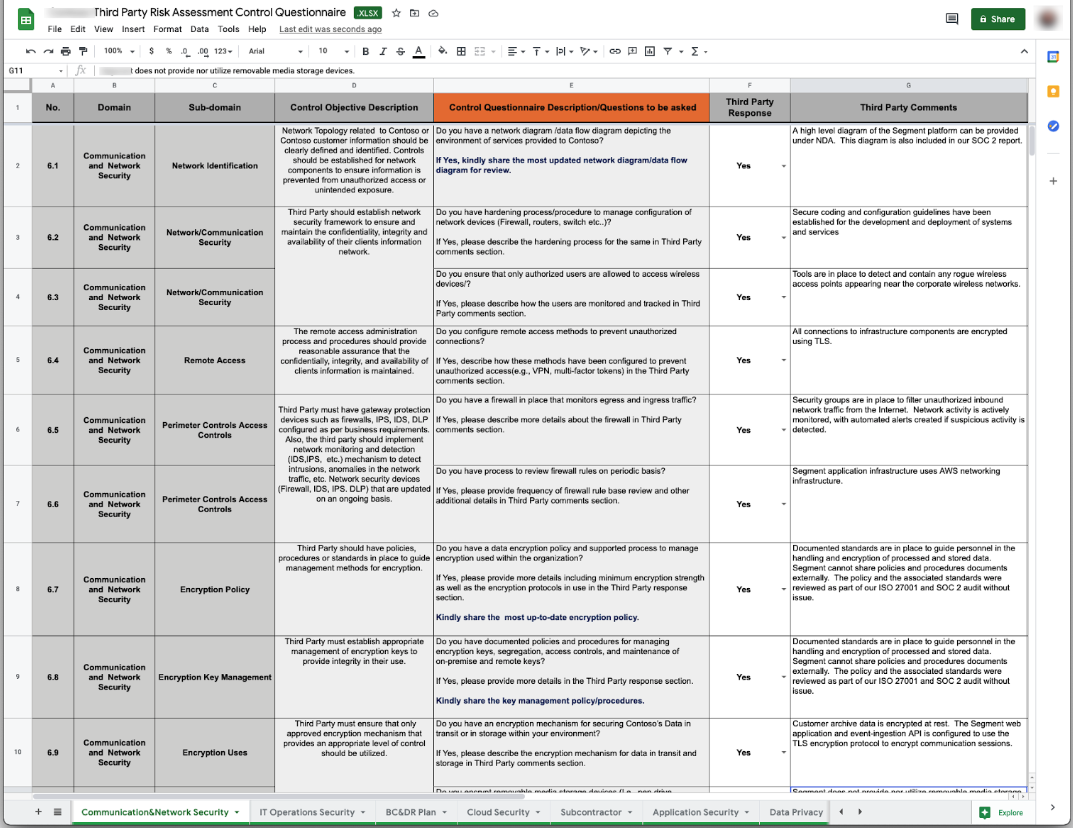
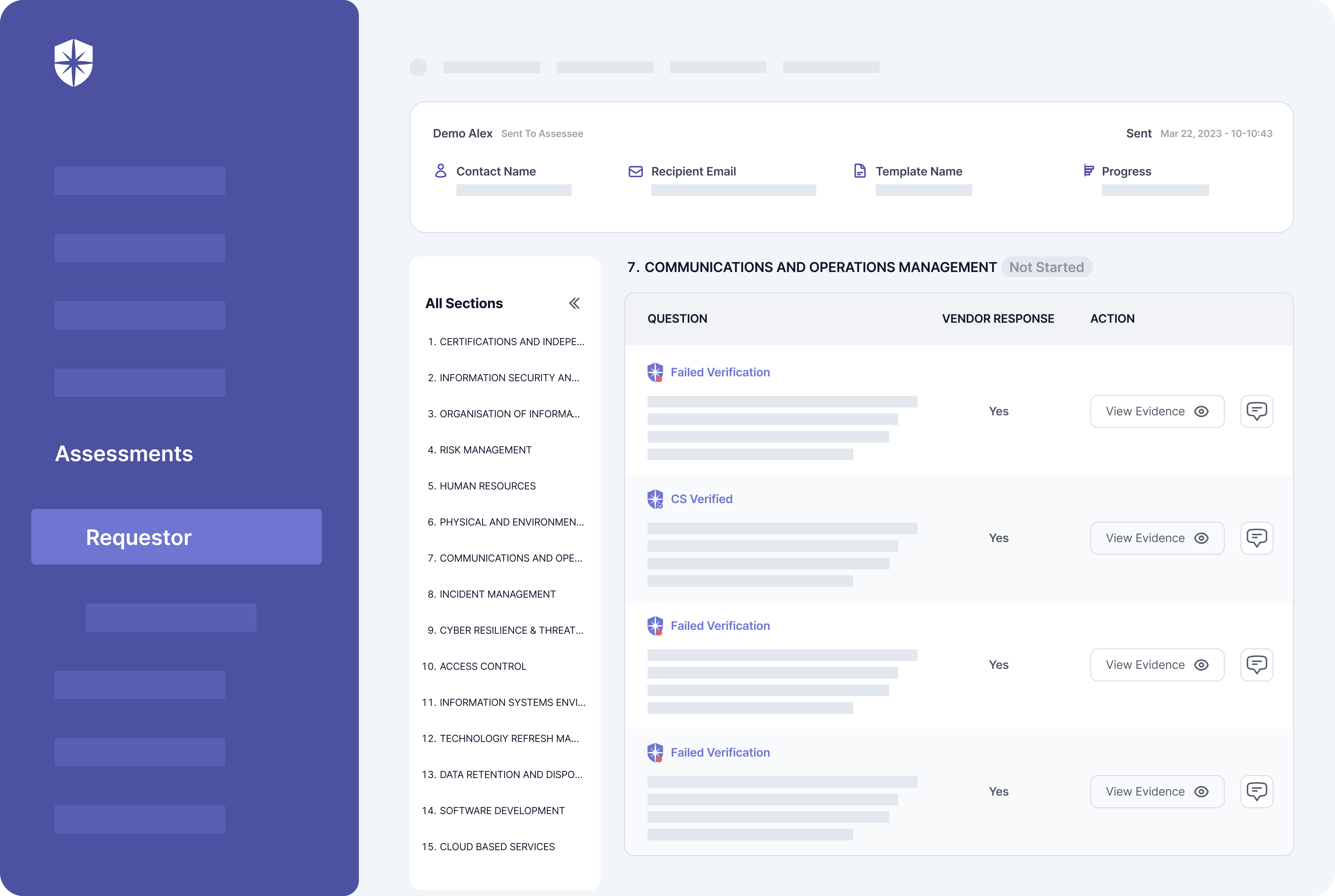
Cybersecurity CCM Tools Recommended for Enterprise Companies





















Join thousands of professionals and get the latest insight on Compliance & Cybersecurity.
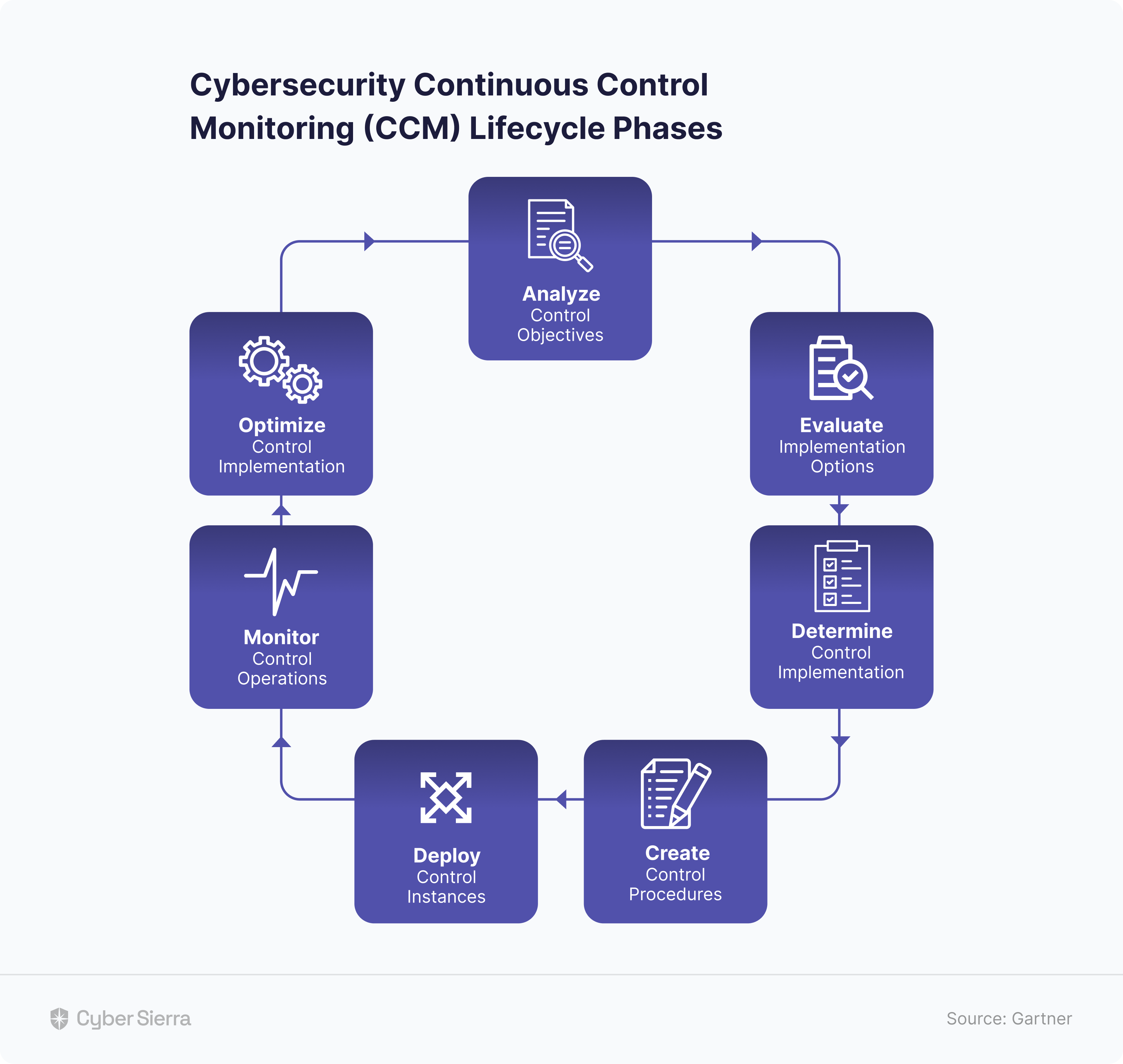
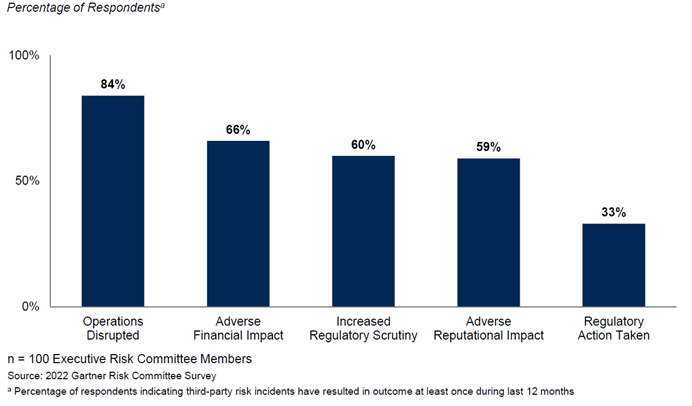
According to Gartner:


This is a not-so-good situation for two reasons:
- On the one hand, GRC vendors may not offer the full scale of capabilities required to effectively achieve CCM.
- On the other hand, CCM tools that can’t address a broad array of threats often end up working in isolation.
In other words, a half-baked or point continuous control monitoring tool working in isolation isn’t worth it, per IBM’s Charles Henderson:


A solution to this?
An Interoperable CCM Platform
Most CCM platforms have full scale continuous control monitoring capabilities. But as Henderson stressed, implementing another point solution isn’t worth it. They often end up posing a threat to efficient cybersecurity. EY’s Asia-Pacific Cybersecurity Consulting Leader, Richard J. Watson corroborates:


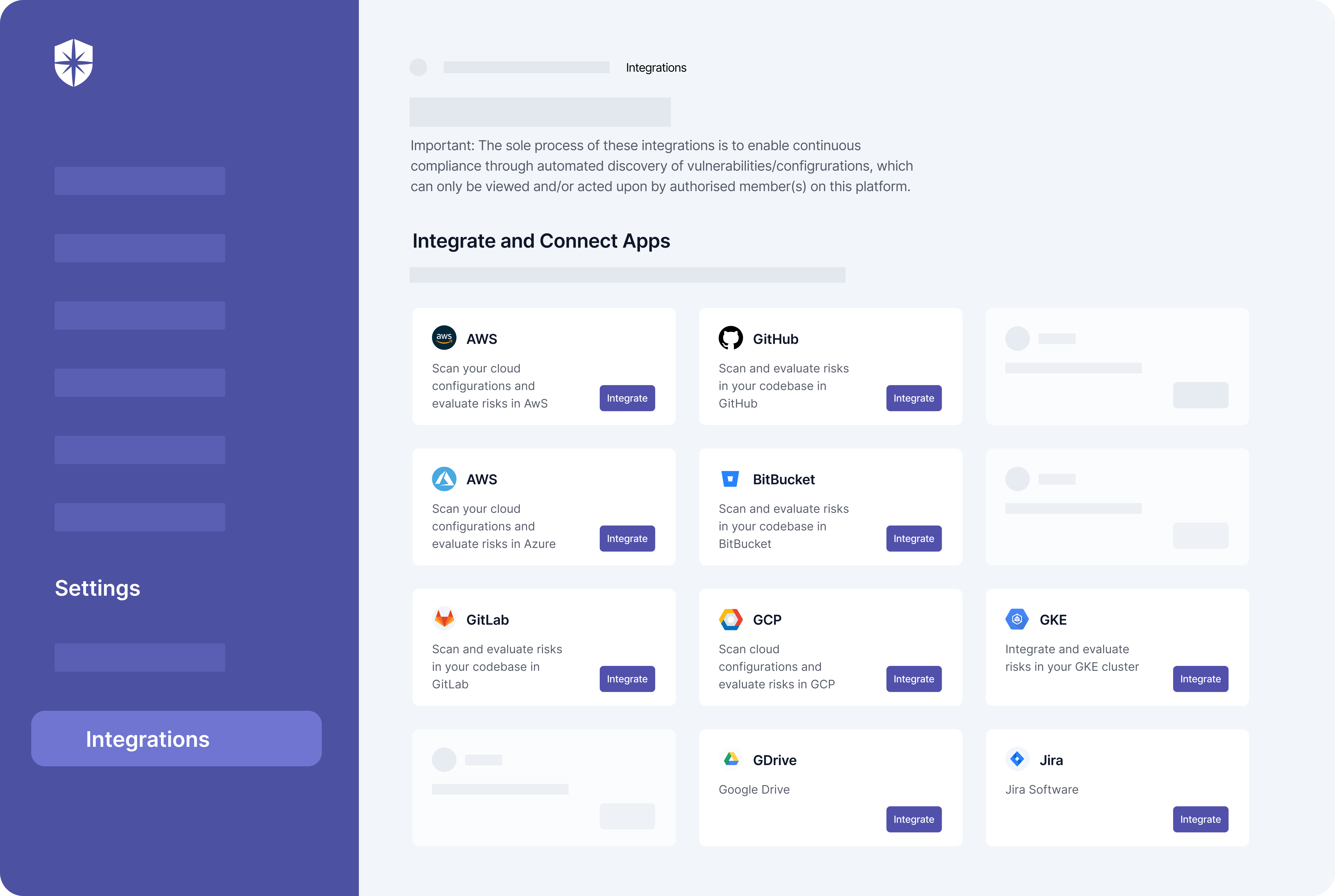
So to help enterprises achieve continuous control monitoring without cluttering their tech stacks, we built Cyber Sierra. You get a pure-play CCM platform with built-in capabilities for remediating other cybersecurity challenges interoperably.
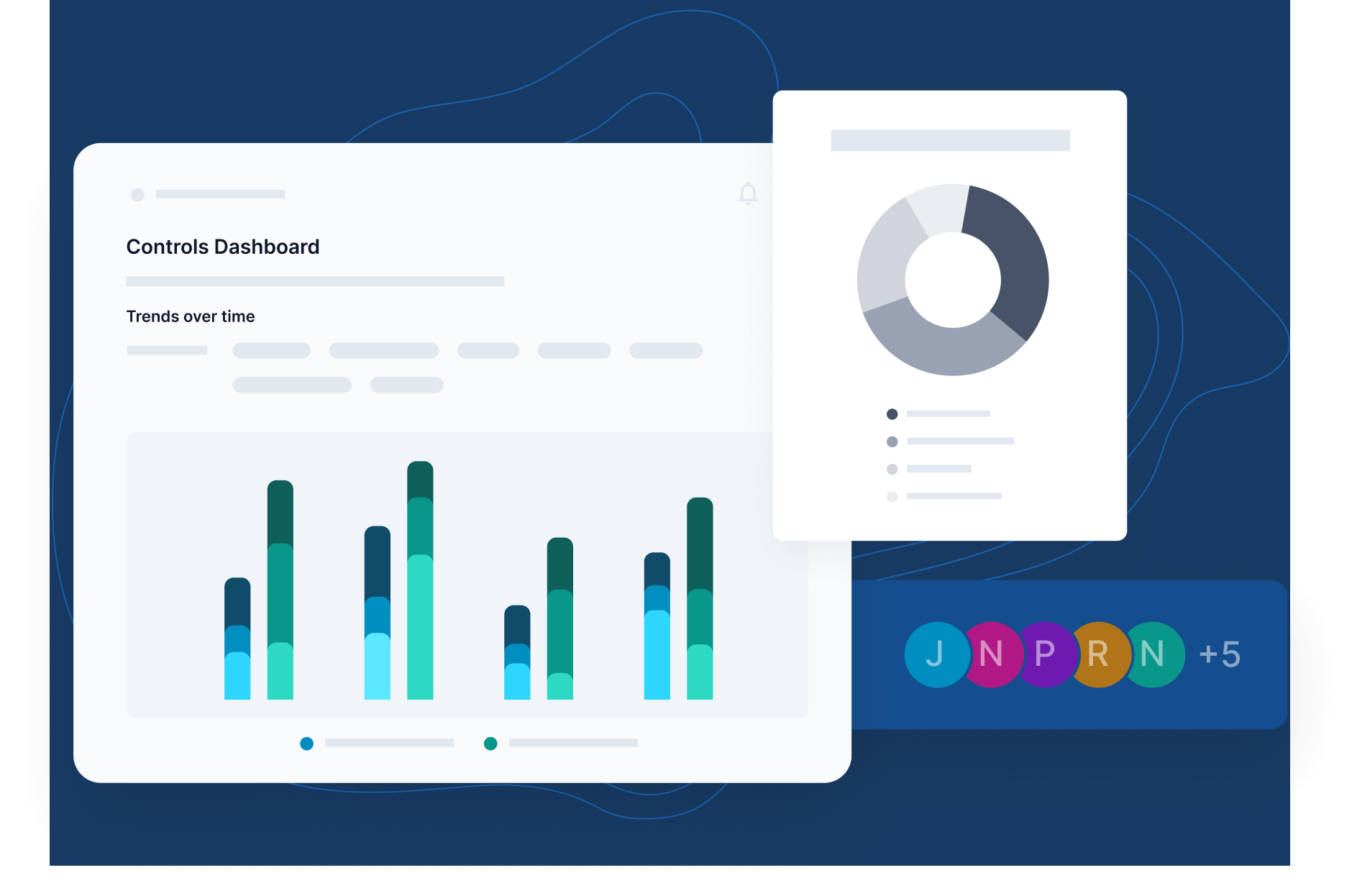
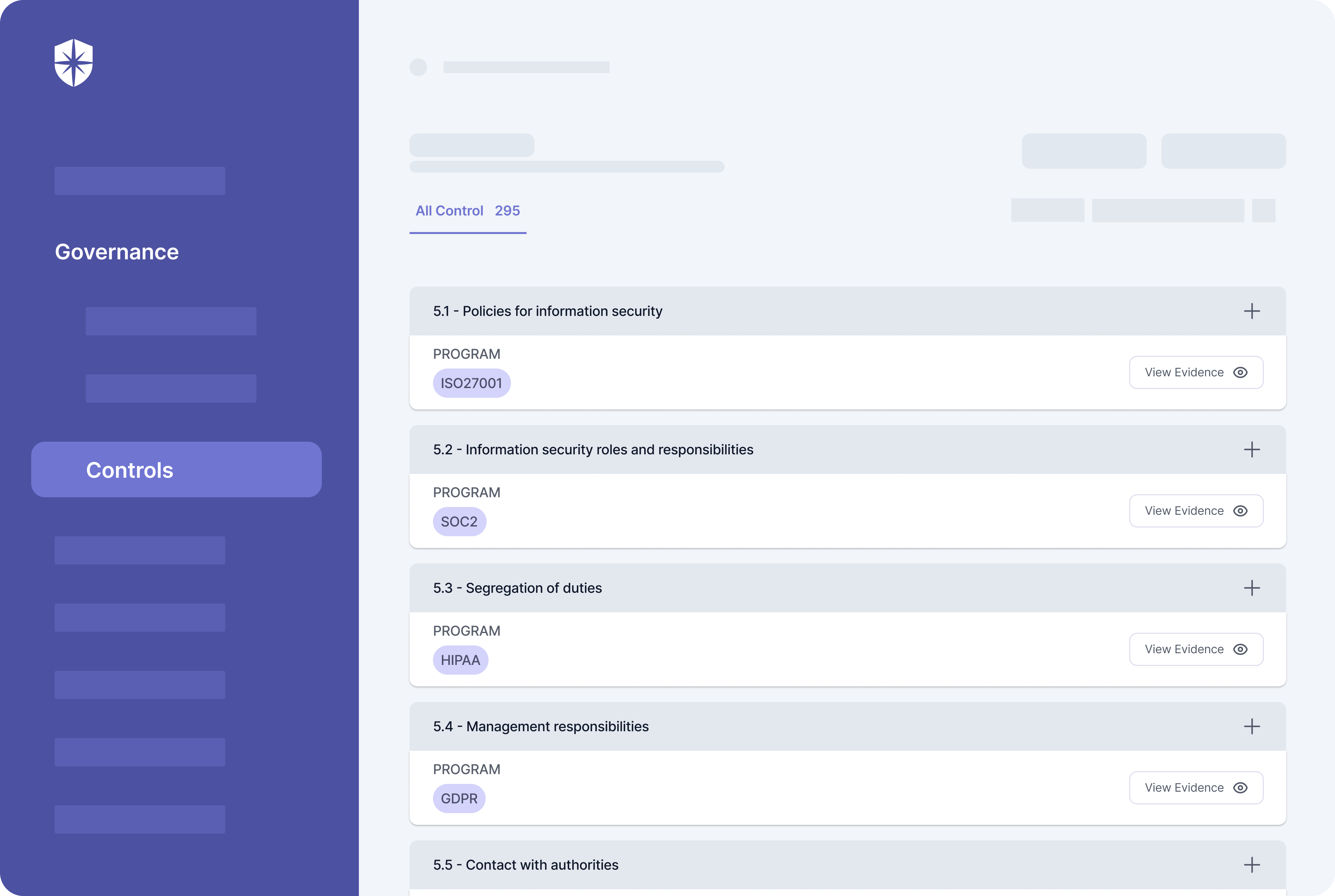
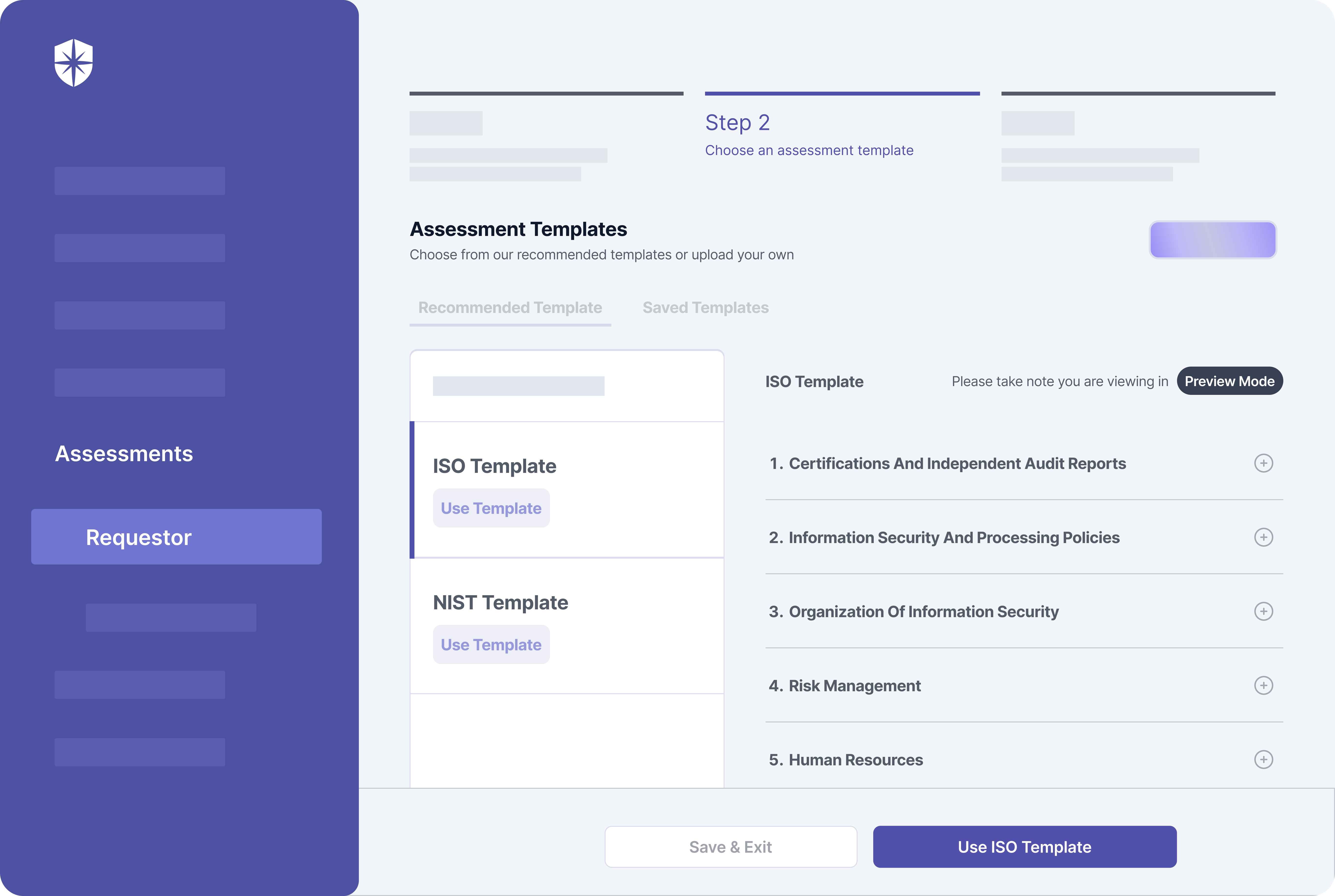
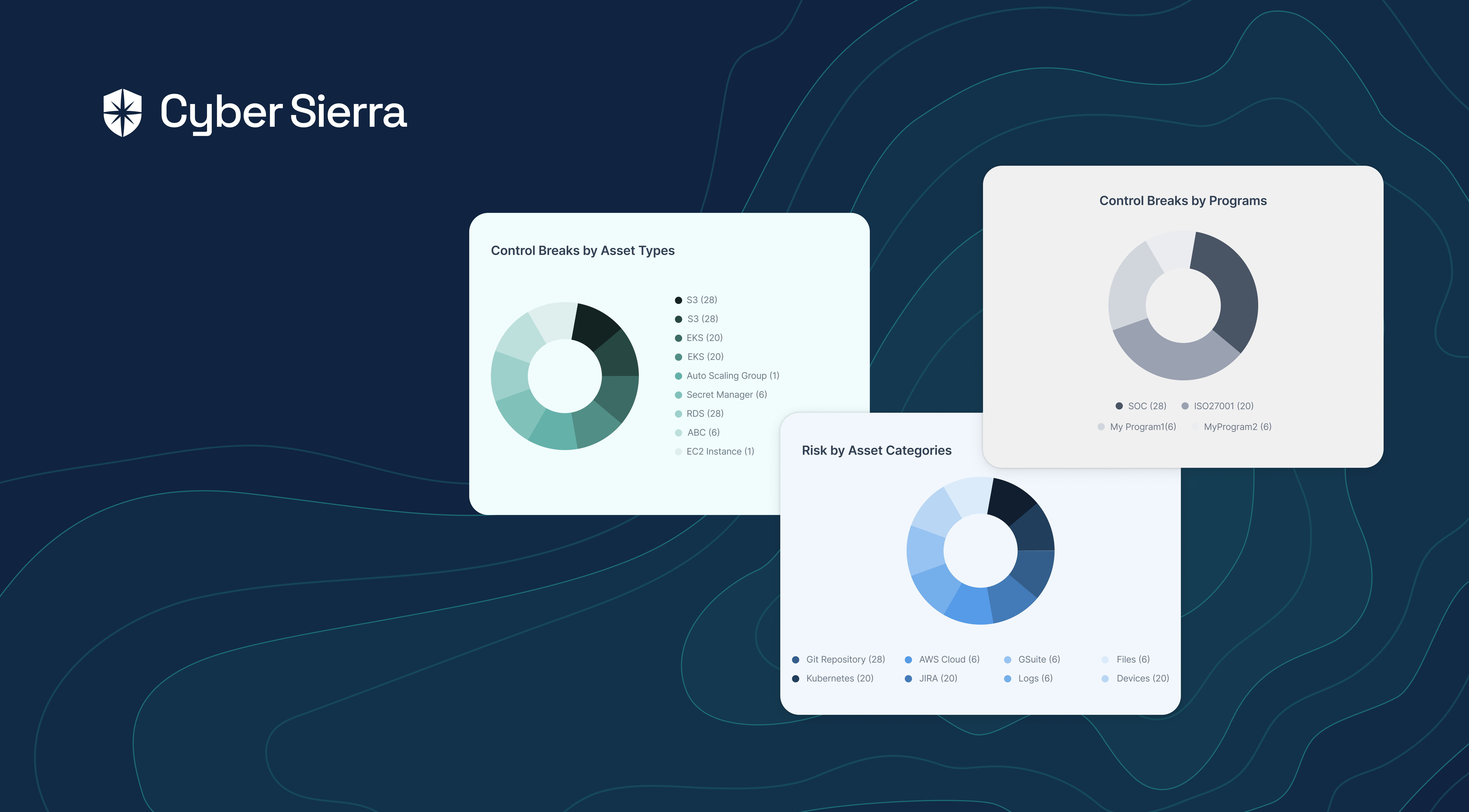
For instance, with our Controls Dashboard, enterprise teams can continuously monitor security controls by:
- Asset categories or asset types
- Compliance programs or frameworks:

As shown, you can assign risks associated with control breaks to teammates and monitor remediation status in real-time. And with other built-in functionalities, achieving continuous control monitoring while addressing core cybersecurity challenges interoperably is possible.
An interoperable CCM platform like Cyber Sierra is optimal for CISOs and enterprise security execs looking to achieve more with less. To show you how it compares, let’s walk through some cybersecurity CCM tools recommended by Gartner.
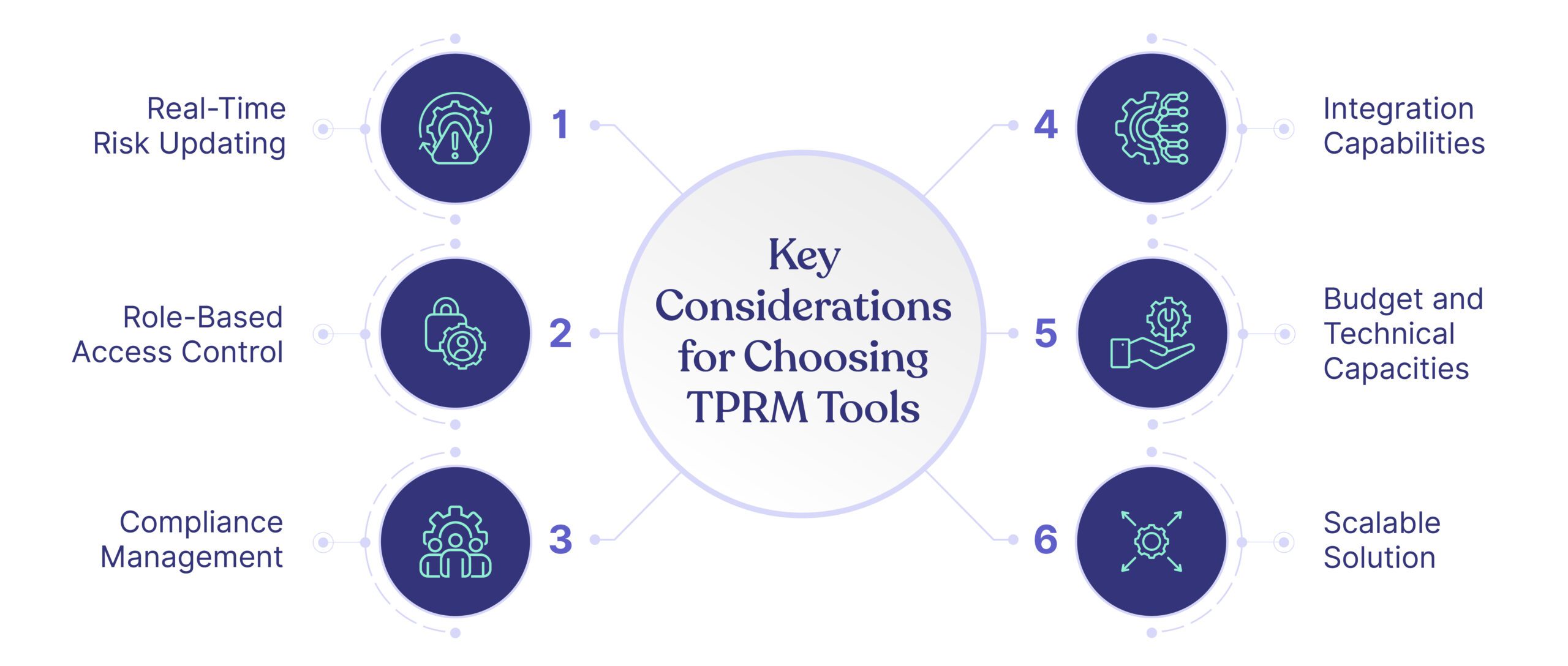
Enterprise Cybersecurity Continuous Control Monitoring (CCM) Tools Gartner Recommends
In their cybersecurity CCM study, Gartner recommended ten tools. We streamlined the list to five exclusive to CCM based on conversations with customers, prospects, and enterprise security experts.
Panaseer

The Panaseer CCM tool ingests data from security, cloud and on-premise IT and business tools. The software then normalizes, augments and correlates this data, giving security teams:
- Continuous visibility of assets and controls status
- Insights for prioritizing security resources
- Automated security posture reports.
According to Panaseer’s CCM feature page, they optimize and monitor controls across eight cybersecurity domains:
- Vulnerability analysis
- Endpoint analysis
- Patch analysis
- Identify and access management
- Privileged access management
- Security awareness management
- Application security analysis, and
- Cloud security.
Given these covered domains, the Panaseer CCM software is ideal for cyber asset and security controls’ management, reporting, and evidenced remediation. But it falls short in two crucial areas.
- Enterprise security teams can’t use Panaseer to assess security risks from third-party vendors that can lead to control breaks.
- You can’t establish compliance governance and monitor corresponding security controls mapped to implemented compliance frameworks and policies.
Cyber Sierra has these solutions built-in.
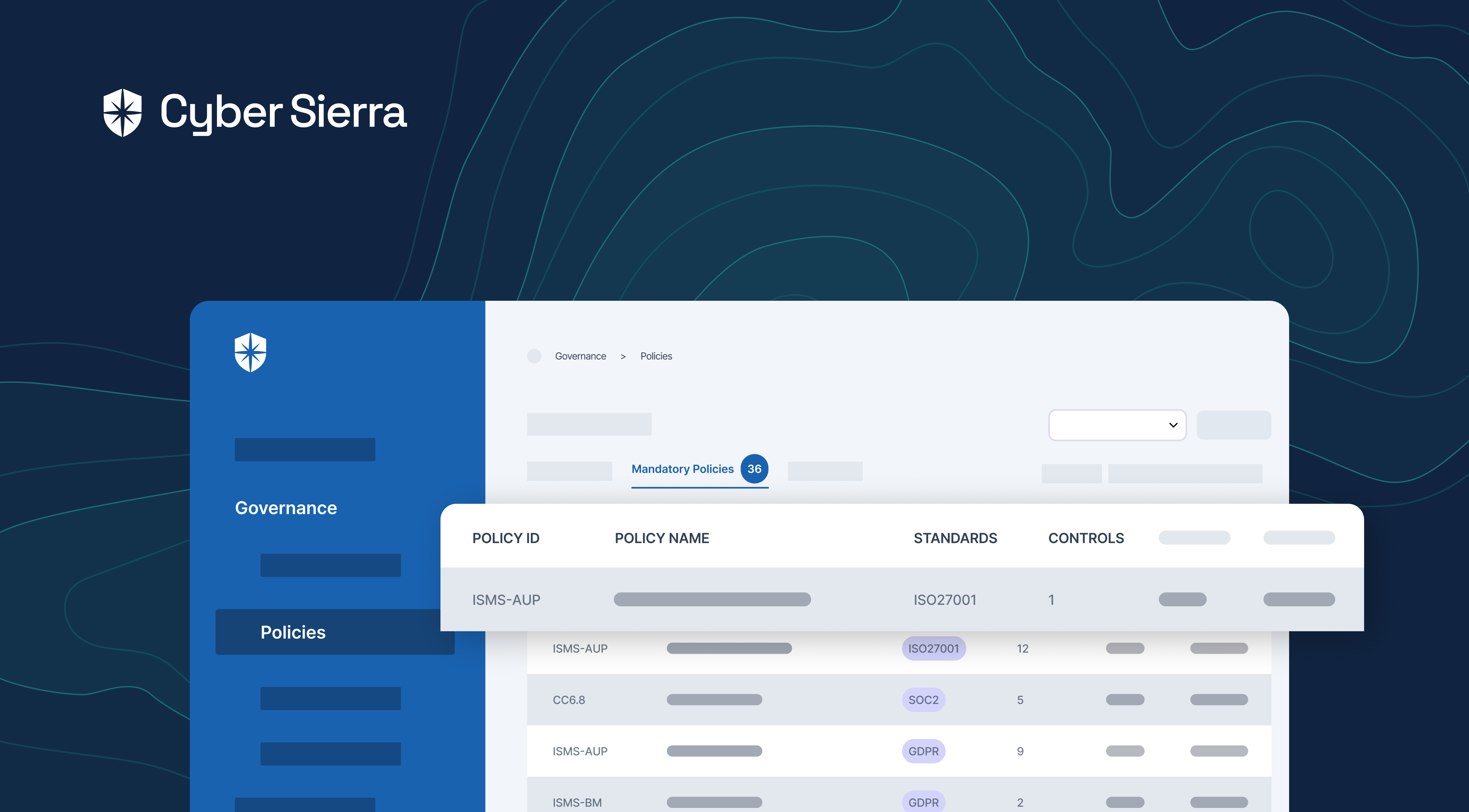
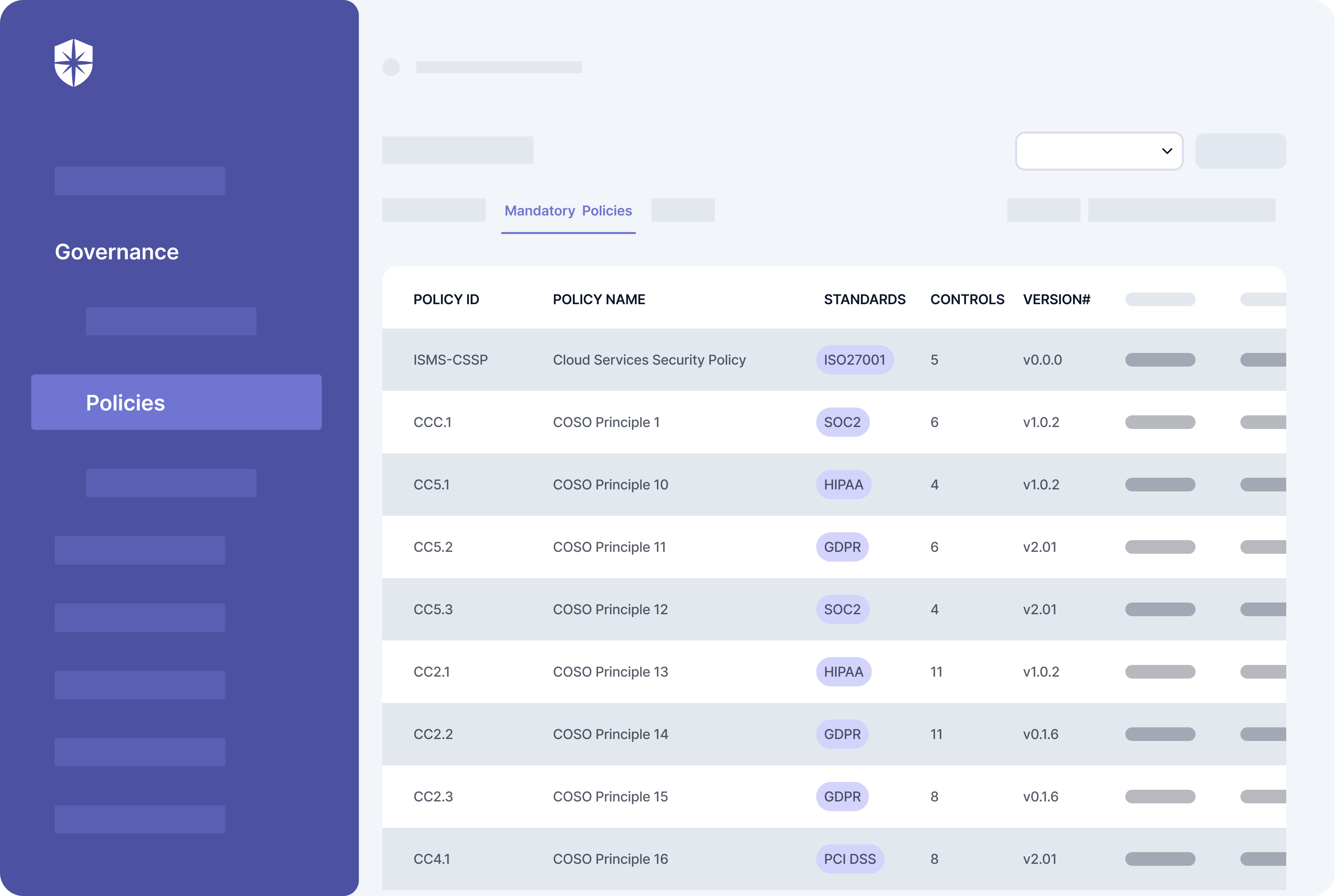
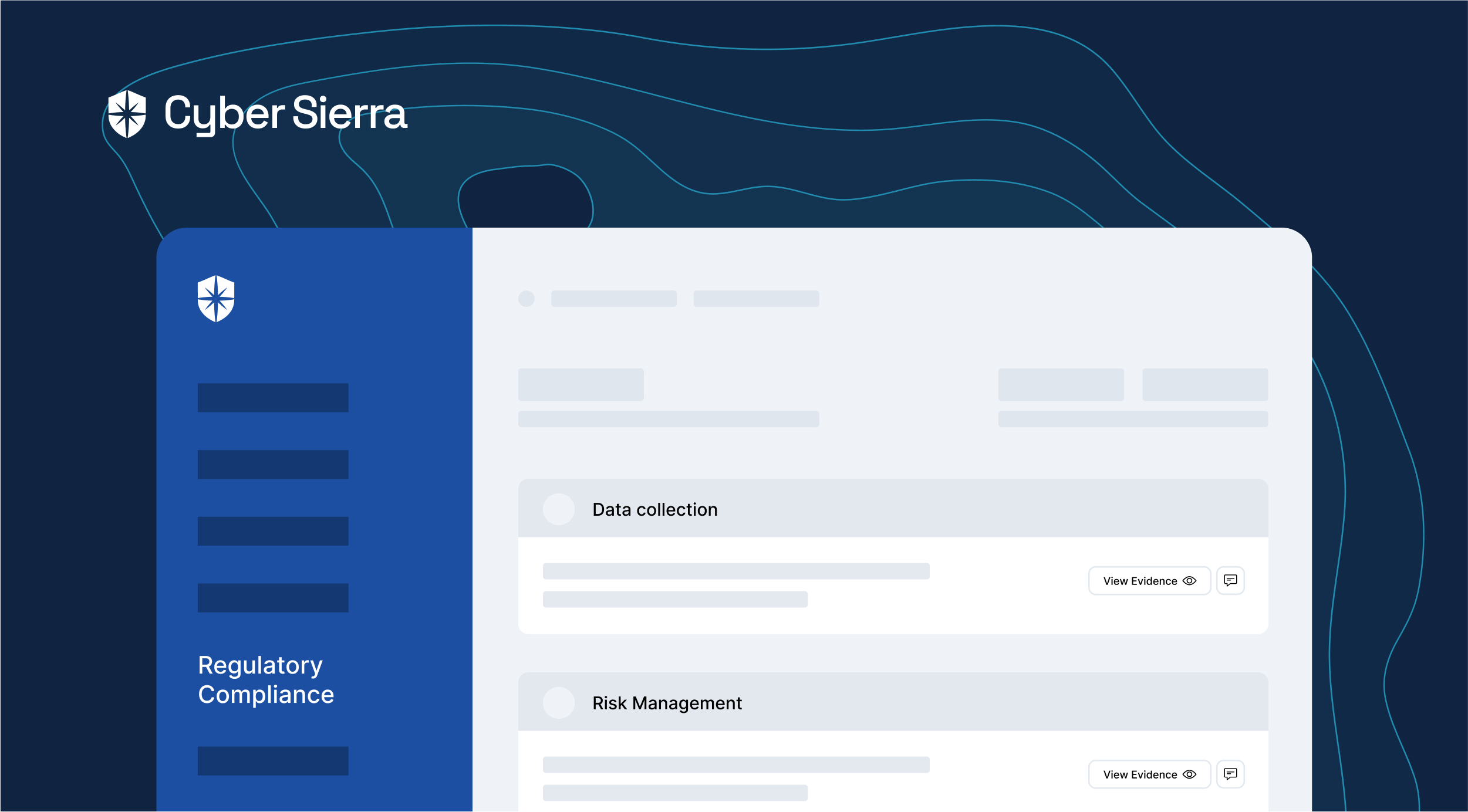
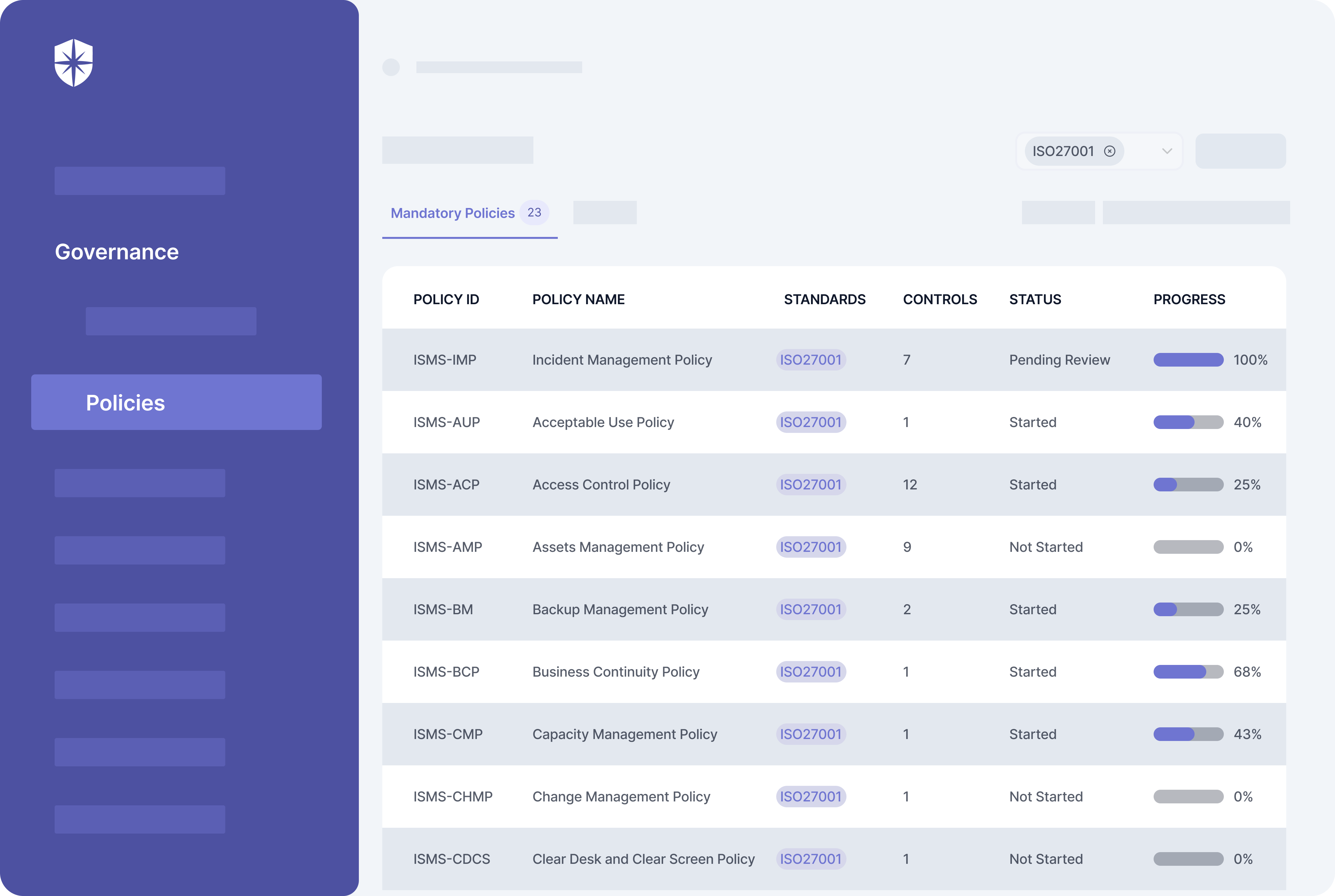
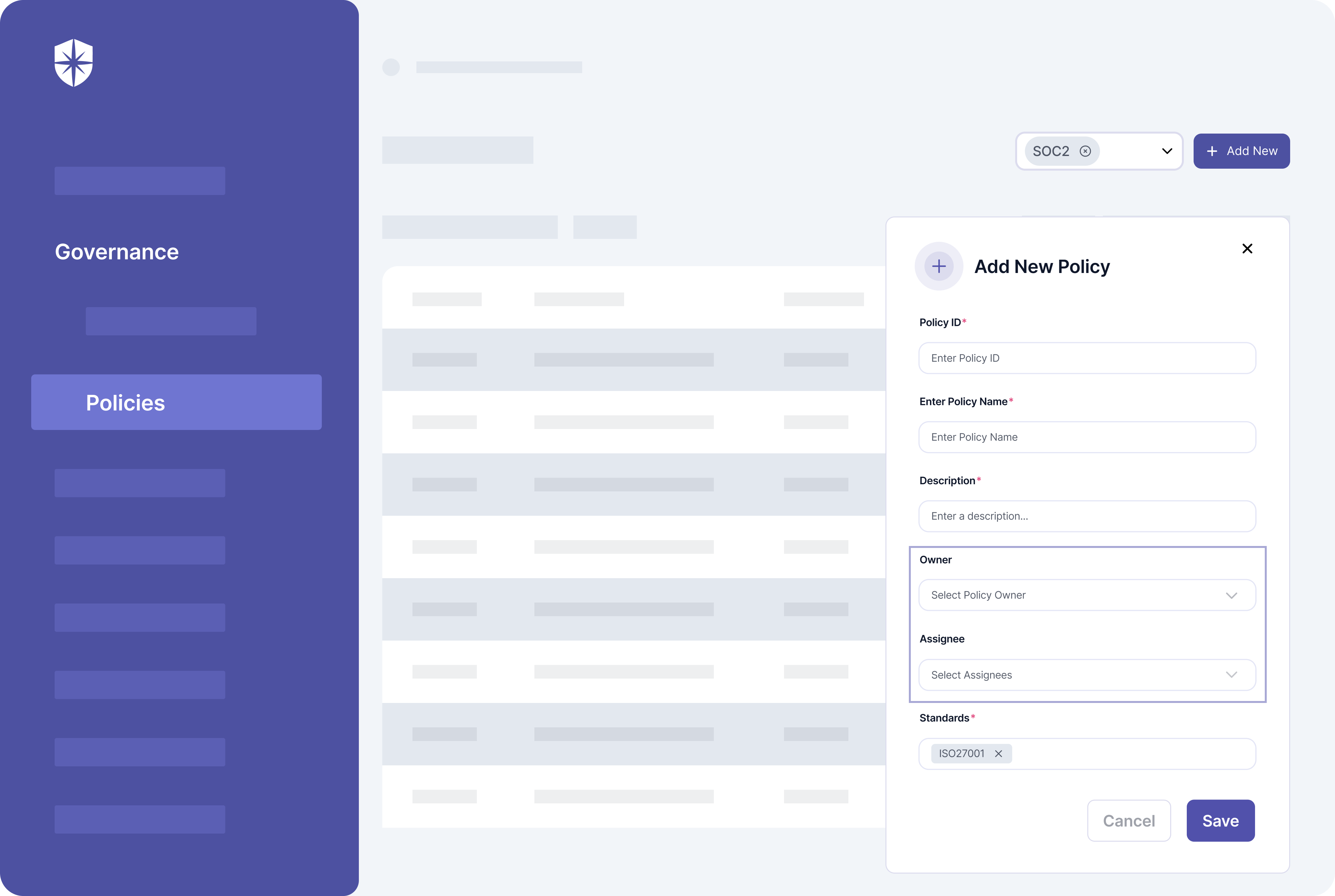
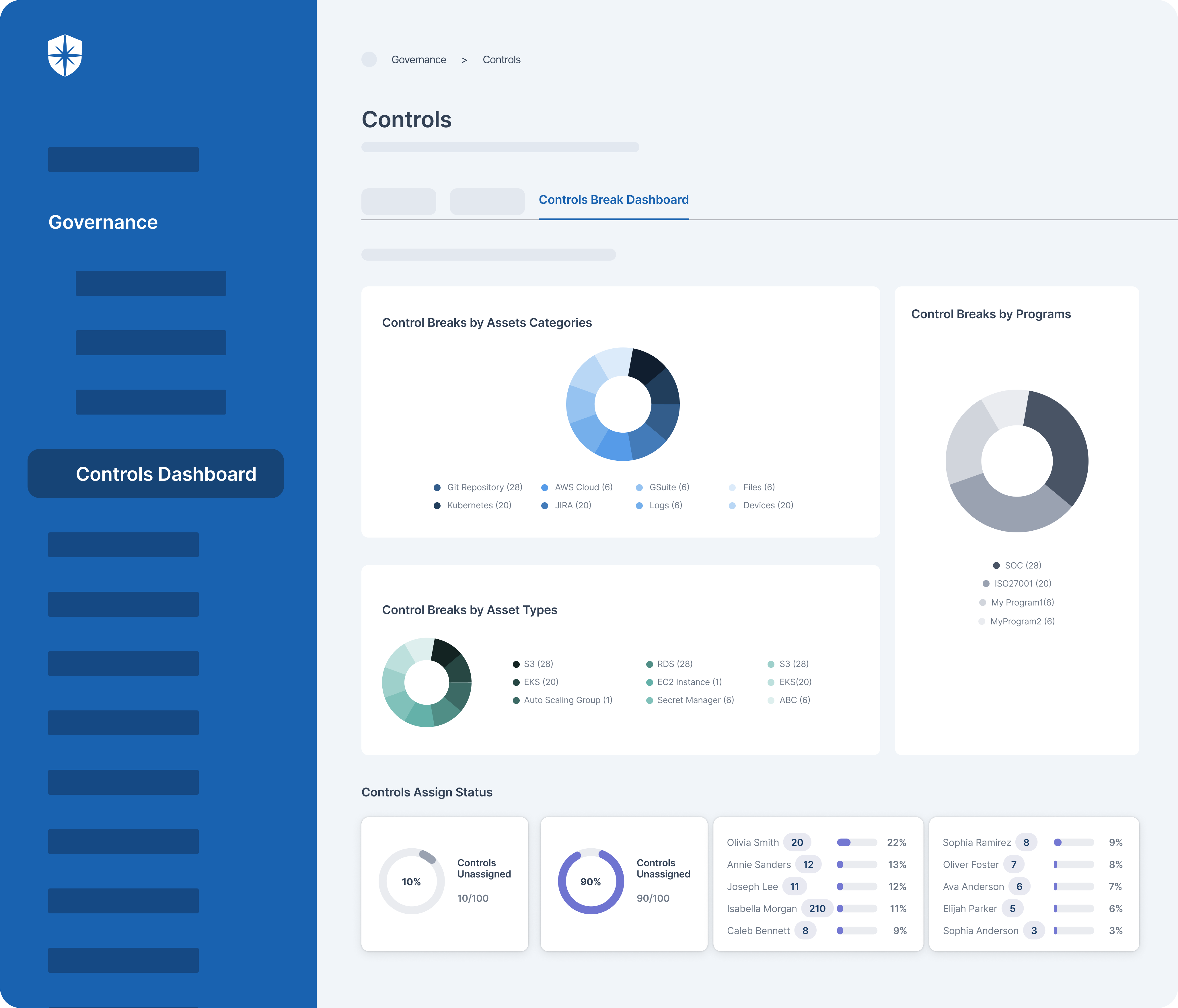
For instance, with our platform your team can map and monitor controls for all implemented compliance programs:

Quod Orbis
Quod Orbis is another tool dedicated to CCM:
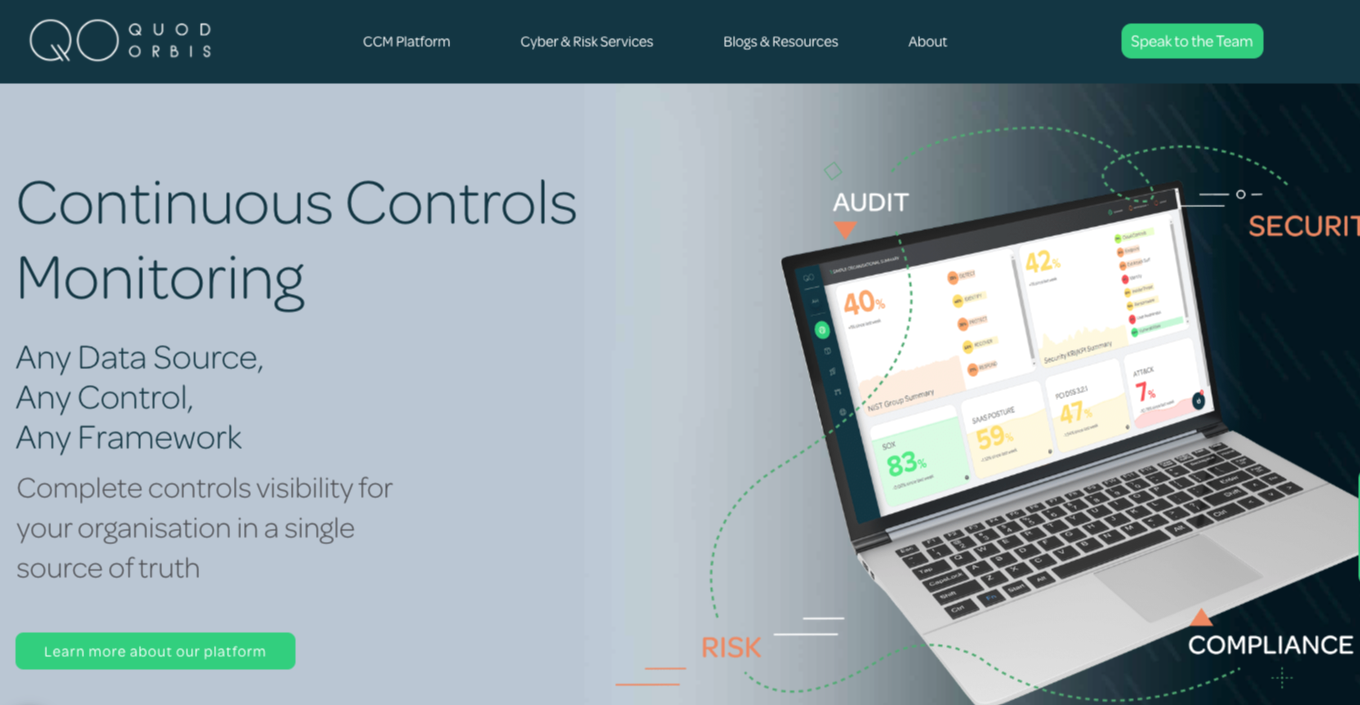

The software audits a company’s cloud assets and monitors risks and security controls continuously from data sources and compliance frameworks. Unlike Panaseer, Quod Orbis focuses more on monitoring the security controls of compliance programs.
You get:
- Continuous compliance
- Real-time compliance controls visibility
- Enhanced security and compliance posture
- Cyber risk quantification, and
- Expert-led management of their platform.
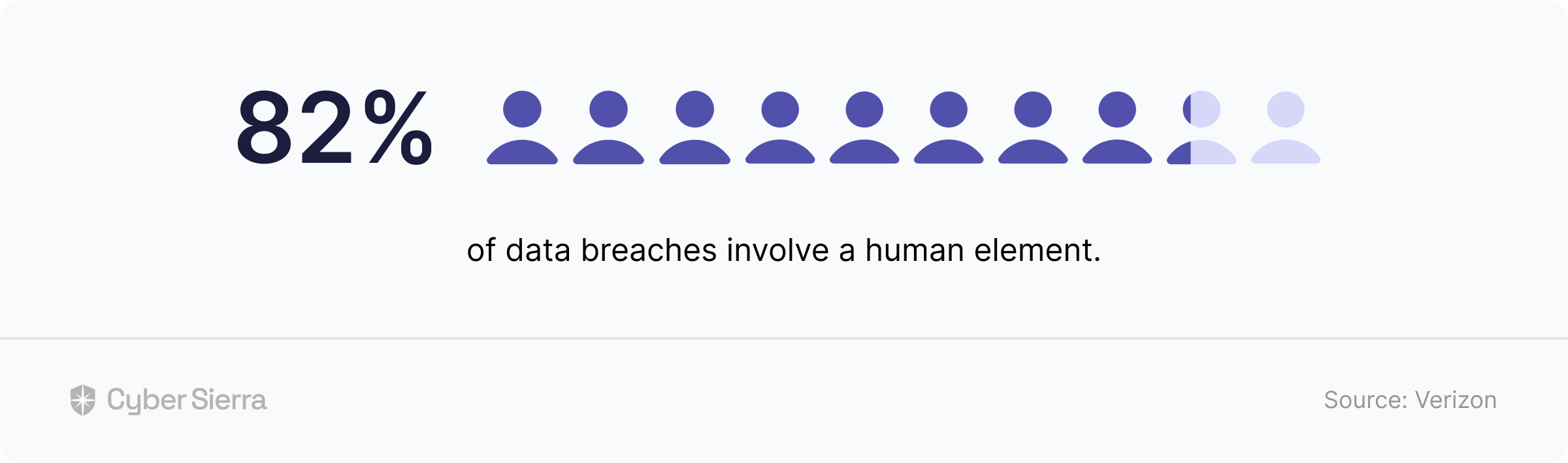
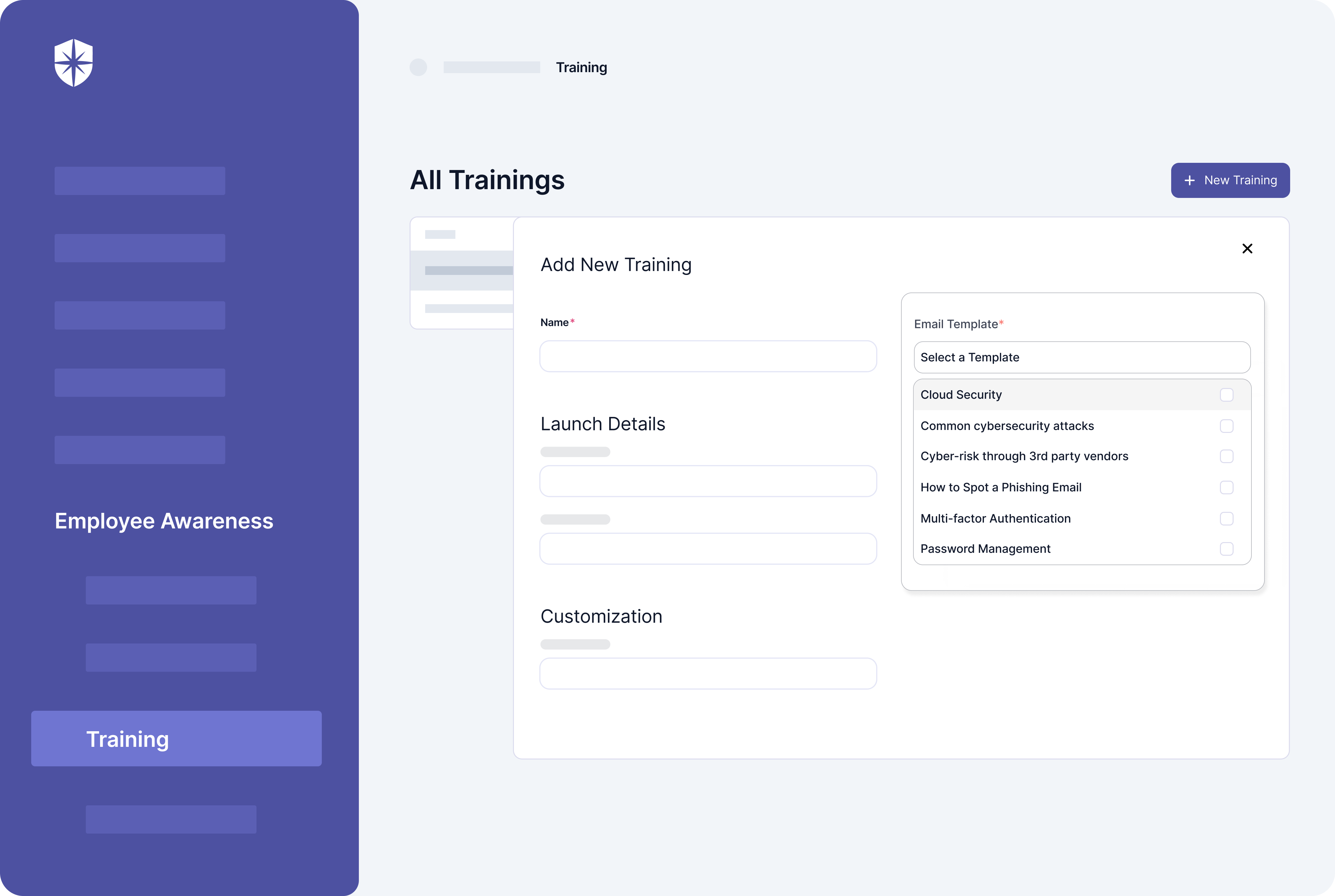
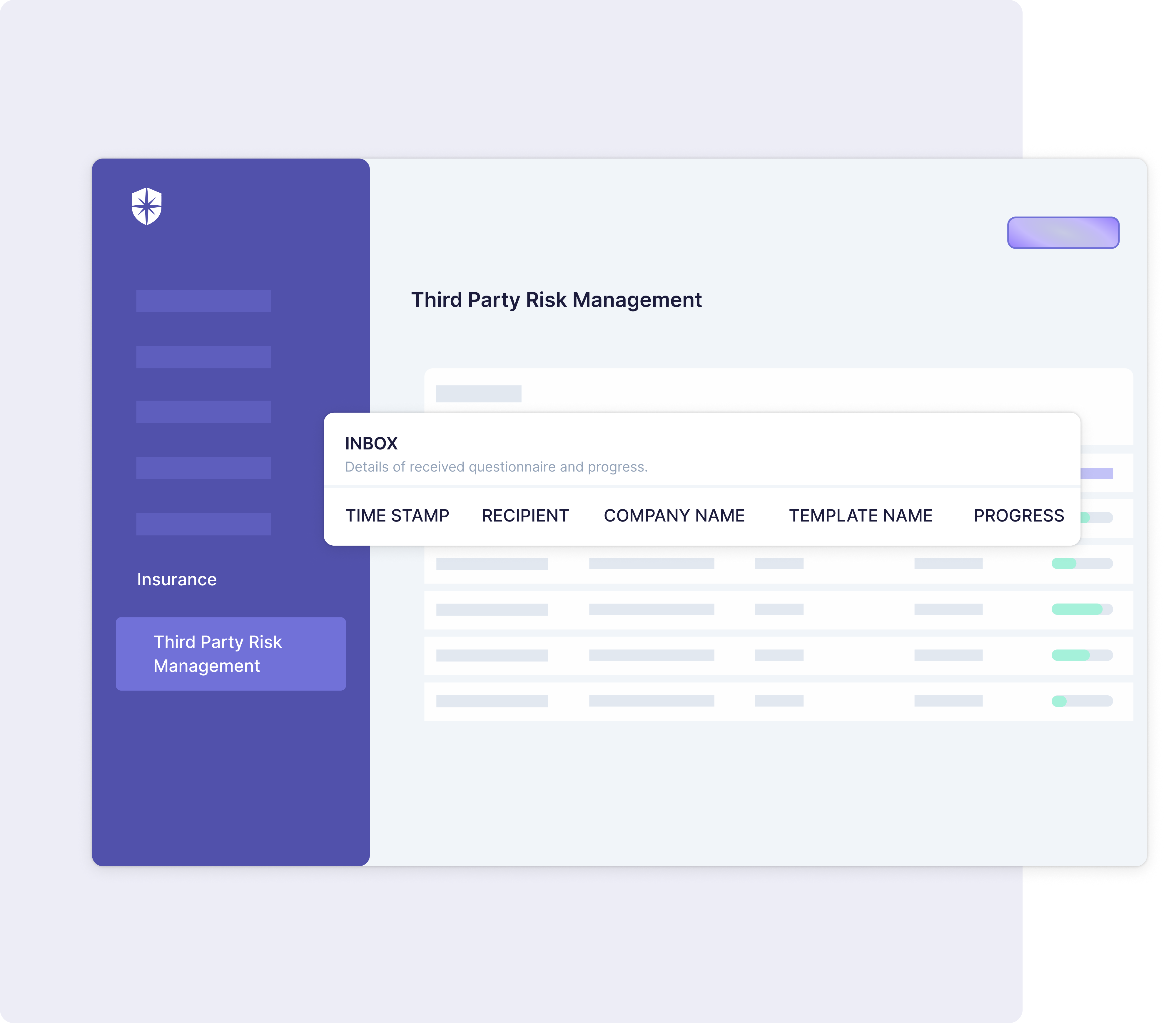
Like Panaseer, you can’t track third-party risk assessments, provide, or monitor continuous employee security awareness training with Quod Orbis. And these are crucial for ensuring the security controls being monitored are adhered to by third-parties and employees.
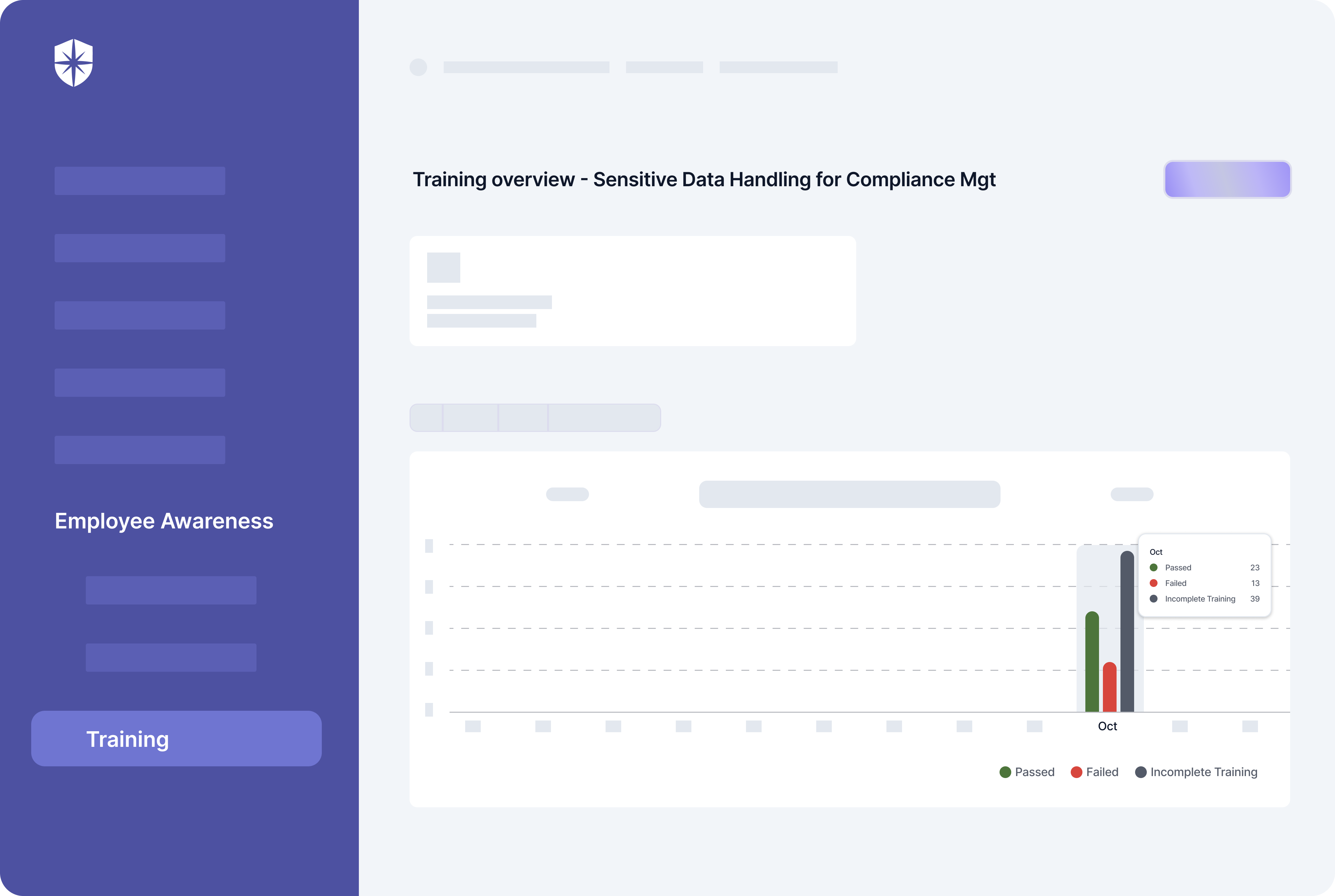
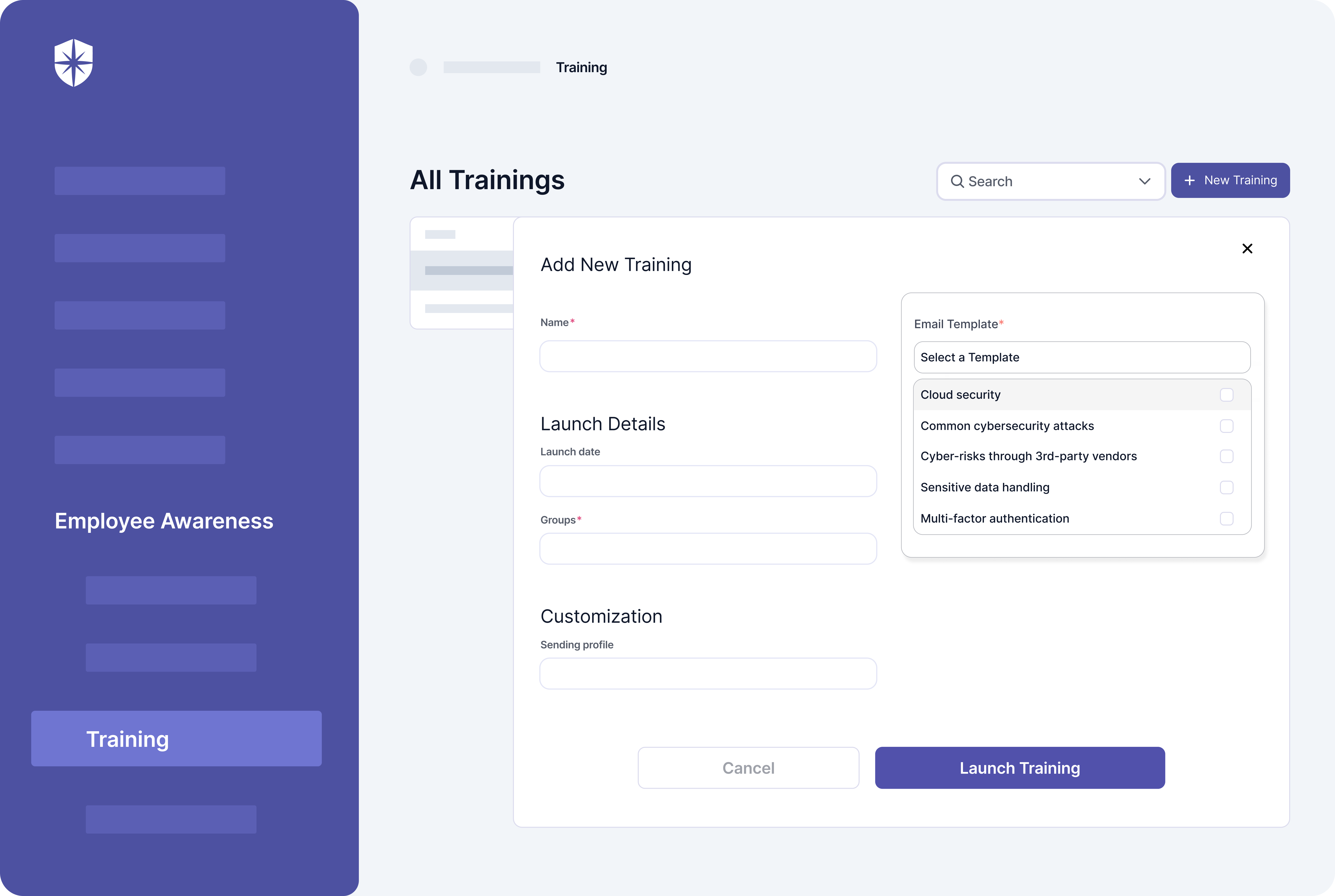
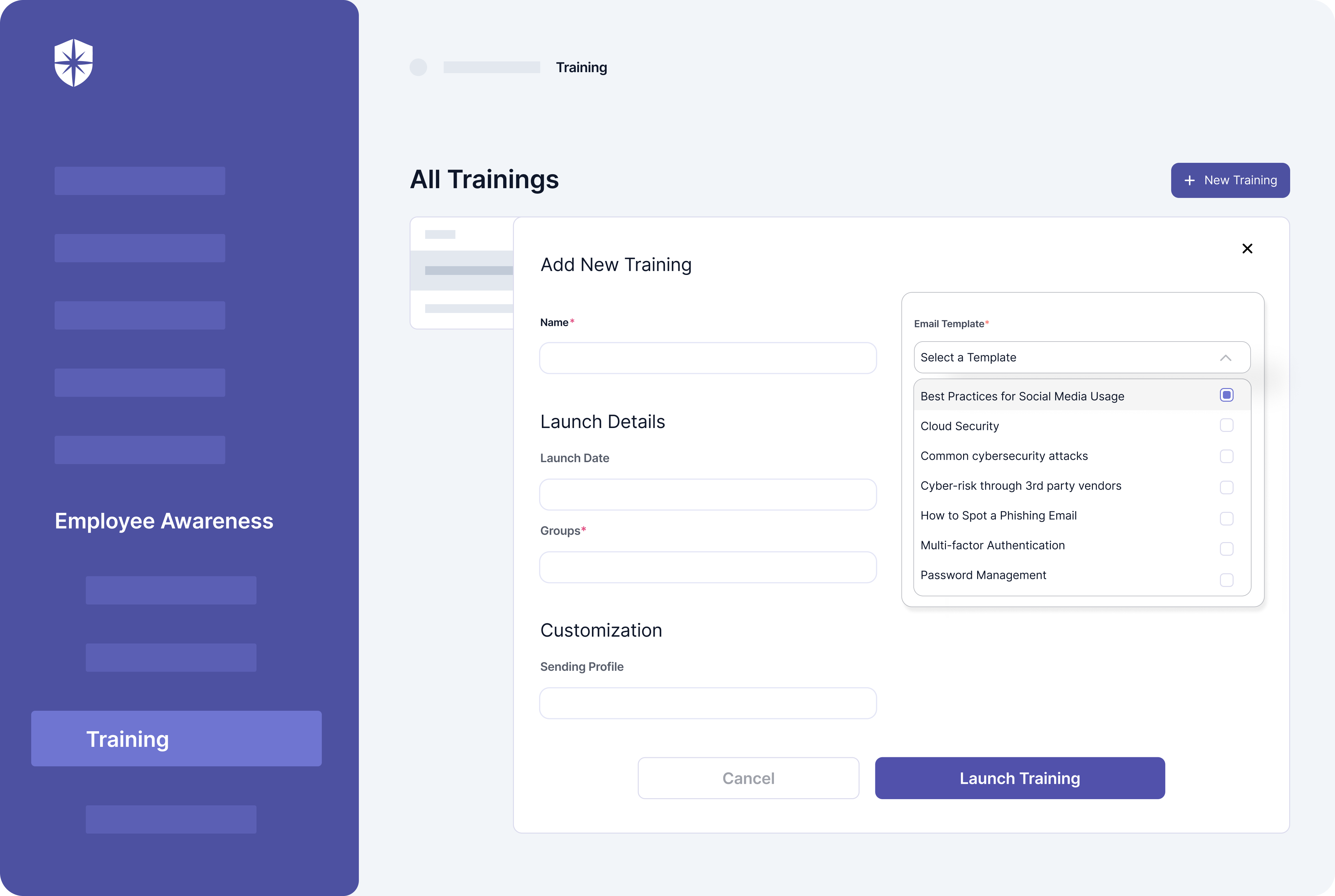
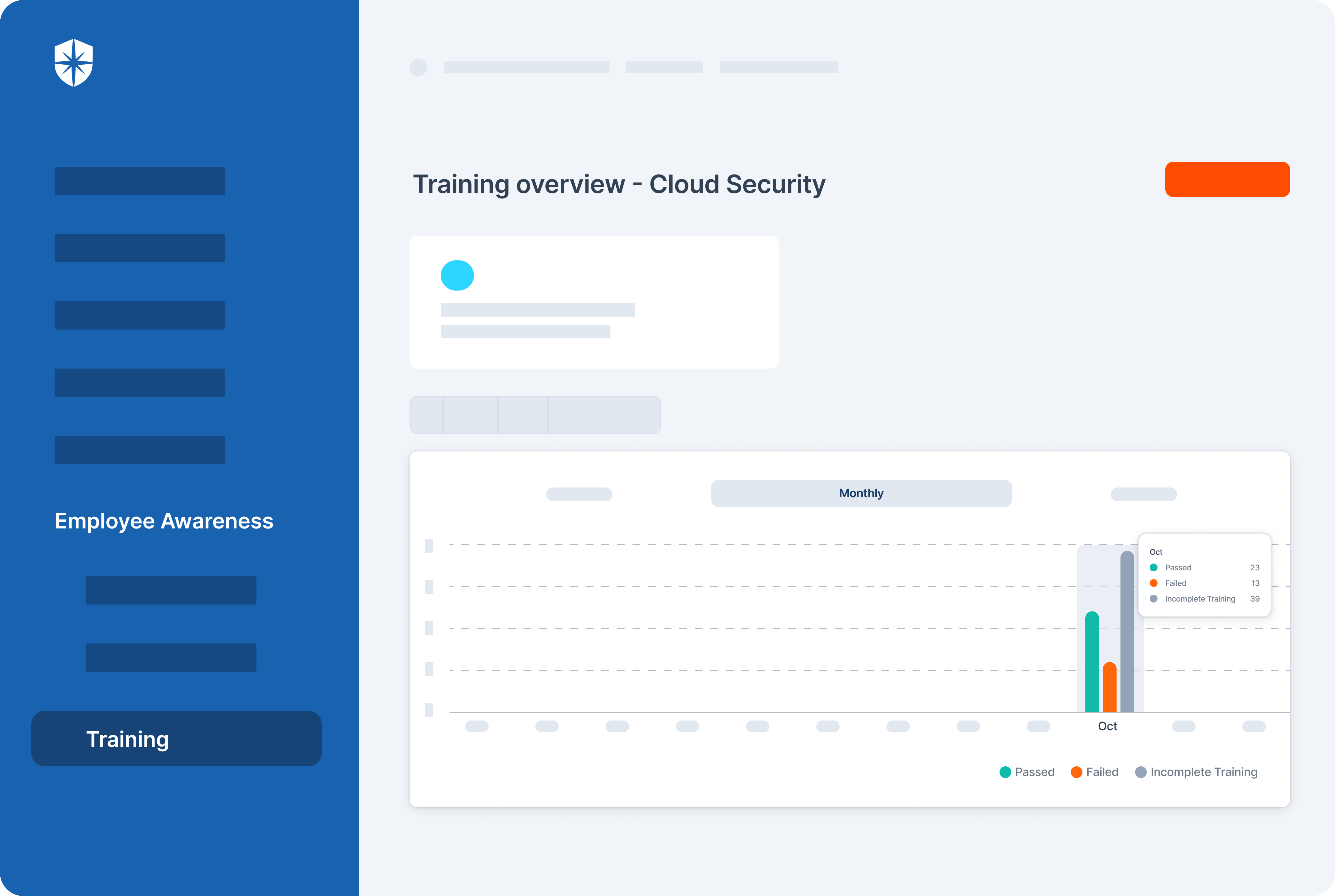
With Cyber Sierra, in addition to having core CCM capabilities, you can launch and monitor ongoing security awareness training:

Metricstream
Positioned as ‘the connected GRC software,’ Metricstream offers continuous control monitoring capabilities for:
- IT & Cyber Risk
- Compliance
- Audit, and
- ESG:
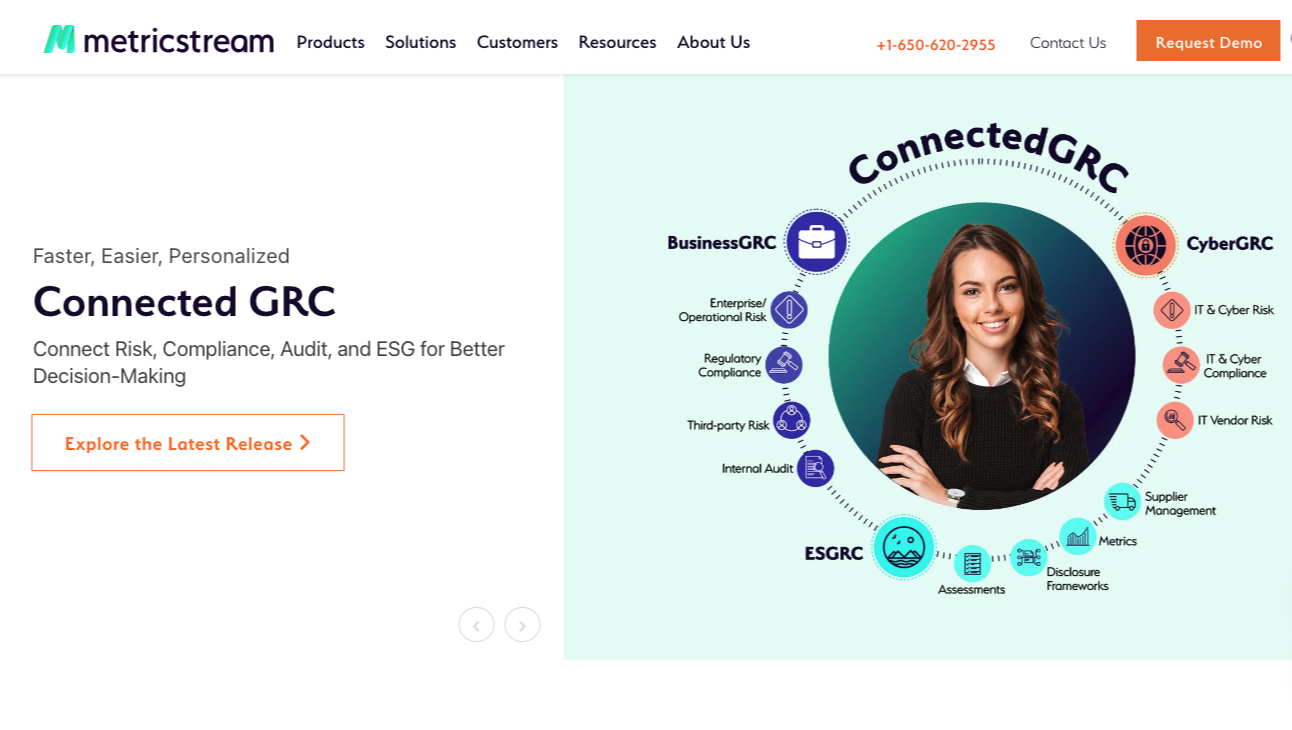

As shown above, Metricstream is more of a GRC solution with continuous control monitoring features for:
- Gaining a unified, real-time view of risks, threats, and vulnerabilities for effective risk and IT control assessments.
- Staying on top of evolving regulatory requirements relevant to compliance risks, policies, cases, and controls.
Like the others, two areas where Metricstream is lacking are vendor risk assessment monitoring and ongoing employee security awareness training. You need both to ensure security controls being monitored are adhered to by vendors and employees.
Another reason to consider a cybersecurity CCM platform like Cyber Sierra with such capabilities built-in.
JupiterOne
This tool has extensive integration for various apps used across different categories by enterprises. To that effect, JupiterOne is mainly a cyber asset attack surface management (CAASM) solution with continuous compliance monitoring capabilities:
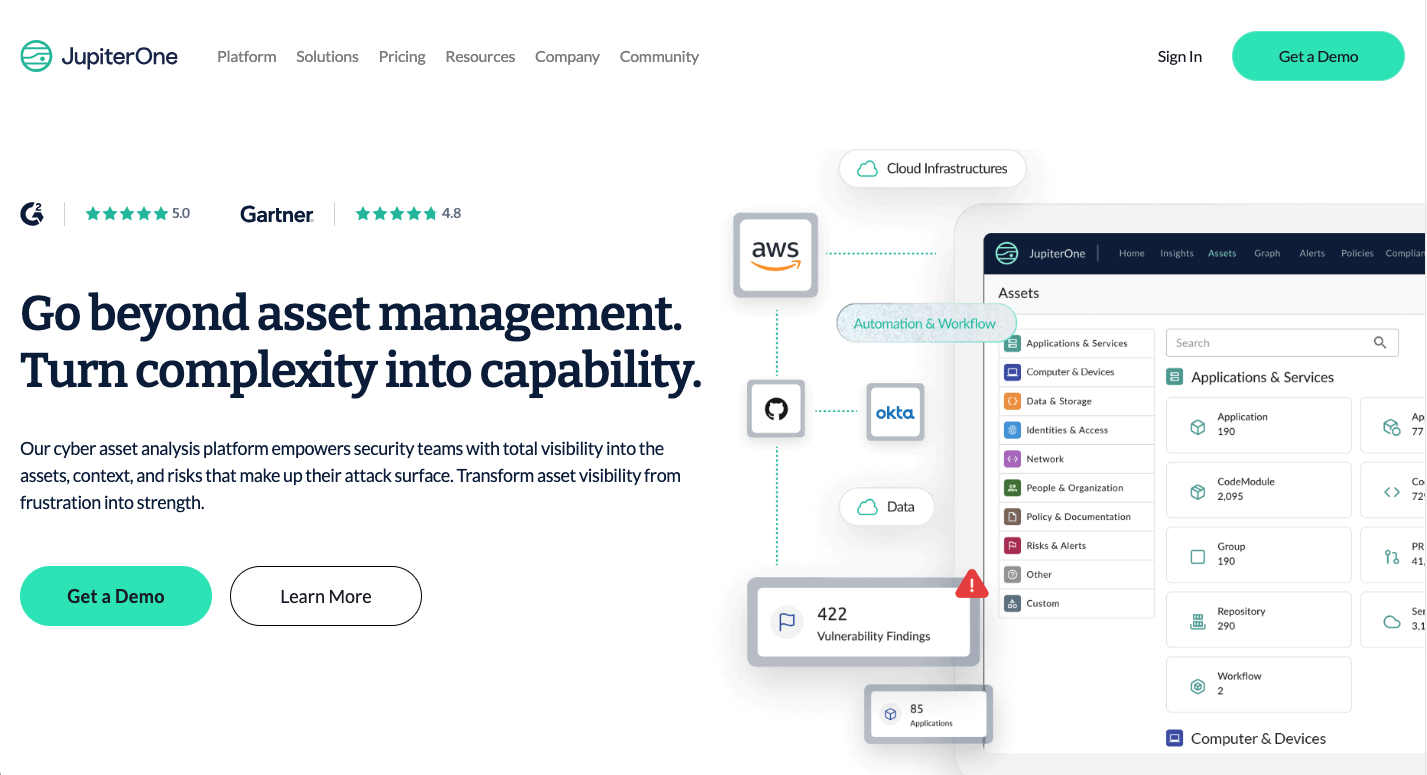

With this tool, security teams can have vulnerabilities from their cloud assets ingested and normalized in a single platform.
You get:
- Cloud asset inventory
- Granular data segmentation of integrated assets
- Continuous compliance, and
- Graph-based context.
The graph-based context is JupiterOne’s stand-out feature. Security leaders use it to view the connections between their cloud assets, constantly monitor, and identify any risks involved. Without this feature, JupiterOne would probably not be considered a continuous control monitoring tool.
And that’s because it mainly collects and normalizes assets’ data, maps out cloud assets relationships, and provides visibility. Being an interoperable pure-play CCM platform, Cyber Sierra does these out of the box.
We even have a more advanced graph-based context built-in:
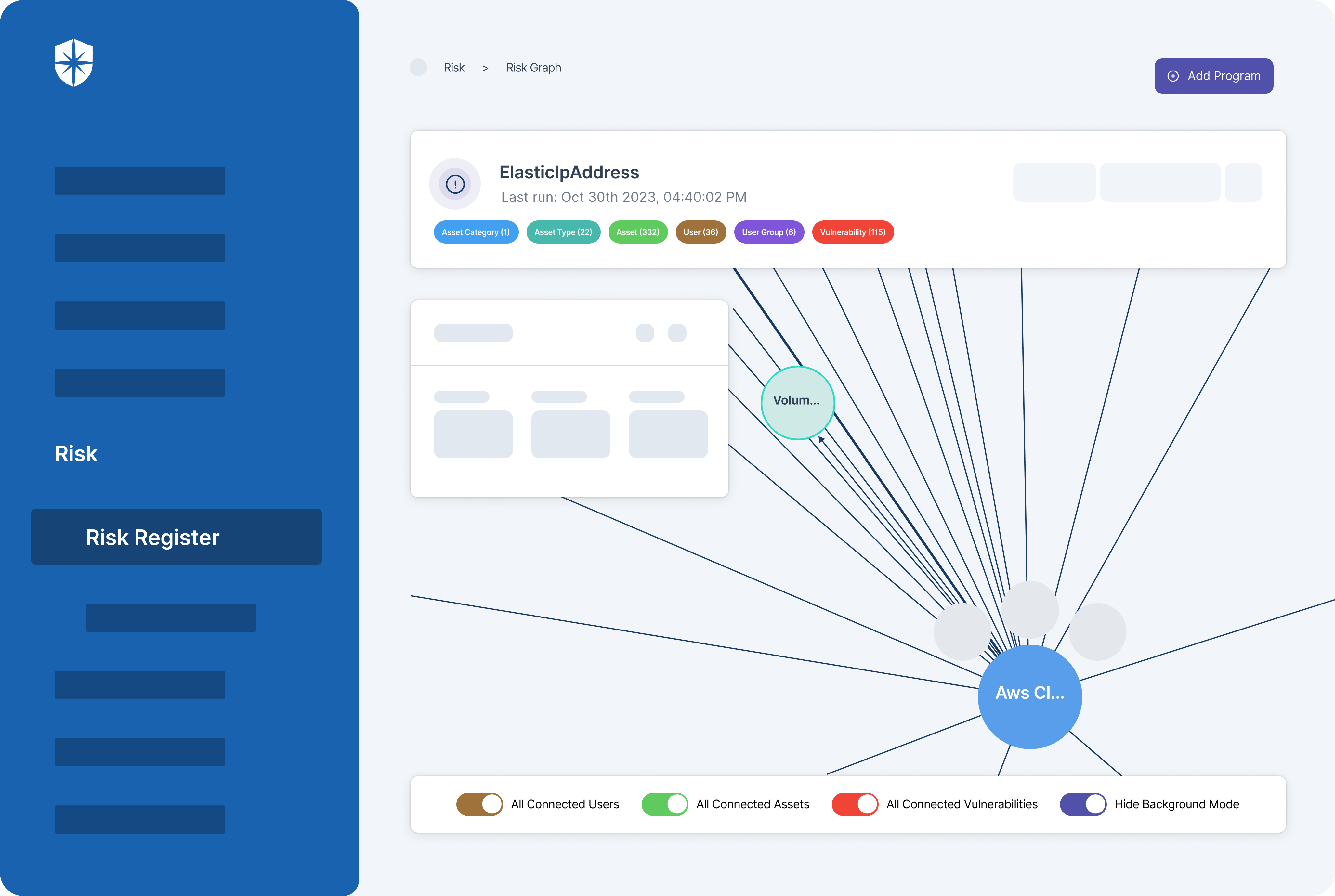

As shown, not only can you integrate and ingest data from your cloud assets to Cyber Sierra. But in a graph-based context you can also:
- View how each asset connects to others.
- Monitor vulnerabilities between connected assets.
- Track security controls broken by specific users of those assets.
RiskOptics
Formerly Reciprocity, RiskOptics bears similarities to Metricstream being that it is more of a GRC platform:

However, RiskOptics’ ROAR (Risk Observation, Assessment and Remediation) feature offers some continuous control monitoring capabilities. It is mainly suited for monitoring and providing insights for closing control gaps in implemented compliance frameworks.
The tool does that in two ways:
- Reducing audit fatigue by enabling teams to reuse controls and evidence across frameworks and continuously test control effectiveness, making organizations always audit-ready.
- Connecting threats, vulnerabilities and risks, and continuously testing compliance and security controls to surface risks.
RiskOptics does not offer the ability to monitor third-party risk assessments, provide or track continuous employee security awareness training, just like other CCM tools Gartner recommends. These are crucial because they ensure security controls being monitored are adhered to by third-parties and employees.
Even though Cyber Sierra isn’t on Gartner’s recommended CCM tools (yet), the platform shines in those areas. Ours is an enterprise-grade pure-play CCM system that also solves other cybersecurity monitoring and remediation challenges interoperably.
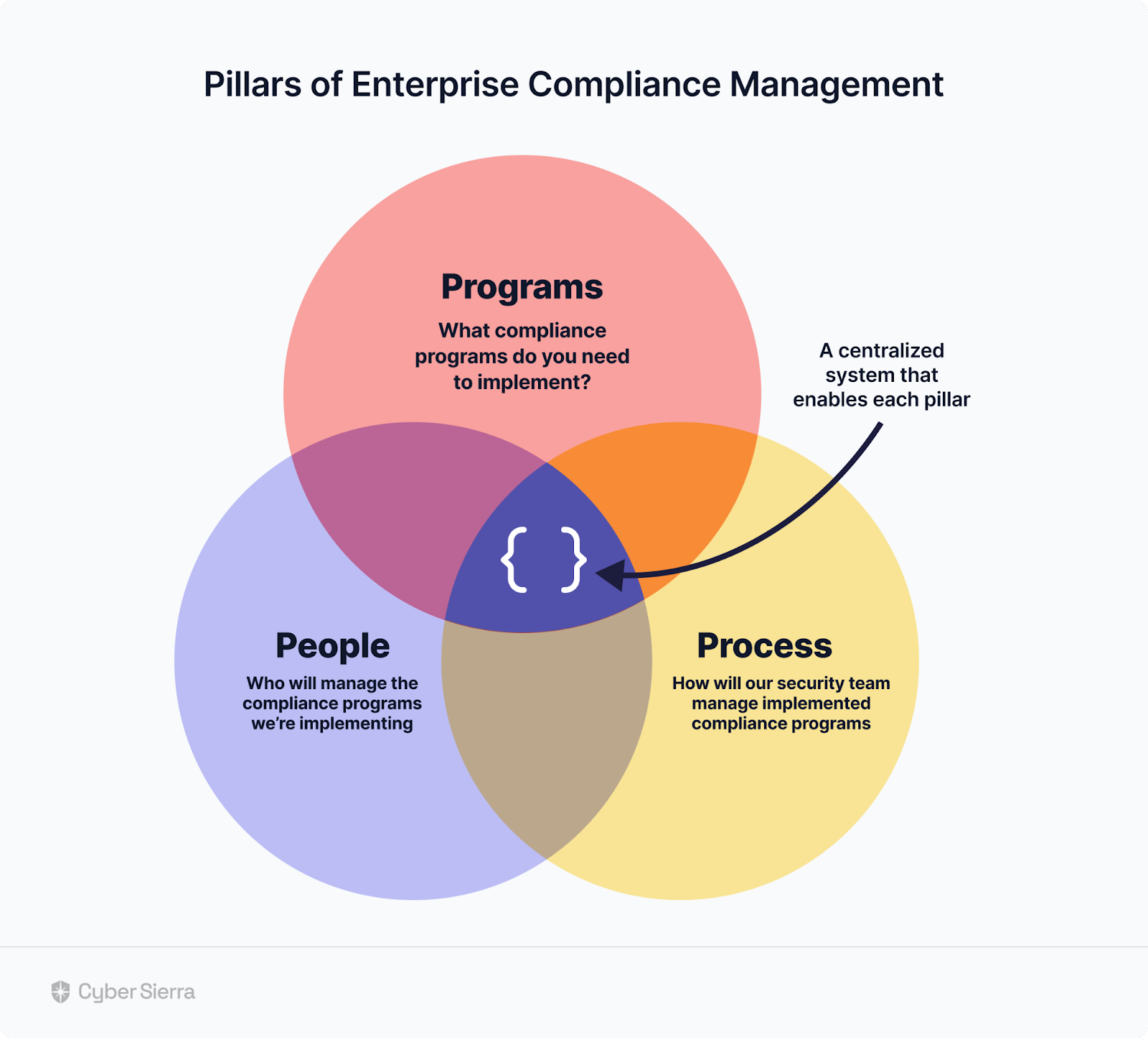
Advantages of a Cybersecurity Continuous Control Monitoring System Like Cyber Sierra
Continuous control monitoring wasn’t added to Cyber Sierra as an afterthought or in response to the growing demand. Unlike other platforms, our CCM feature isn’t built separately. You get full-scale continuous control monitoring capabilities built into core cybersecurity areas like:
- Governance and compliance
- Managing cloud assets
- Risk management and remediation
Governance and Compliance
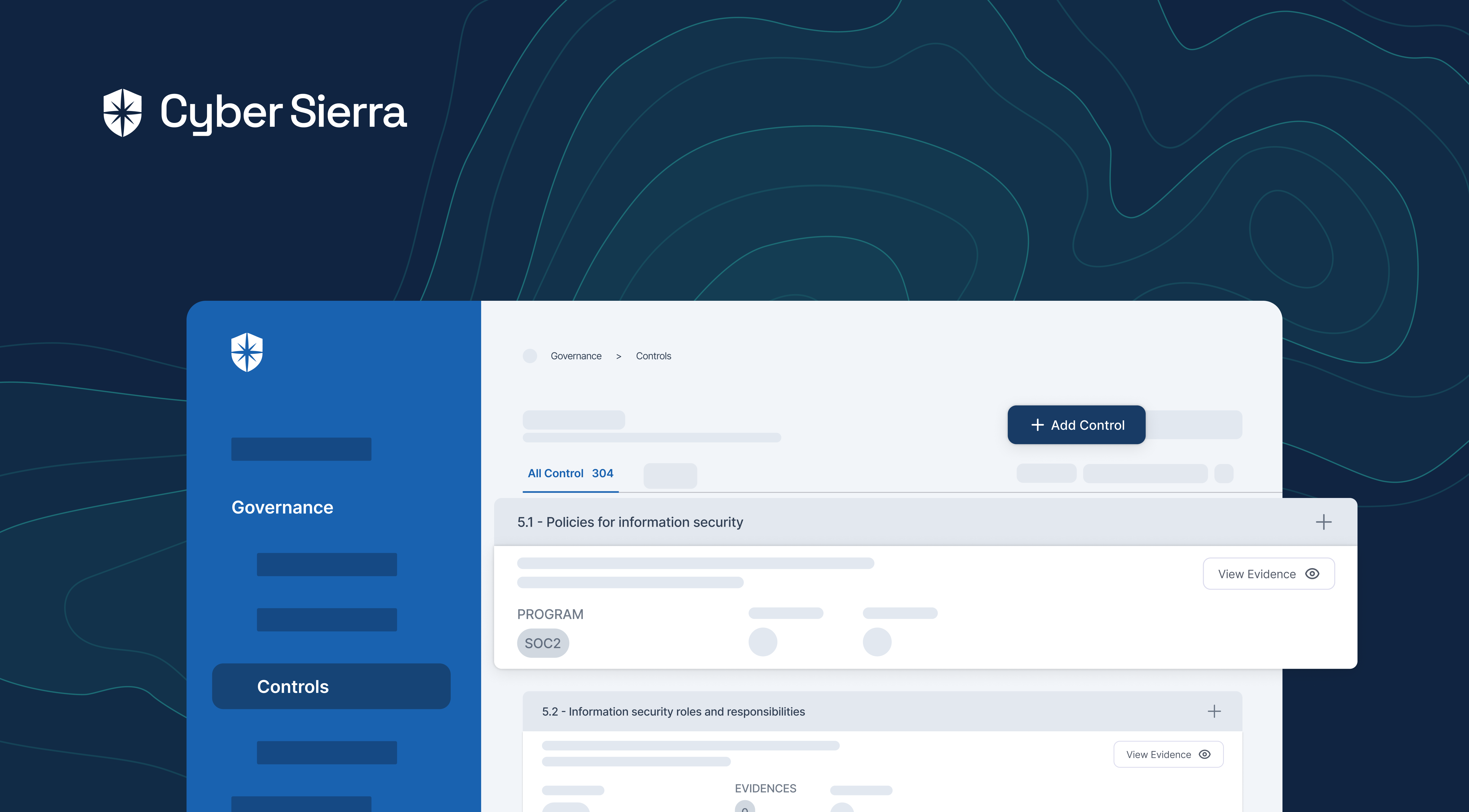
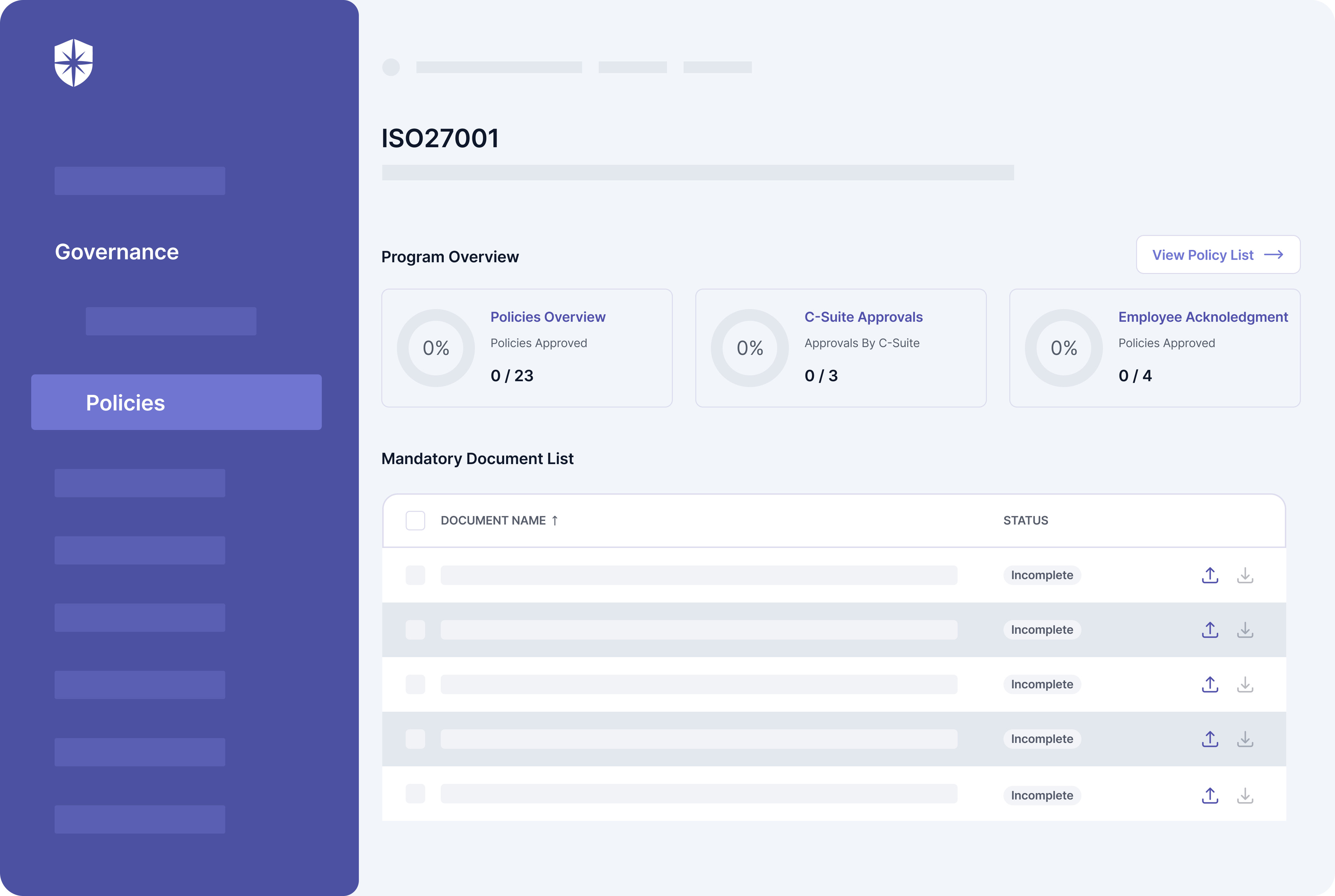
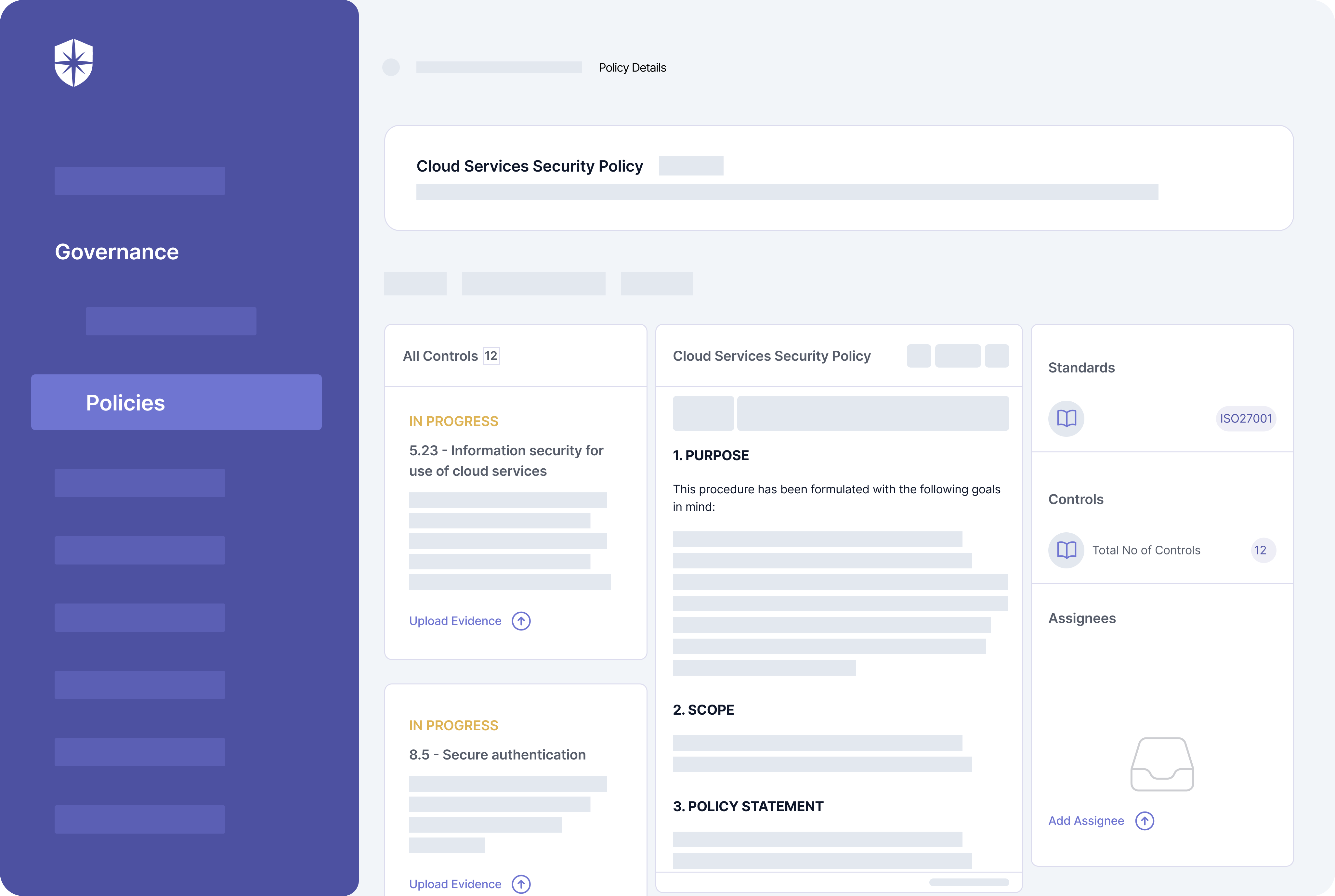
Here, continuous monitoring of security controls associated with compliance programs, frameworks, and policies happens in two ways. Cyber Sierra first consolidates controls from all implemented security governance and compliance programs into one view. From there, it automatically monitors and adds any control that breaks into a dedicated view for easier discovery and remediation:
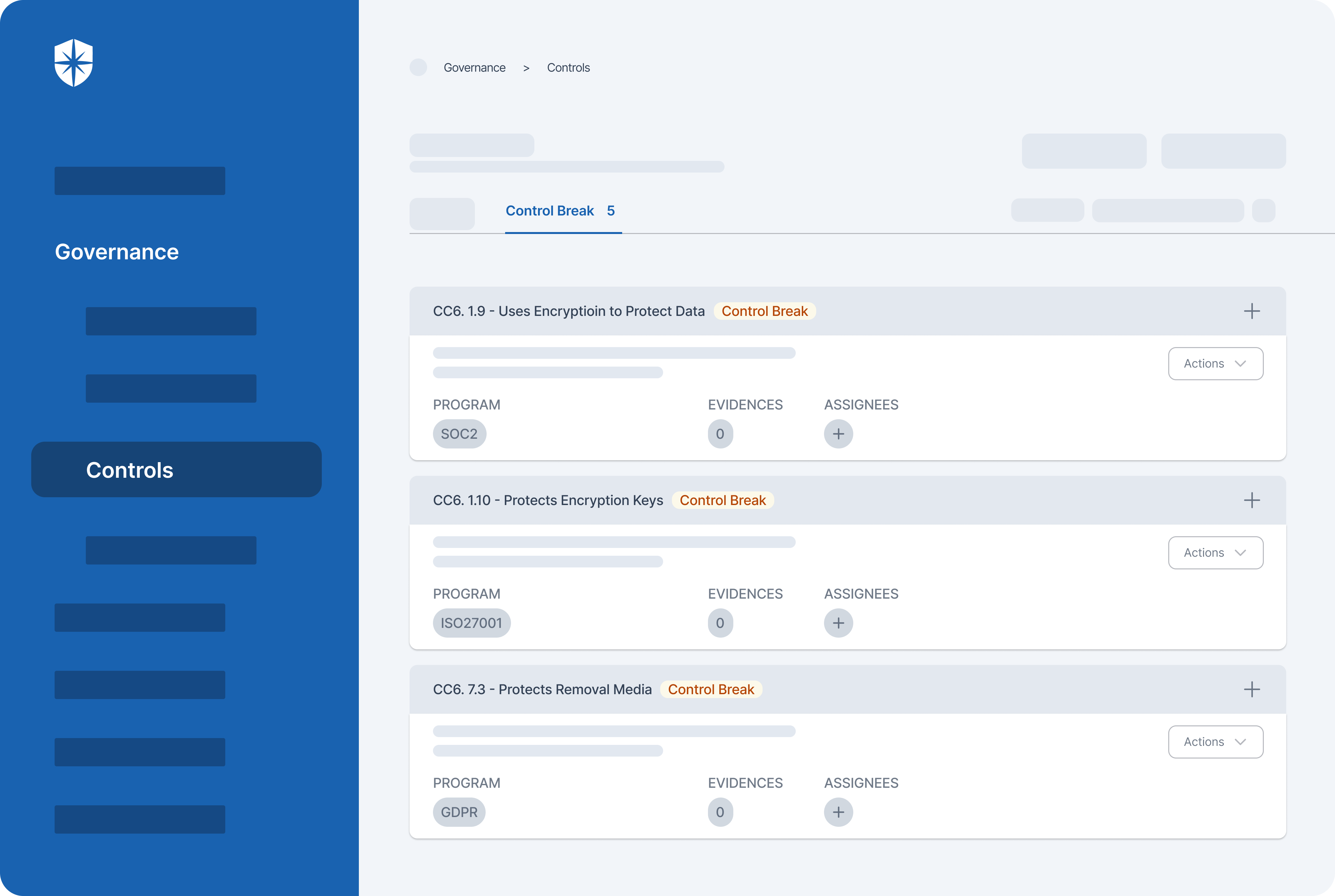

Second, you also get a more comprehensive ‘Controls Dashboard’ under governance. Enterprise teams use this to monitor security controls relative to compliance programs and integrated cloud assets.
Here’s a sneak peek:


Managing Cloud Assets
Enterprise security teams can integrate and maintain a holistic inventory of all cloud assets used with Cyber Sierra. But to enable the management of risks and vulnerabilities from those assets, our platform takes it one step further.
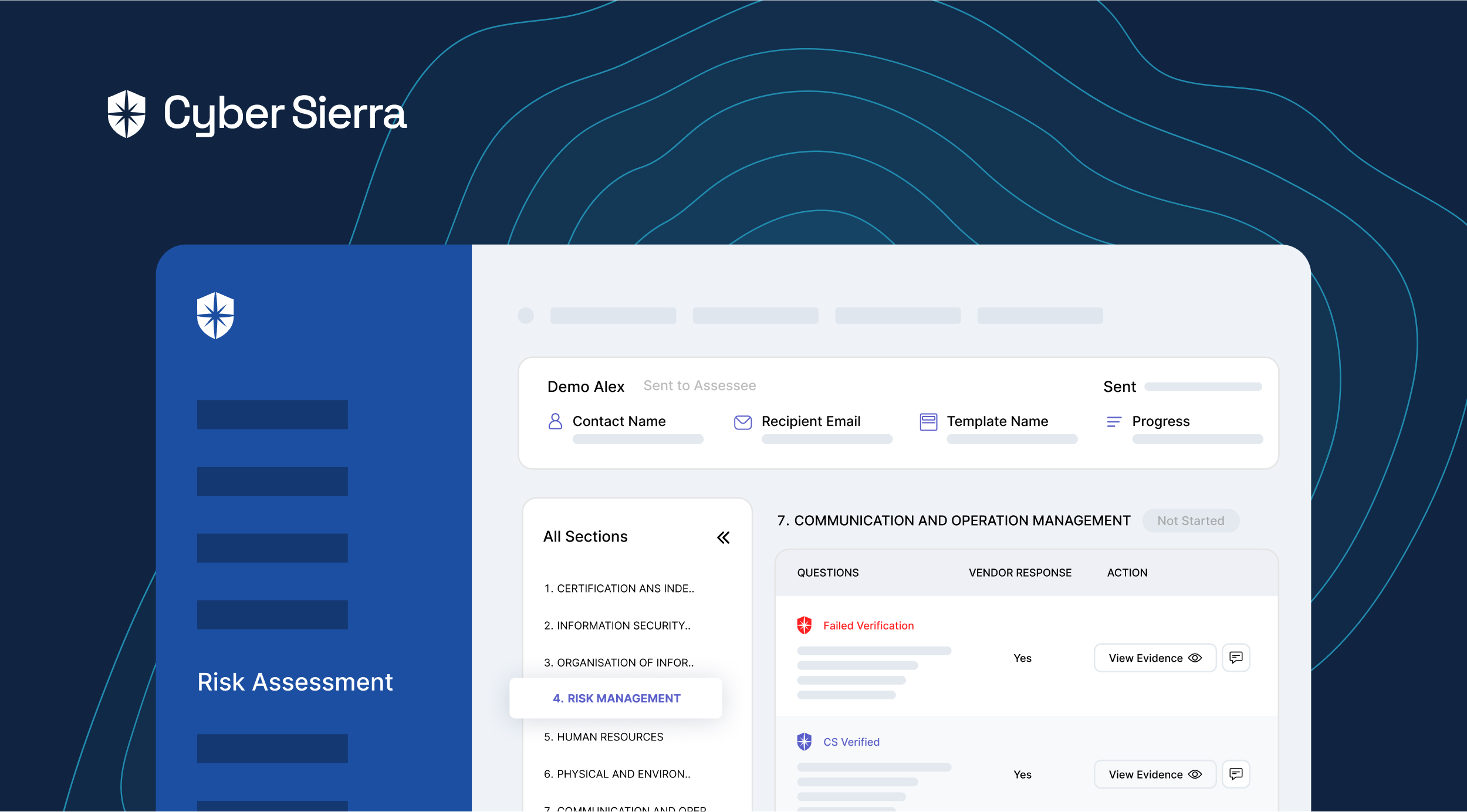
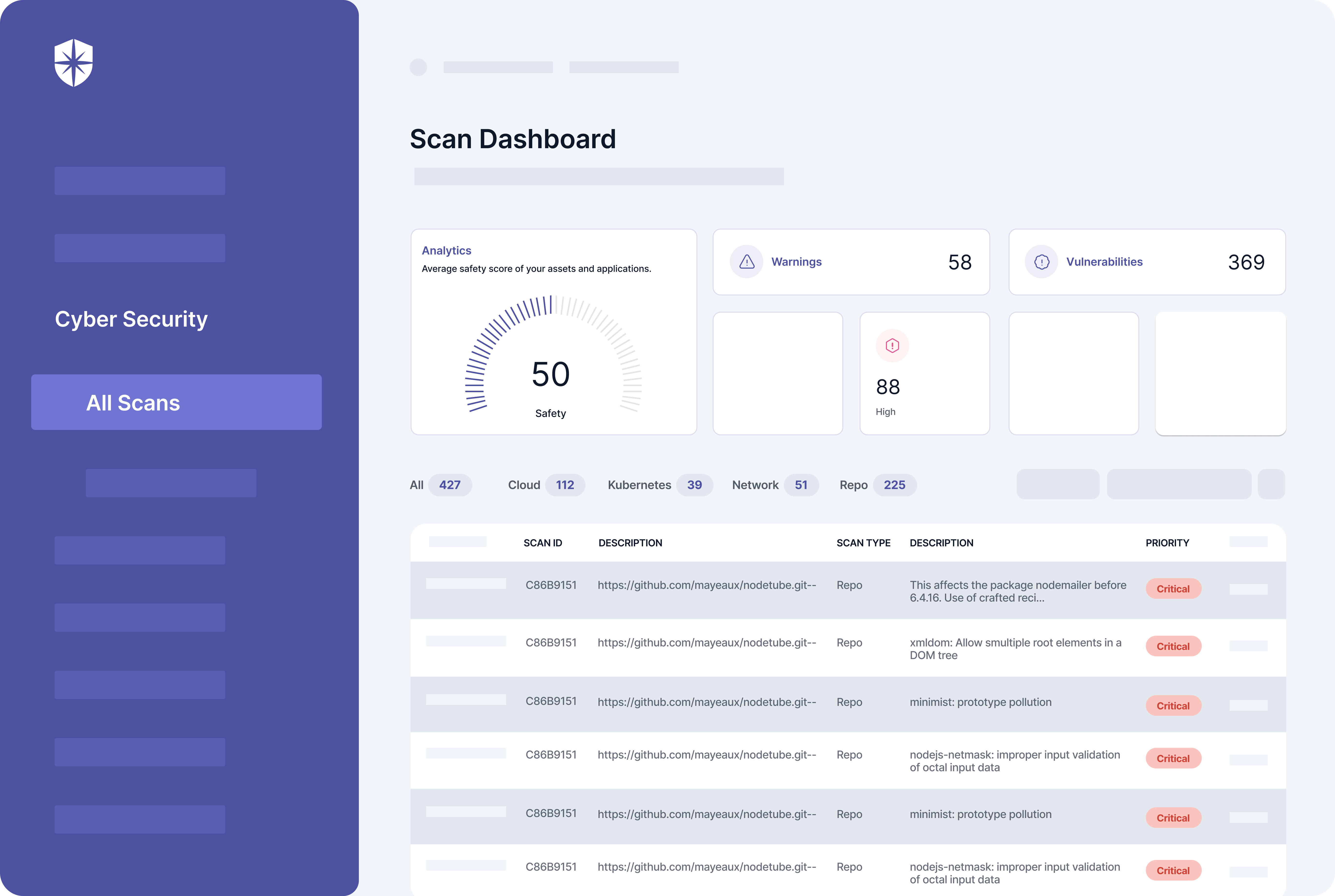
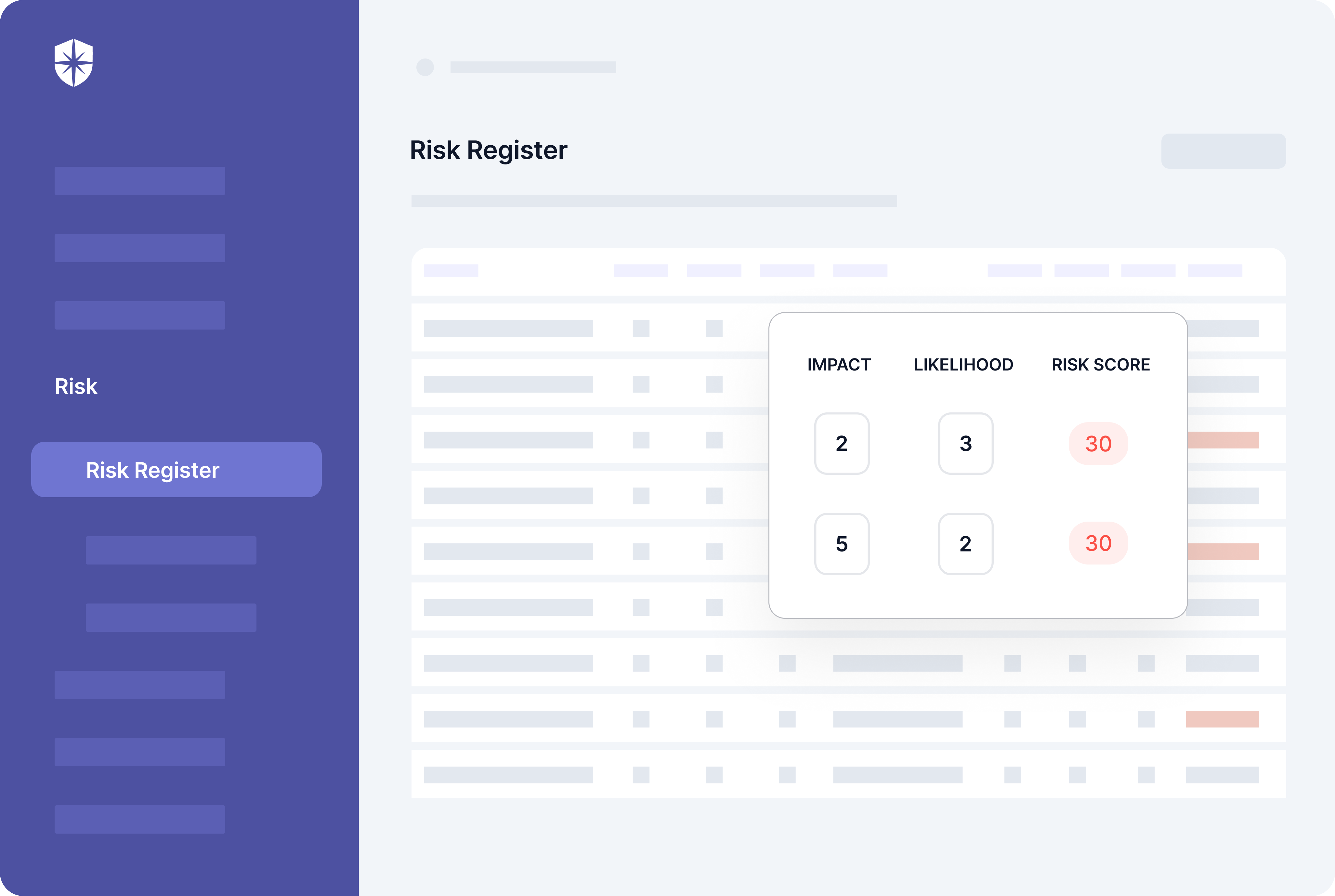
You get a Risk Dashboard to continuously monitor risks by asset categories and security control breaks by asset types:
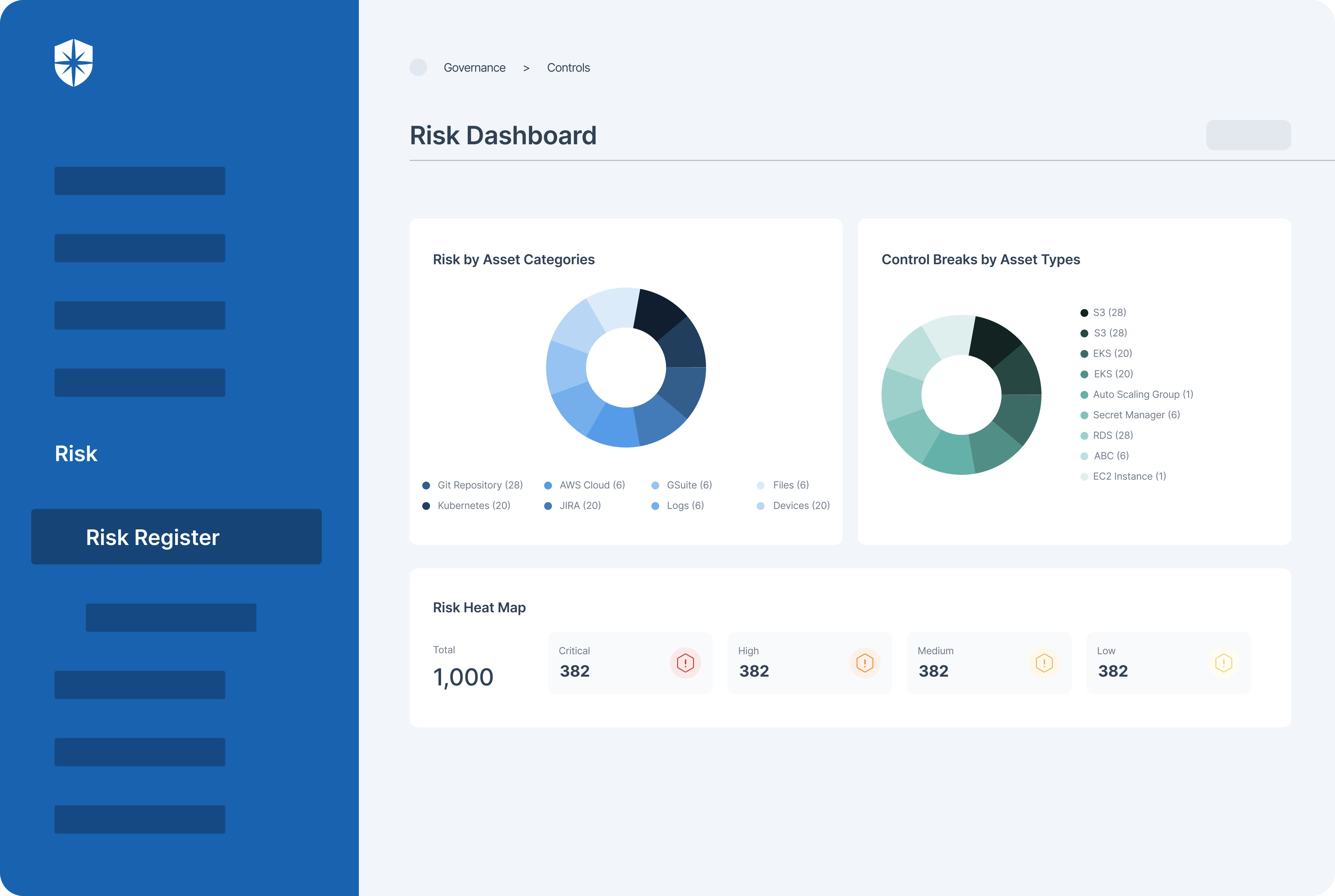

As shown, the risk heat map gives your team a unified view of all critical to low risks mapped to all affected cloud assets.
Risk Management and Remediation
The whole purpose of continuous monitoring is to detect, manage, and remediate risks proactively. To do that, a CCM platform shouldn’t just enable enterprise teams to monitor controls. It should facilitate the remediation of risks associated with monitored controls.
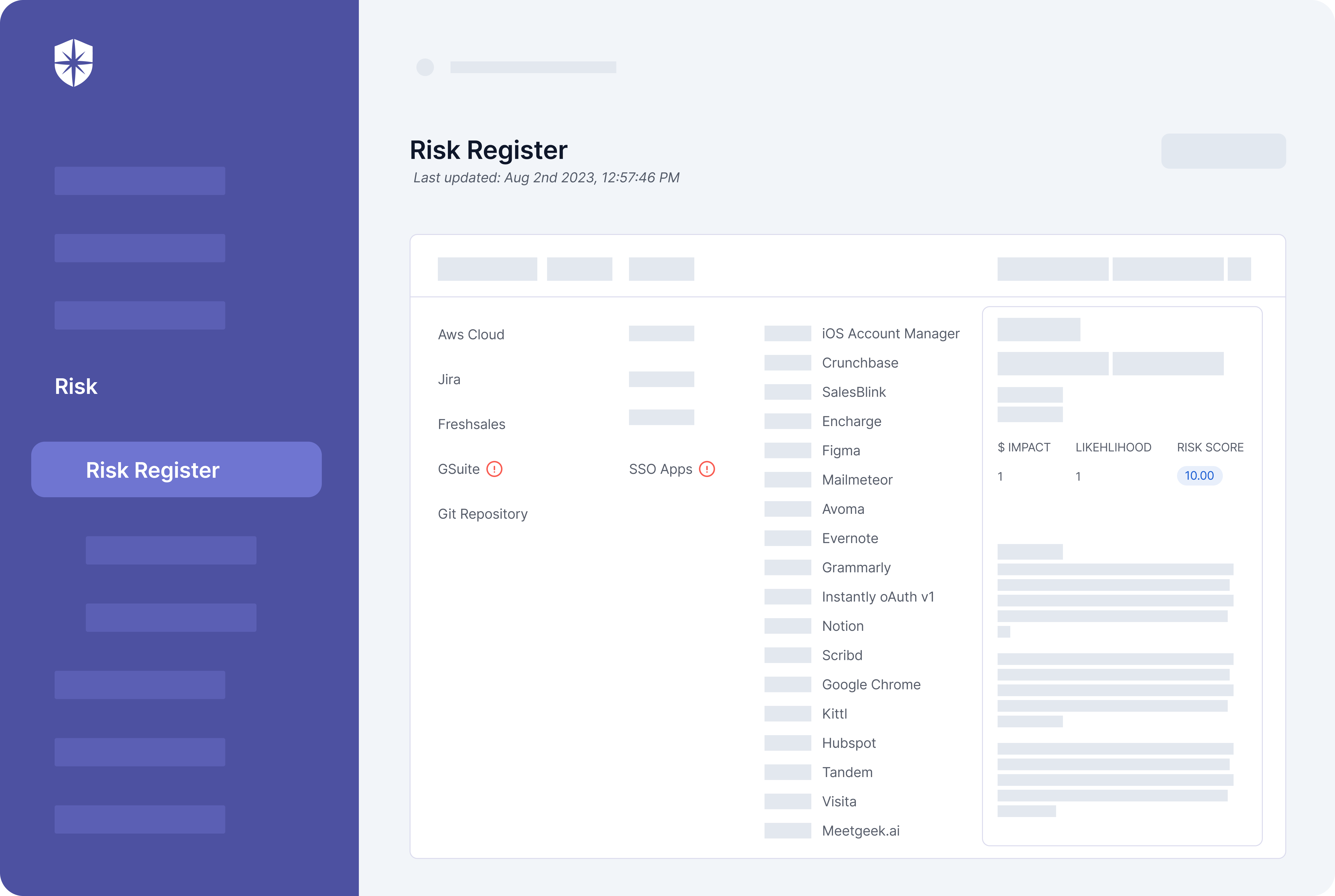
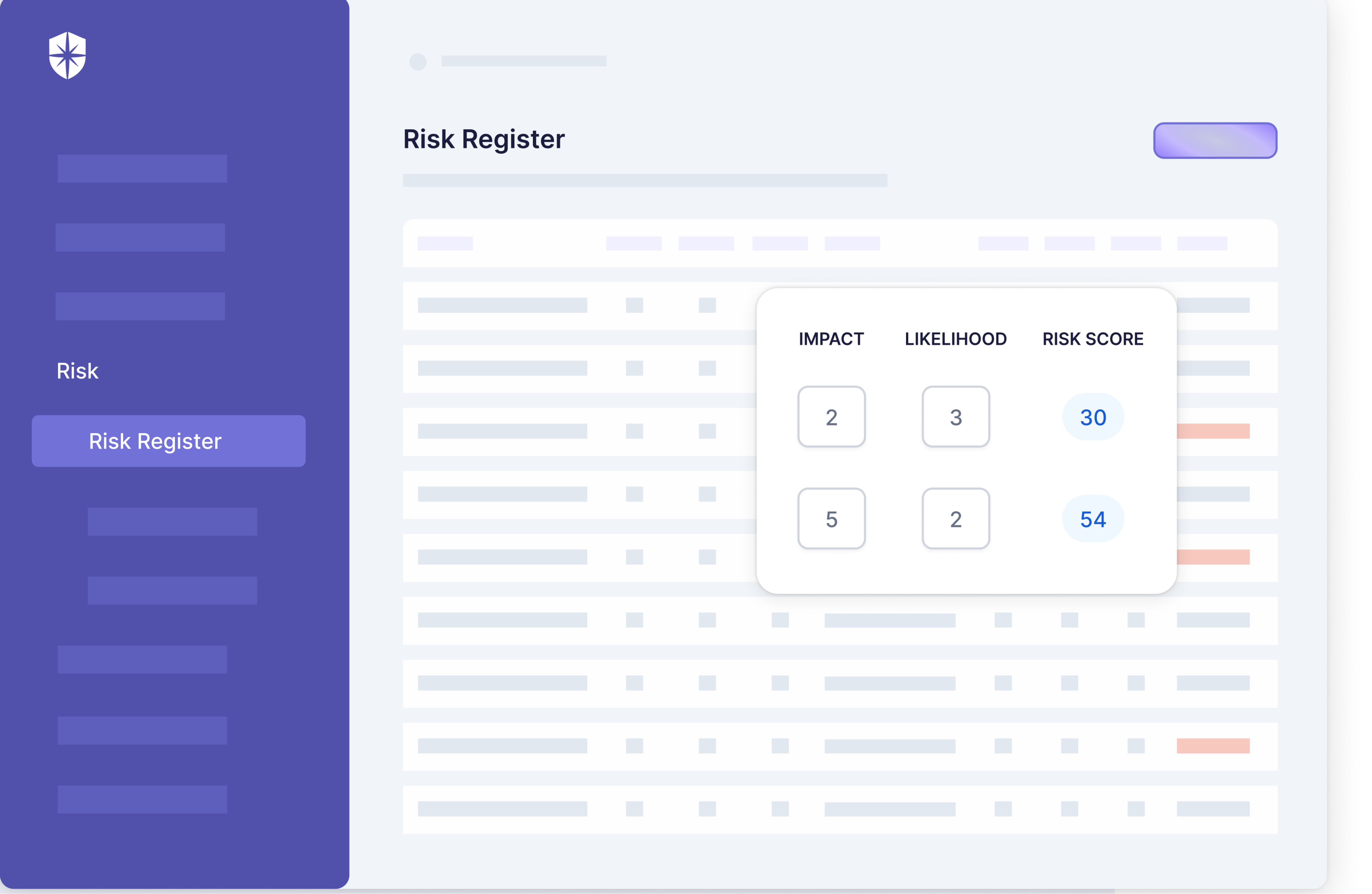
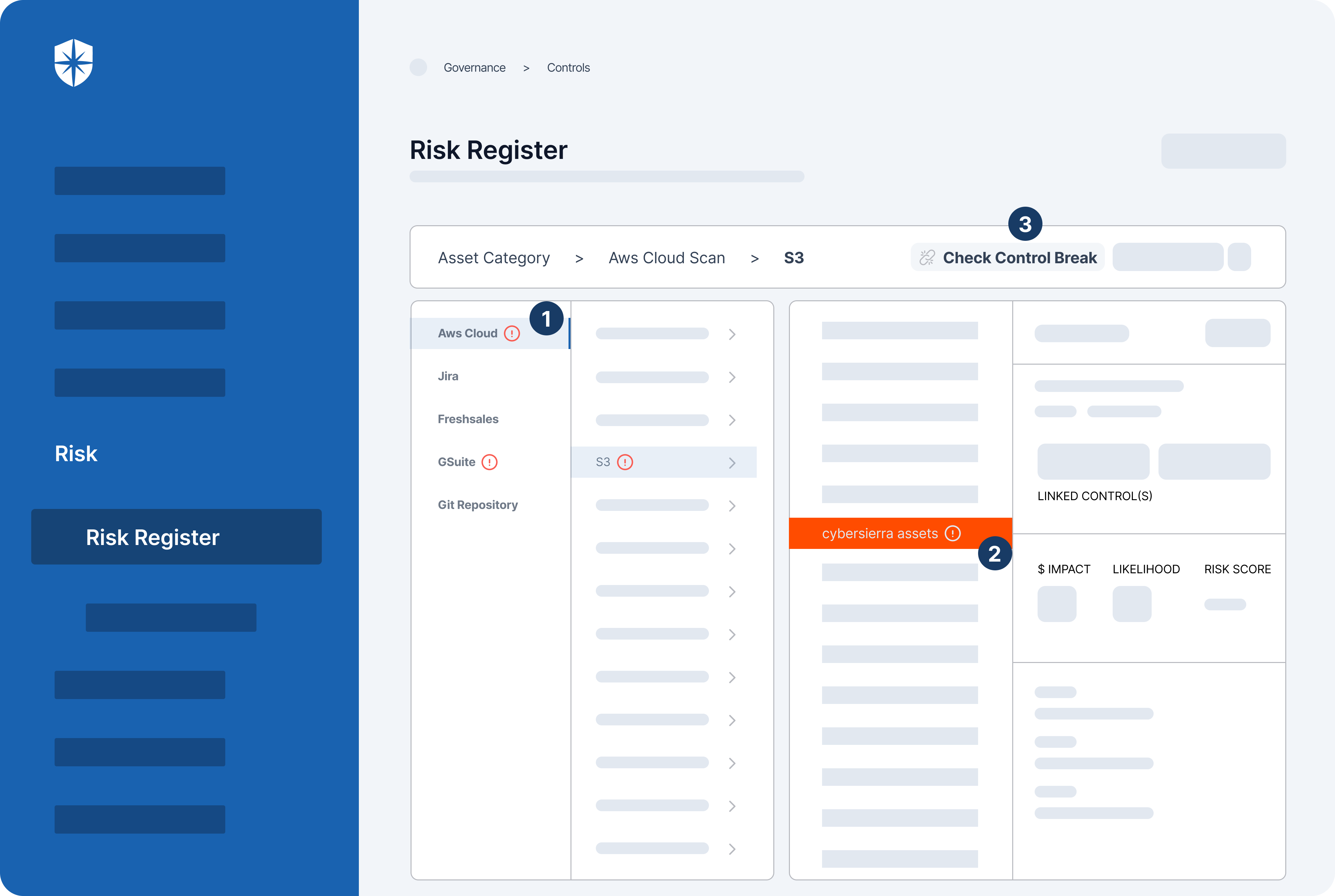
Cyber Sierra’s Risk Register enables that.
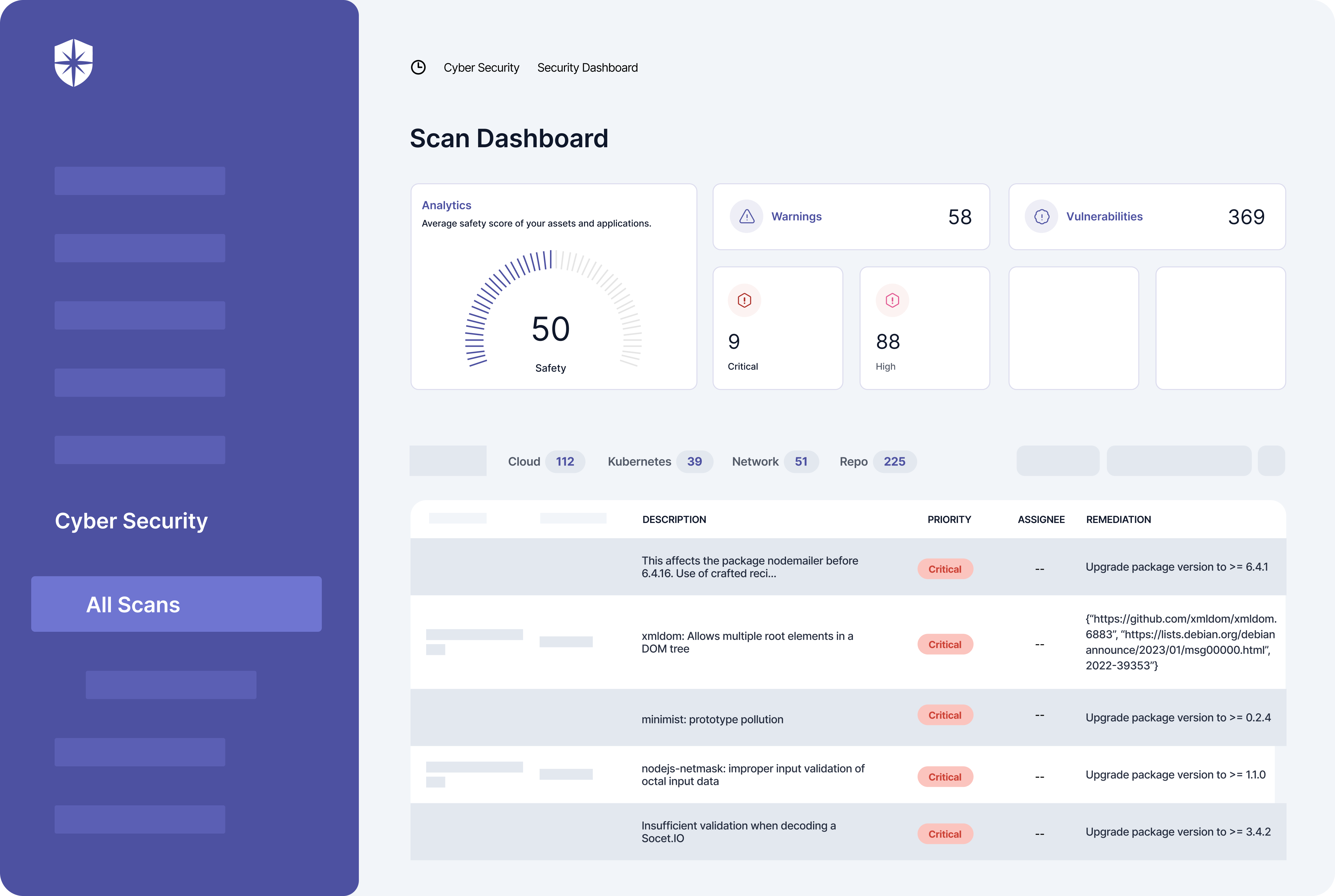
With it, enterprise security teams can scan all integrated assets (it takes ~10 mins) to:
- Identify assets that are vulnerable to threats.
- See a breakdown of security controls linked to those assets.
- Easily check the control break in one button click:

Implement an Interoperable CCM Tool
Cyber Sierra consolidates the core capabilities for cybersecurity continuous control monitoring into one interoperable technology platform. This is recommended, according to EY’s 2023 Global Cybersecurity Leadership Insights Study.
A key finding of the study went:


Based on this, achieving cybersecurity continuous control monitoring with a consolidated platform is logical. And with Cyber Sierra, you get one that monitors and detects incidents efficiently while also tackling other cybersecurity challenges.
Imagine your team doing more with less.




















A weekly newsletter sharing actionable tips for CTOs & CISOs to secure their software.
Thank you for subscribing!
Please check your email to confirm your email address.
Find out how we can assist you in
completing your compliance journey.