Top 7 GRC Tools You Should Consider in 2024























Join thousands of professionals and get the latest insight on Compliance & Cybersecurity.
Data breaches, regulatory nightmares, compliance headaches – running a successful business can feel like navigating a minefield. Managing modern-day risks that are complex, interconnected, and constantly evolving can be equally challenging.
To successfully navigate these challenges, you need to implement robust Governance Risk, and Compliance strategies. The right GRC tools can help streamline operations, ensure adherence to regulatory requirements, mitigate risks, and drive long-term business growth.
By automating Governance Risk, and Compliance processes, GRC software can help companies come up with a robust plan to address security vulnerabilities, prevent reputational damage, and avoid insane fines attributed to failure to protect critical customer data.
In March 2024 alone, the EU data protection authorities imposed approximately €4.5 million in fines due to breaches of the General Data Protection Regulation(GDPR).
But how do you choose the software you can trust from the host of GRC solutions out there?
This guide unveils the top 7 GRC tools that can help you conquer risk, ensure compliance, and focus on what matters the most – growing your business.
But before that, let’s get the basics straight.
What are GRC Tools?
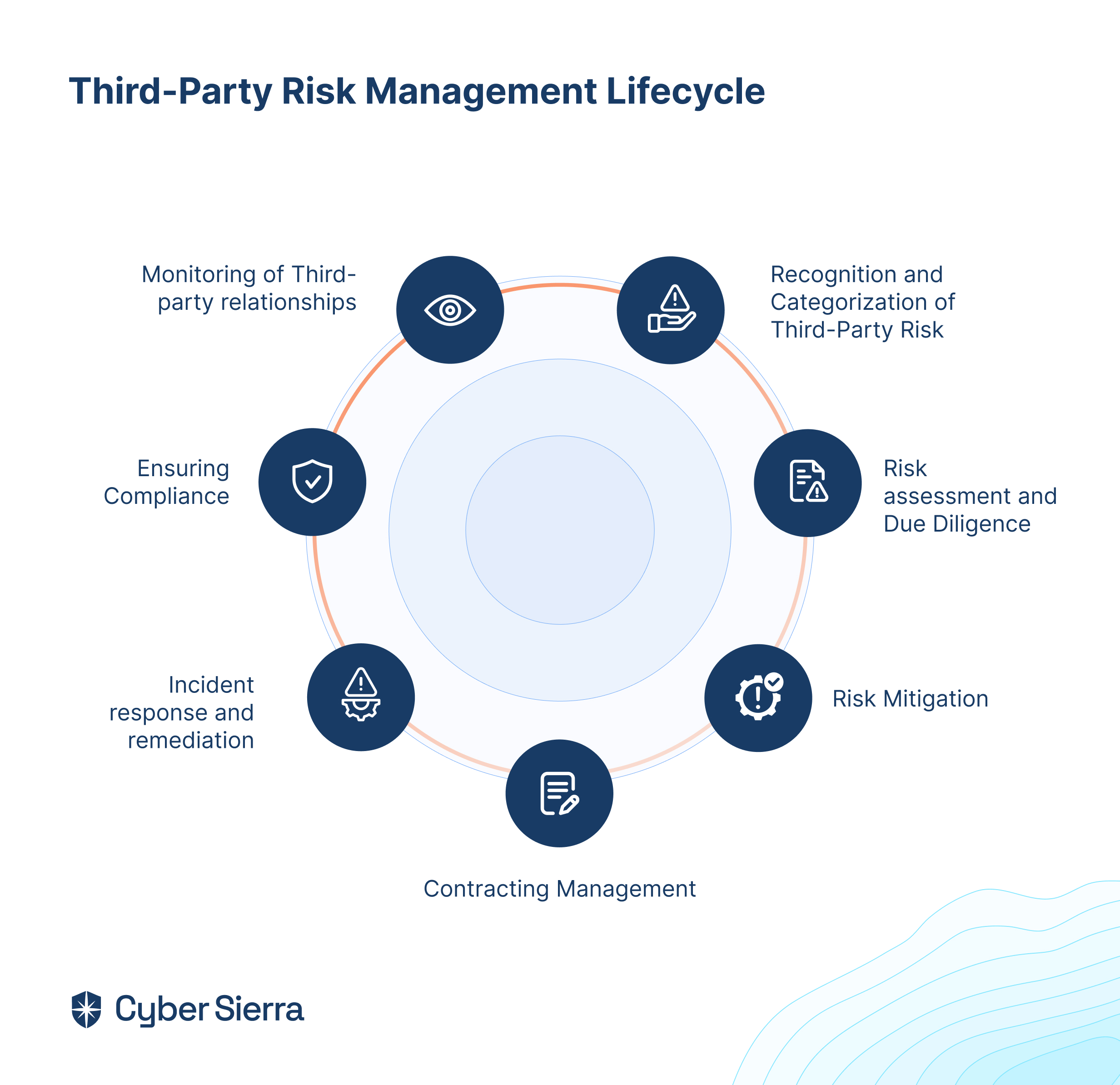
GRC tools, or Governance, Risk, and Compliance tools are software applications that provide organizations with a centralized platform to manage risks, and compliance requirements, and implement security best practices effectively.
They are an essential component in today’s complex regulatory environments. Some of the key functions of a GRC platform include the consolidation of information from various departments into a unified data environment.
GRC tools also automate processes, eliminating the need for manual processes and scattered spreadsheets. This reduces errors and saves money and time.
By implementing these software solutions, organizations can gain near real-time visibility into their compliance status, enabling them to make informed decisions, improve efficiency, and reduce the risk of fines and penalties.
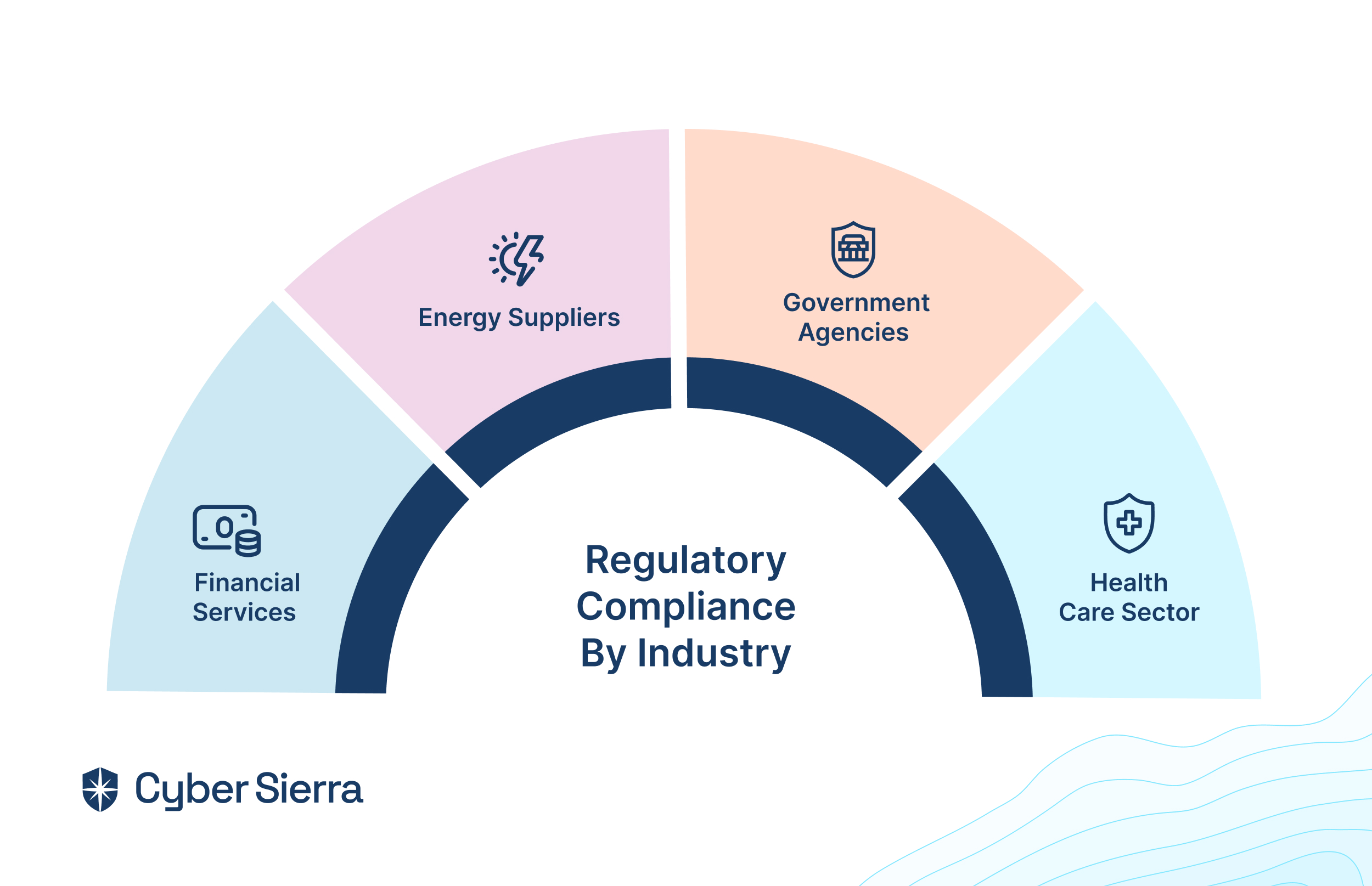
GRC tools cater to a wide range of organizations across various industries. They are particularly beneficial for large enterprises with intricate regulatory obligations as they help navigate complex compliance landscapes efficiently.
Similarly, small to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) can leverage GRC tools to streamline their business processes and ensure compliance without the need for extensive resources.
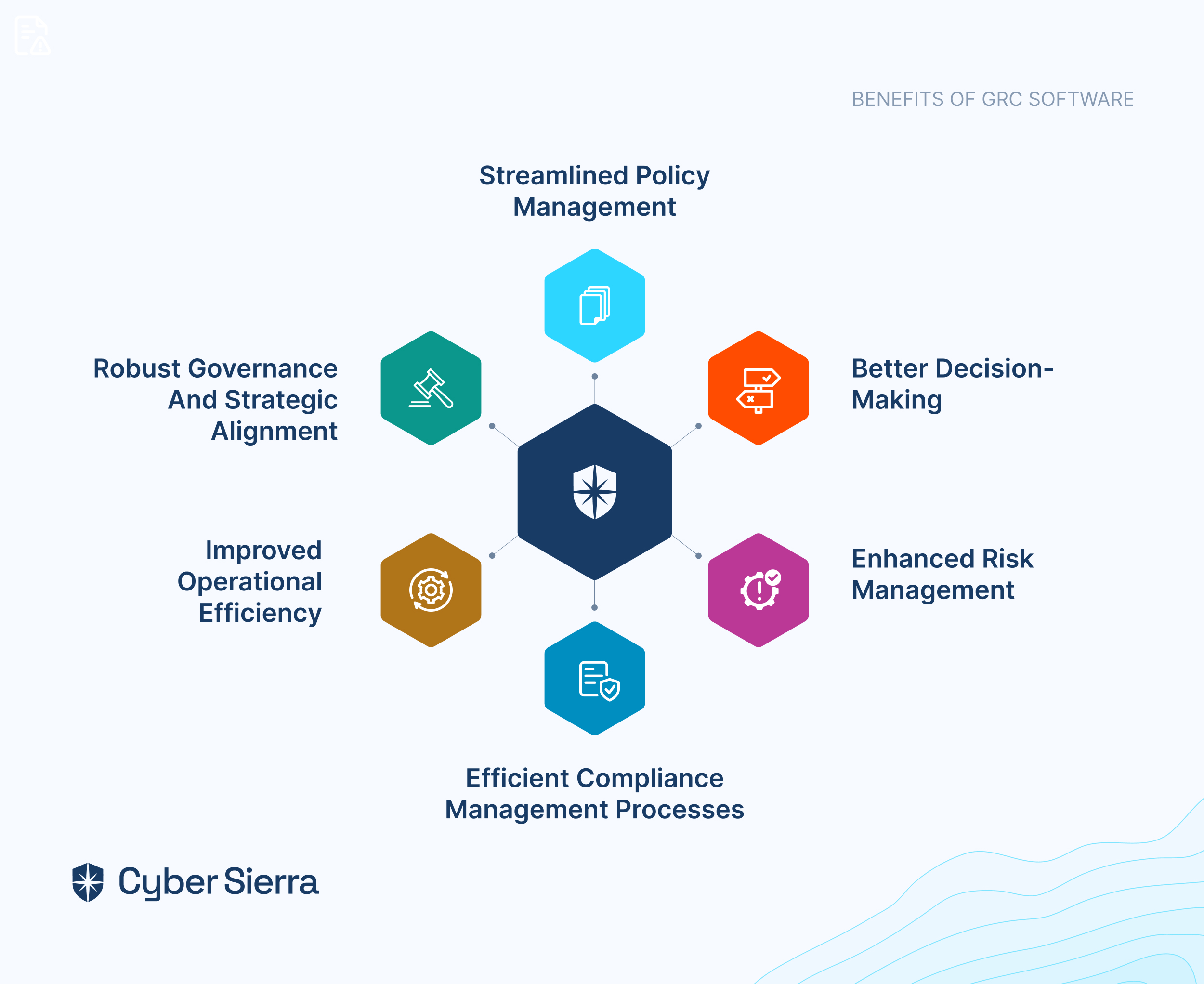
Overall, GRC software provides a host of benefits to businesses including:
- Better decision-making
- Enhanced risk management
- Efficient compliance management processes
- Improved operational efficiency
- Robust governance and strategic alignment
- Streamlined policy management

Best GRC Tools to Simplify Compliance and Boost Efficiency


Let’s dive into the details of each GRC system.
1. Cyber Sierra

Best for: Small to large enterprises looking for a robust GRC solution to manage all parts of their GRC program in one place.
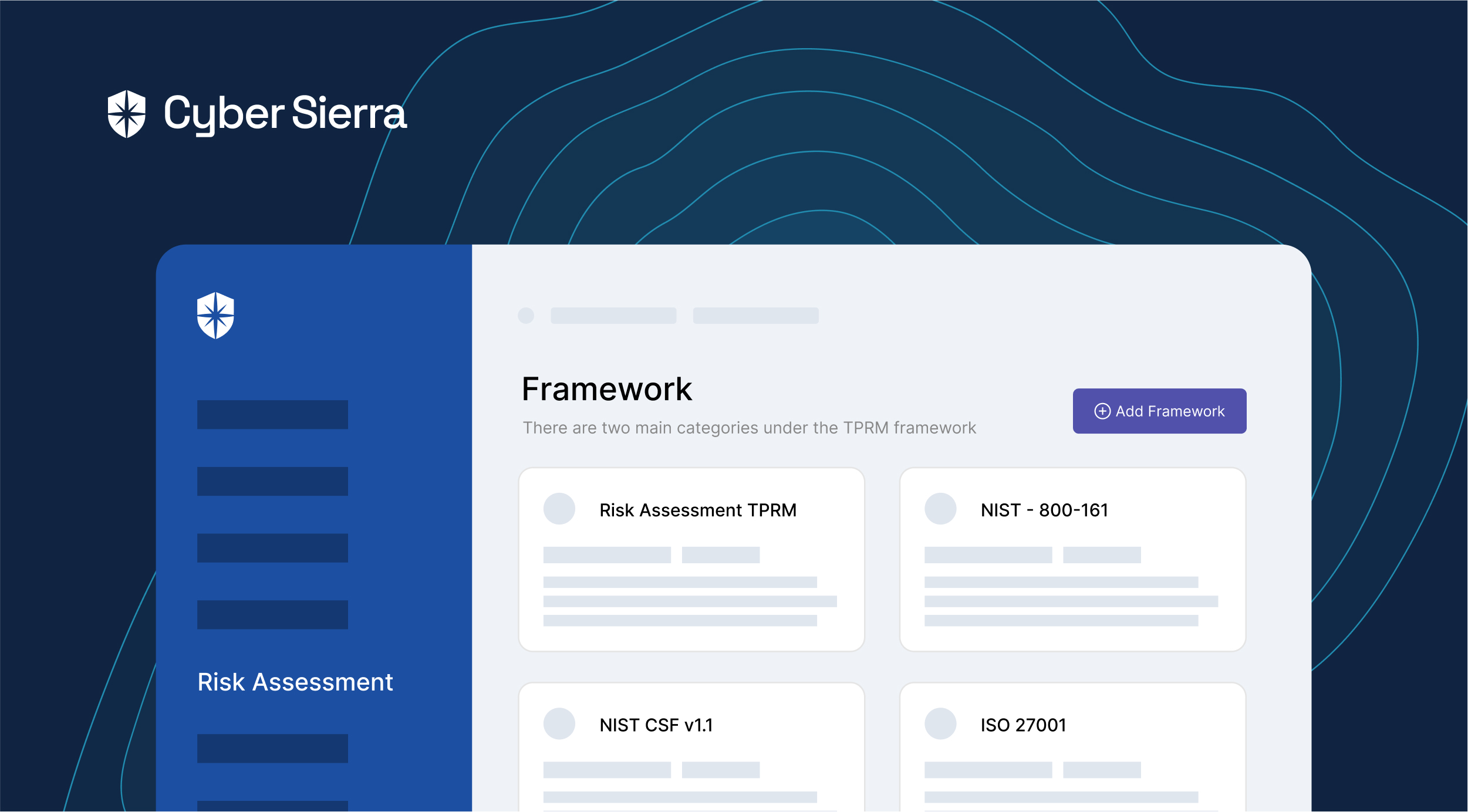
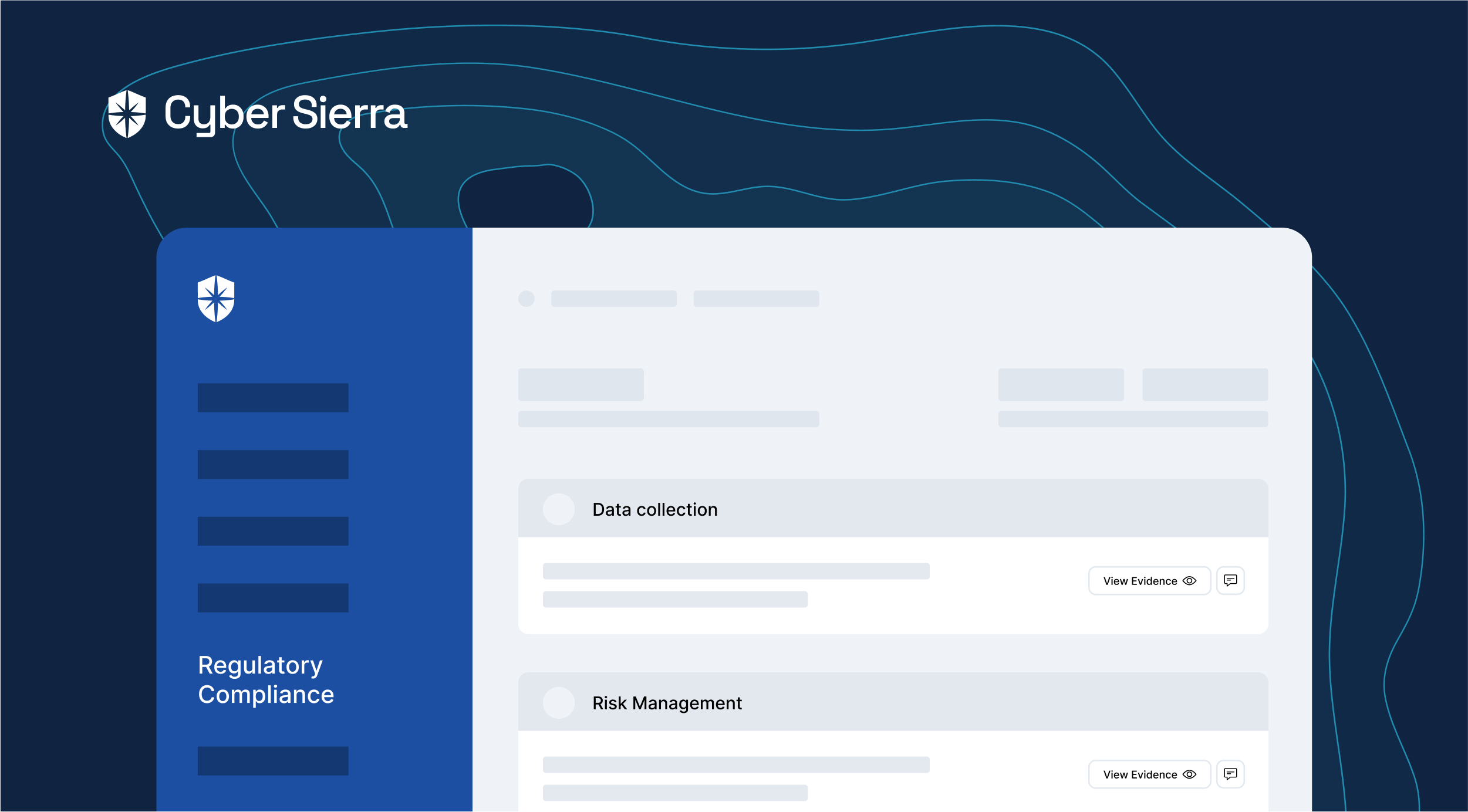
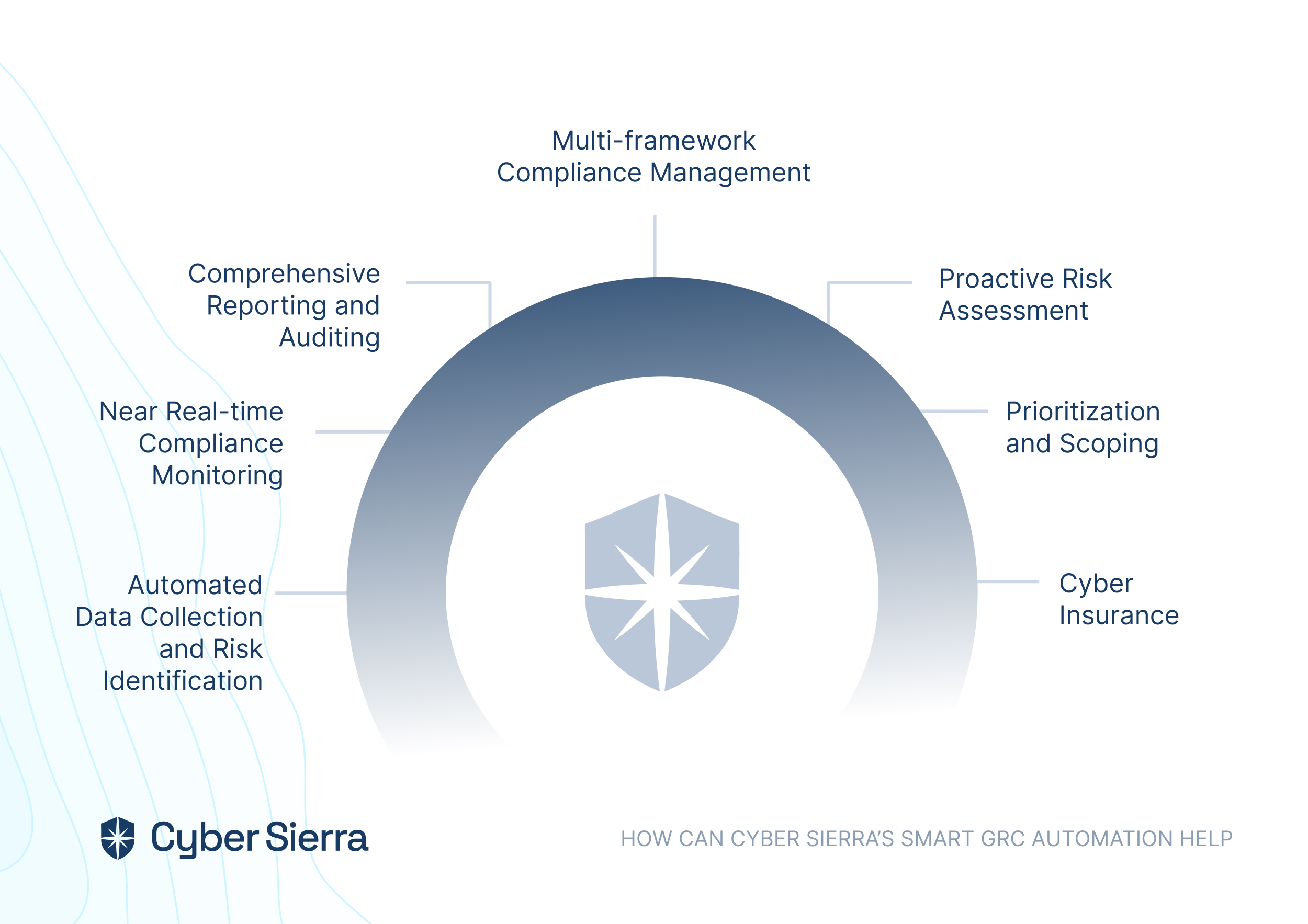
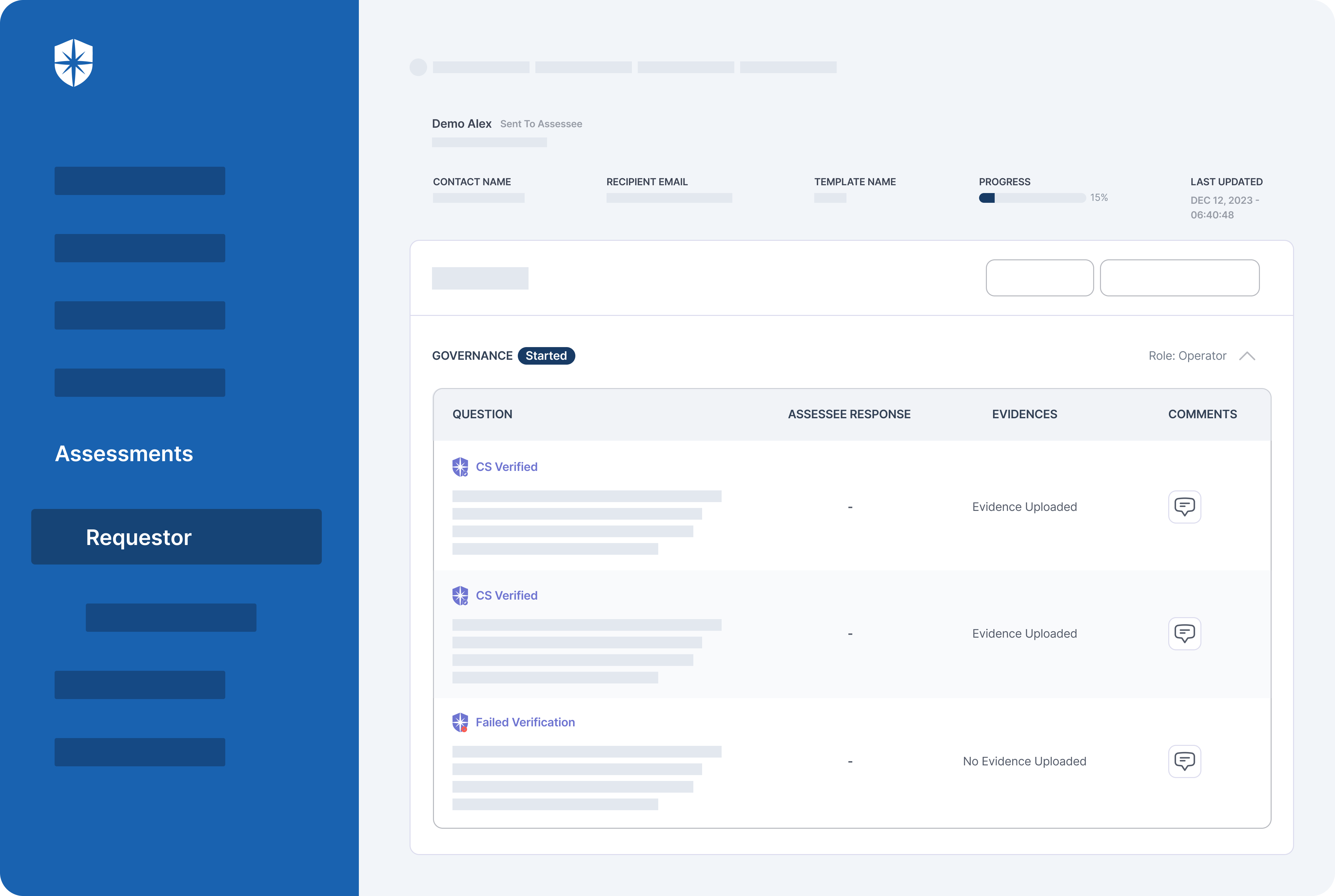
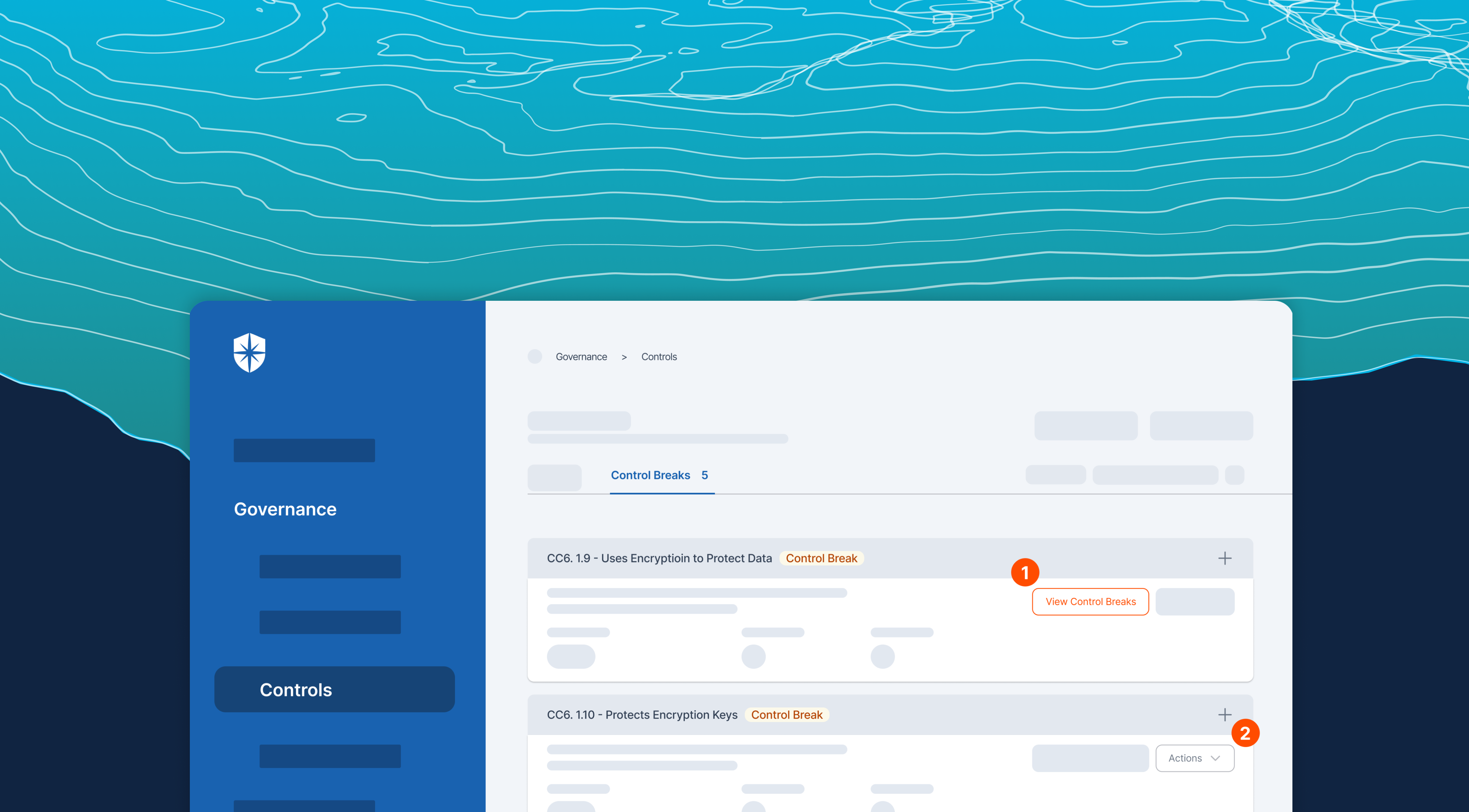
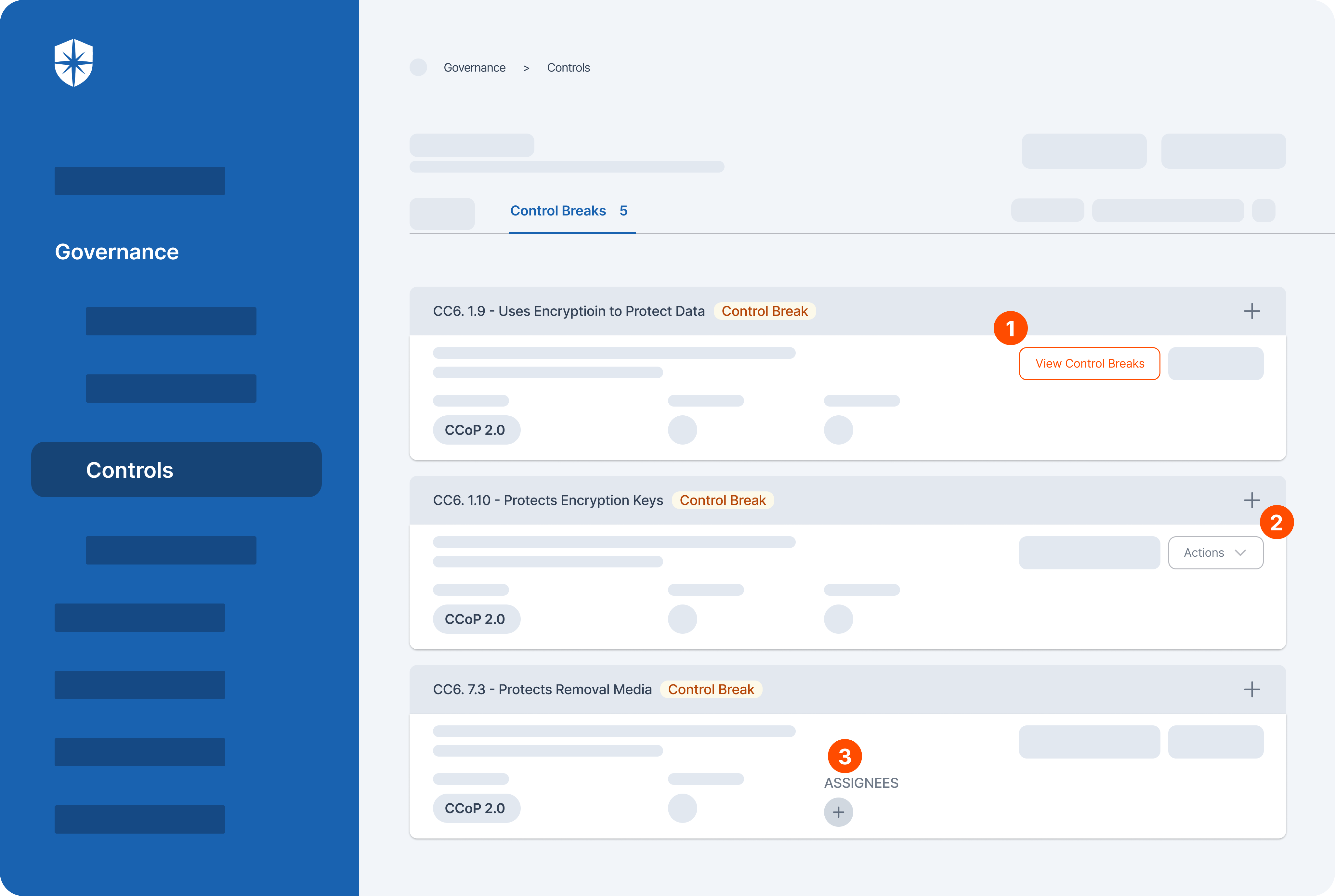
Cyber Sierra’s GRC solution is a premier tool for seamlessly managing all GRC needs via automation. The software is designed to help organizations of all sizes manage all aspects of their GRC program (compliance, risk management, auditing, controls management, and more) in one place.
It integrates cutting-edge technology to streamline GRC processes and ensure regulatory compliance effortlessly.
Through automation, the tool simplifies tasks, reducing manual efforts and enhancing operational efficiency. This enables organizations to allocate resources more strategically and focus on core objectives.
One of the key strengths of Cyber Sierra’s GRC system lies in its adaptability to evolving regulatory frameworks. The software continuously updates its algorithms to align with the latest compliance standards, keeping organizations ahead of regulatory changes. This ensures that businesses remain compliant and mitigate risks effectively, thereby safeguarding their reputation and financial integrity.
Moreover, this tool prioritizes security, employing robust encryption protocols to safeguard sensitive data. For instance, it offers role-based access control, limiting access to authorized personnel and protecting against potential breaches. This commitment to security instills confidence in users, assuring them of the platform’s reliability and trustworthiness.
Furthermore, the software enhances collaboration across departments, fostering seamless communication and alignment of objectives. To facilitate cross-functional teamwork the platform provides a centralized repository for documentation and workflows. This promotes transparency and accountability, enabling stakeholders to make informed decisions and drive organizational success.
Key features
Here are Cyber Sierra’s standout features that make it the ultimate solution for organizations of all levels:
- Intuitive user interface: Cyber Sierra’s GRC software offers a user-friendly interface that simplifies navigation and enhances user experience.
- Customizable workflow automation: Unlike other GRC tools which may offer limited customization options, the software provides extensive capabilities for tailoring workflow automation to specific organizational needs, allowing for greater efficiency and adaptability.
- Comprehensive risk assessment: Cyber Sierra’s GRC software stands out for its robust risk assessment module, which enables thorough identification, evaluation, and mitigation of risks across the enterprise, providing organizations with a clearer understanding of potential threats.
- Real-time monitoring and reporting: Cyber Sierra’s software offers real-time monitoring capabilities coupled with advanced reporting features that allow organizations to proactively identify and address compliance issues as they arise, rather than reacting to them after the fact.
- Scalability: It is designed to accommodate the evolving needs of organizations of all sizes. It is best suited for small businesses to large enterprises, with scalability built into its architecture to support growth and expansion without compromising performance.
- Advanced analytics and insights: The GRC system distinguishes itself with its advanced analytics and reporting capabilities, leveraging data-driven insights to help organizations make informed decisions and optimize their governance, risk, and compliance strategies effectively.
Pricing
Cyber Sierra offers three different pricing plans. Their prices are available upon request based on your chosen plan.
2. SAP GRC

Best for: Large enterprises seeking comprehensive governance, risk management, and compliance solutions integrated with SAP systems for real-time visibility and control over business risks.
SAP GRC platform is a comprehensive suite of management, auditing, and compliance tools designed to streamline and enhance organizational governance processes.
With the software, enterprises can navigate regulatory landscapes effectively while mitigating risks and ensuring compliance adherence.
At its core, the platform offers robust management tools that facilitate seamless oversight of various aspects of governance, risk, and compliance within an organization. They include auditing tools that enable comprehensive assessment and monitoring of internal controls, ensuring adherence to regulatory requirements and industry standards.
For compliance management, the GRC system employs a broad range of functionalities aimed at proactively addressing regulatory obligations and mitigating security risks.
SAP GRC also provides users with real-time visibility into compliance efforts, enabling them to make data-driven decisions based on insights derived from the platform’s predictive analytics.
The platform’s workflow management features streamline processes enabling efficient collaboration and coordination across departments. This is particularly crucial in enterprise risk management and compliance where timely responses to emerging threats are vital.
Utilizing user access control management capabilities, SAP GRC helps organizations safeguard sensitive information and prevent unauthorized access.
Additionally, by identifying and addressing security vulnerabilities, enterprises can boost their defenses against potential breaches and ensure regulatory compliance.
Furthermore, the platform caters to the evolving regulatory landscape by offering tools tailored to meet the requirements of government agencies and regulations. This facilitates seamless alignment with regulatory frameworks, reducing compliance-related complexities and enhancing operational efficiency.
While powerful, its high cost, complex setup, and need for SAP expertise make it less ideal for smaller businesses.


Source : G2
Key features
- Enterprise risk compliance and management: Enables organizations to identify, assess, and mitigate various types of risks across different business processes and functions.
- International trade management: Streamlines global trade compliance to ensure minimal trade risks.
- Cybersecurity and data protection: SAP GRC continuously monitors cyber threats, safeguarding sensitive data.
- Identity and access governance: Ensures proper access controls, reducing security vulnerabilities.
- Integrated solutions: The software integrates seamlessly with existing systems for streamlined risk management.
Pricing
SAP GRC costs anywhere from $500 to $15,000 per license. Free demo available.
3. MetricStream GRC

Best for: Organizations requiring a scalable, integrated GRC platform with flexible and customizable modules for various compliance needs.
MetricStream is a cloud-based GRC platform that offers a variety of robust features to help organizations manage their enterprise risk management (ERM) program. They include internal audits, internal controls, and compliance with internal policies and external regulations.
The platform’s auditing tools can automate many internal audit processes such as risk assessments, control assessments, and incident management. This can help organizations streamline internal audits and improve audit efficiency.
Its centralized repository allows organizations to store audit trails and other audit documentation, which can facilitate collaboration between internal audit teams and other departments.
As a compliance management solution, MetricStream GRC can help organizations automate compliance tasks such as regulatory reporting and compliance training.
The platform also provides a way to track compliance activities and identify potential gaps in compliance. This can help organizations reduce their risk of non-compliance and associated fines or penalties.
MetricStream’s user-friendly interface makes it easy for users with varying levels of technical expertise to navigate the platform and complete GRC tasks.
Additionally, it offers robust integration capabilities, allowing it to connect with other enterprise systems such as ERP and CRM systems. This can help organizations streamline data collection and reporting for GRC activities.
Overall, MetricStream appears to be a comprehensive GRC platform that can help organizations improve their risk management, compliance, and internal audit processes.
Note that the specific features and benefits of MetricStream may vary depending on the specific needs of your organization.
A drawback to note is that its advanced customization may lead to complexity. Besides, it has a hefty license fee and requires ongoing maintenance costs.
Key features
- Intuitive reports and analytics: The platform provides built-in analytical dashboards and reports with rich visualizations and real-time insights to enable stakeholders to make informed decisions promptly.
- Integrated risk management: The GRC platform offers comprehensive risk management capabilities, allowing organizations to identify, assess, mitigate, and monitor risks across the enterprise.
- Audit management: It offers capabilities for managing internal audits and assessments efficiently.
Pricing
MetricStream GRC pricing is available upon request.
4. StandardFusion


Best for: Ideal for small to mid-sized businesses looking for a user-friendly GRC platform with easy deployment.
Compliance can be a complex process for organizations but StandardFusion makes it simple to understand.
StandardFusion stands out as a comprehensive GRC platform, offering a reliable solution for organizations seeking an integrated risk management solution.
This cloud-based platform excels in providing source solutions for risk management, audit management, compliance management, vendor management, policy management, privacy management, and compliance automation.
With a user-friendly interface, StandardFusion enhances the management of internal controls and fosters a risk-aware culture within organizations.
One of the key strengths of the software is its diverse deployment options, catering to the needs of organizations at different stages of growth.
Besides, it streamlines the compliance process by centralizing internal policies and procedures, making it a valuable tool for business users across various industries.
The platform’s robust features make it a complete security solution, ideal for audit purposes and ensuring adherence to multiple standards like ISO, SOC 2®, NIST, HIPAA, GDPR, and more.
StandardFusion’s emphasis on being a single source of truth for all compliance-related activities sets it apart, offering a seamless experience for users to manage their governance processes efficiently.
Its ability to adapt to organizational growth, coupled with its user-friendly design and focus on internal controls, makes it a top choice for organizations looking to enhance their risk management practices and maintain a strong compliance posture.
A downside of the software is that it may lack advanced features for complex GRC requirements. Also, it provides limited scalability for larger enterprises.
Key features:
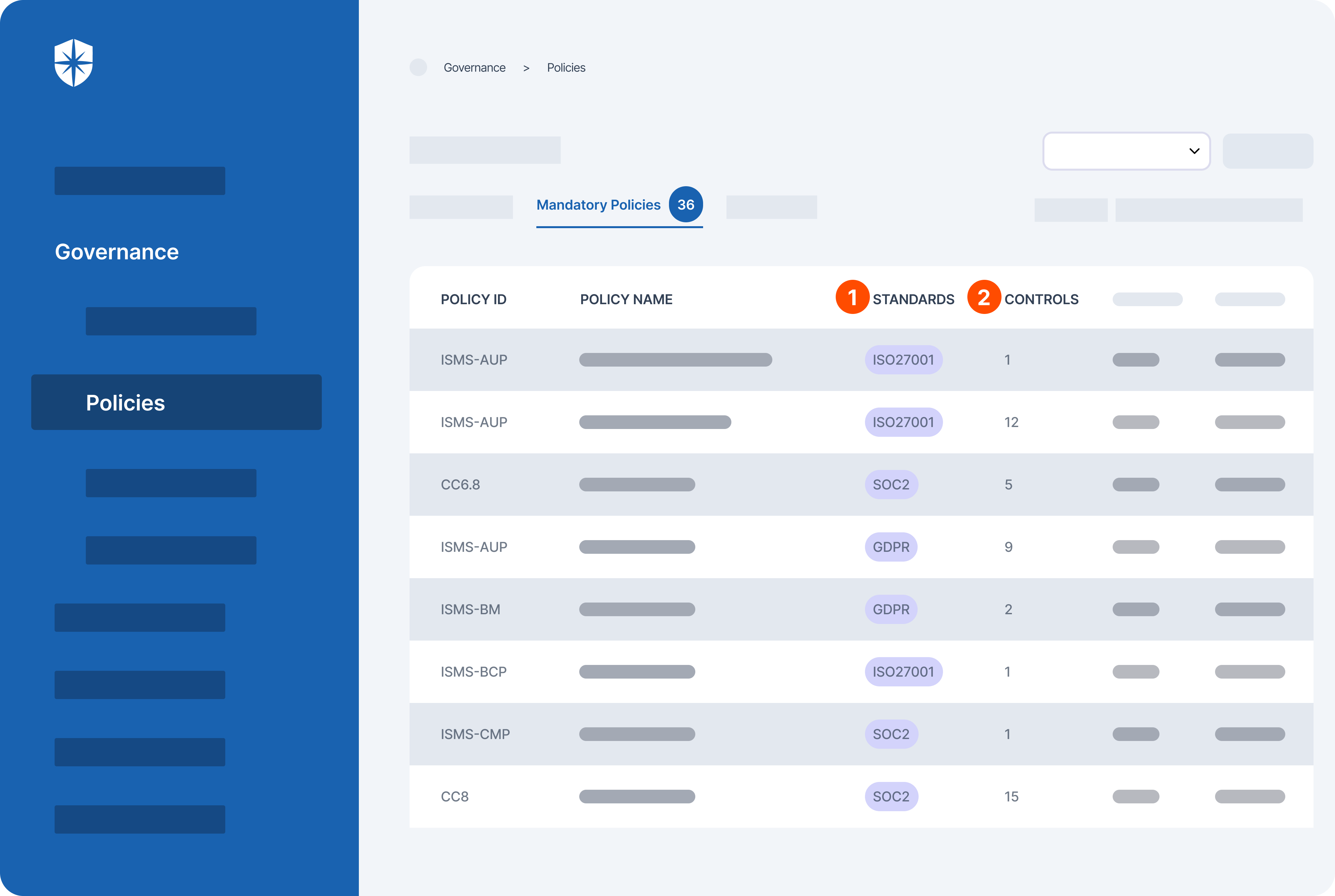
- Unified data environment: Organizations can use the tool to consolidate data from various sources to get a holistic view of internal controls, and compliance processes, and launch effective risk management strategies.
- Simplified compliance management: The platform breaks down compliance requirements into manageable steps, allowing businesses to track progress and identify any gaps.
- Scalability and flexibility: StandardFusion offers various deployment options to cater to organizational growth. Whether you’re a small startup or a large enterprise, the platform can adapt to your specific needs.
- Risk-aware culture: StandardFusion helps foster a risk-aware culture by making risk management a more accessible and collaborative process. It allows for easy identification, assessment, and mitigation of potential threats.
- Complete security solution: The software prioritizes data security with robust features to protect sensitive information. This ensures all GRC data is stored securely and meets audit purposes.
Pricing
Pricing starts from $1,500 per user, per month.
5. ServiceNow

Best for: Automation-focused approach to GRC, ideal for IT-heavy organizations.
With ServiceNow’s GRC software organizations get a comprehensive solution for managing compliance processes and mitigating potential risks by breaking down silos.
Designed to streamline auditing purposes, this cloud-based platform provides organizations with the tools necessary to safeguard their digital assets effectively.
One of the standout features of ServiceNow’s GRC software is its ability to offer insights into risks that could potentially impact organizational growth.
By centralizing compliance tools within a single platform, businesses can assess and address potential risks more efficiently, ensure regulatory compliance, and protect sensitive data.
The platform’s cloud-based GRC tools enable organizations to manage their compliance processes more effectively with greater flexibility and scalability. With the ability to automate various tasks, such as risk assessments and policy management, businesses can reduce the burden on their resources while ensuring continuous compliance.
The GRC software also offers a complete security solution that helps organizations identify and mitigate potential risks to their digital assets. With real-time visibility into compliance status and potential vulnerabilities, businesses can proactively address security threats before they escalate.
One downside to note about this software is that its initial setup and customization can be time-consuming. May also require additional modules for full GRC functionality.
Key features
- Integrated risk management: ServiceNow helps users identify, assess, and prioritize risks across the organization and develop plans to mitigate them.
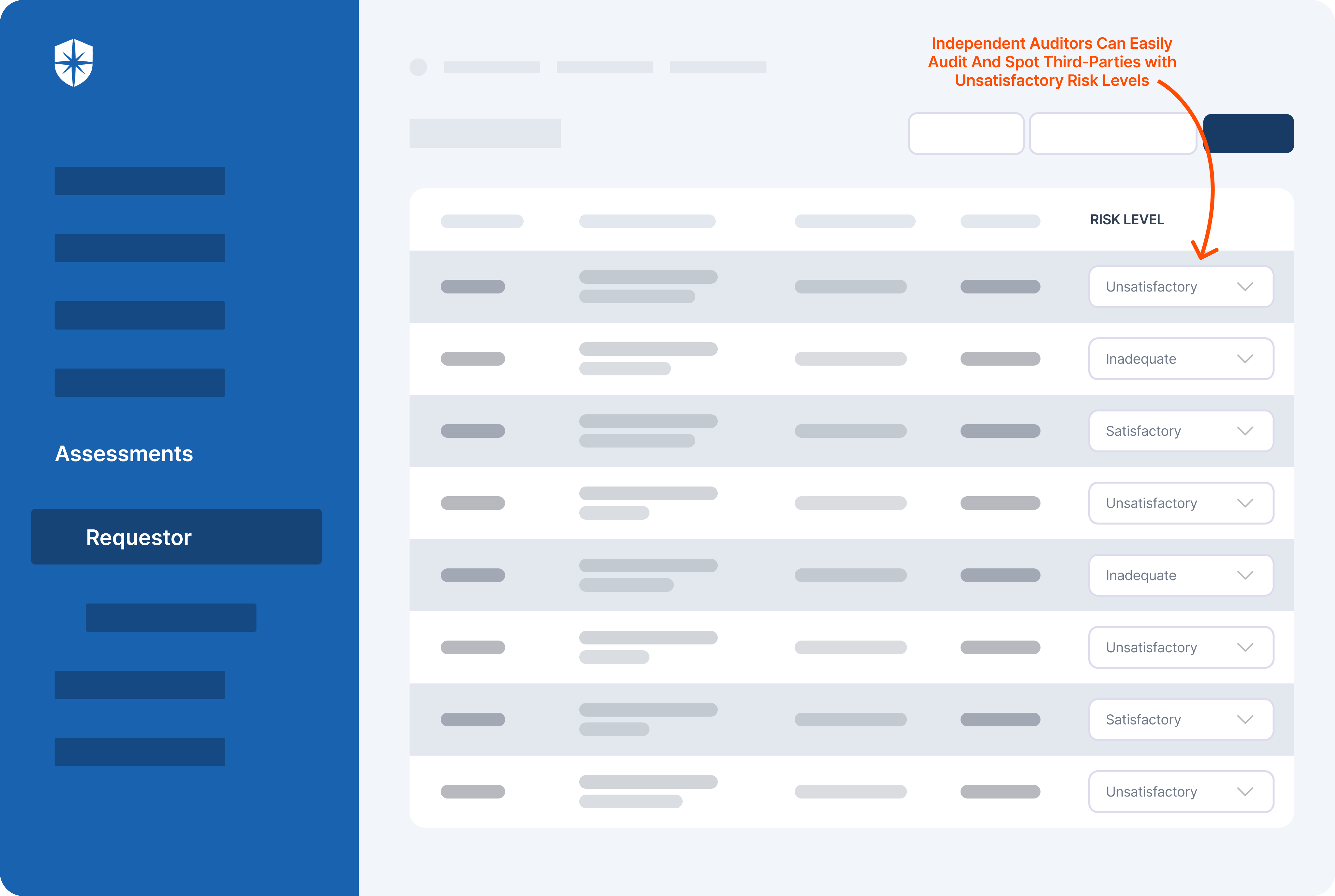
- Third-party risk management: The platform helps to reduce risk, and improve organizational resilience, and compliance by taking control of the third-party risk lifecycle.
- Business continuity management: It helps organizations plan for and recover from disasters
- Policy and compliance management: The software can automate and manage policy lifecycles and continuously monitor for compliance. This can help reduce errors and costs associated with manual processes and improve focus on higher-value tasks.
Pricing
ServiceNow pricing is available upon request.
6. Fusion Framework System


Best for: Organizations prioritizing risk management and business continuity planning. Provides comprehensive data visualization for clear risk insights.
Fusion Framework System is a comprehensive solution for enterprise risk management. With a robust risk management plan, it addresses security, compliance, and critical risks effectively.
The platform’s dashboard reporting provides real-time insights into risks, aiding informed decision-making.
The platform’s integrated risk management features streamline the risk management process, enhancing efficiency.
Fusion’s focus on third-party risk management ensures thorough risk assessment across all business relationships. It also helps users mitigate compliance risks through tailored solutions, ensuring adherence to regulations.
The platform excels in predictive risk analysis which enables proactive risk mitigation strategies. Its emphasis on critical risks ensures timely identification and response to potential threats.
Additionally, the dashboard reporting feature provides clear visibility into risk exposure, facilitating strategic planning. Fusion’s approach to risk management fosters a culture of proactive risk identification and mitigation.
With its comprehensive suite of tools, Fusion’s platform empowers organizations to manage risks effectively. It offers tailored solutions for diverse industries, ensuring relevance and applicability.
Note that the software relies on existing GRC tools for data input and may require additional integration efforts.
Key features
- Access controls/permissions: Organizations can use the software to manage user privileges and ensure data security and regulatory compliance.
- Activity tracking: It can monitor user actions and system events for compliance and risk management.
- Assessment management: It allows users to conduct and track risk assessments to identify and mitigate potential threats.
- Audit trail: Users can maintain a comprehensive record of system activities for accountability and compliance purposes.
- IT incident management: Fusion allows users to manage and resolve IT incidents efficiently to minimize disruptions and risks.
- IT risk management: With the software, users can identify, assess, and mitigate IT-related risks to protect assets and operations.
Pricing
Pricing is available upon request.
7. SAI360 GRC

Best for: Third-party access control and monitoring.
SAI360’s Integrated GRC Solution offers a cutting-edge approach to operational risk management, governance, and compliance.
It provides a comprehensive view of risks, empowering risk managers with valuable insights into risks for informed decision-making. The platform excels in corporate governance, facilitating the management of governance processes effectively.
With a focus on internal auditing and controls, SAI360 ensures robust internal controls and seamless third-party risk management. It stands out in regulatory compliance, helping organizations meet regulatory requirements effortlessly.
The platform’s policy management tools enable efficient creation, distribution, and enforcement of corporate governance policies. Additionally, the software streamlines incident management and conflict of interest processes.
SAI360’s GRC software is a powerful tool that integrates industry-leading technology to deliver efficiency and security. It features tailored modules that address disruptions proactively, safeguarding businesses across various sectors.
The platform’s advanced reporting and analytics capabilities enable quick risk assessment and opportunity identification, supporting data-driven decision-making.
A downside to note is that the software primarily focuses on third-party risk and may also require additional tools for additional GRC needs.
Key features
- Pre-configured modules: The software comes with pre-built modules for common risk management areas like operational risk, IT risk, and internal audit. This saves you time and effort in setting up the system and allows you to get started quickly.
- Robust reporting and analytics: SAI360 GRC provides comprehensive reporting and analytics tools that help you gain insights into your risks. This information can be used to identify trends, track progress, and make better risk management decisions.
- Industry-leading technology: The platform leverages advanced technology to streamline and secure risk management processes. This can include features like artificial intelligence, machine learning, and automation.
Pricing
Pricing is available upon request.
How to Choose the Best GRC Tool

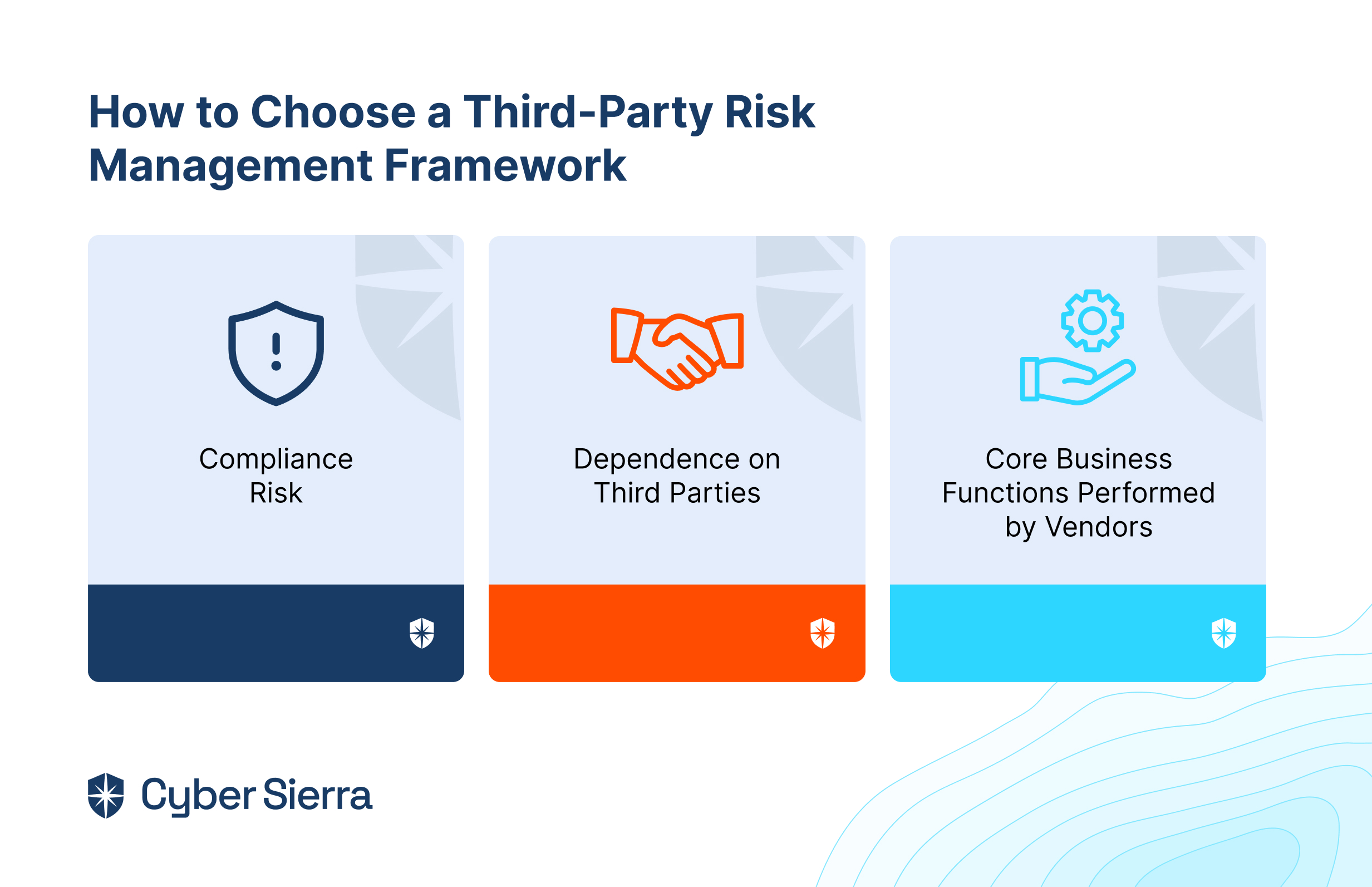
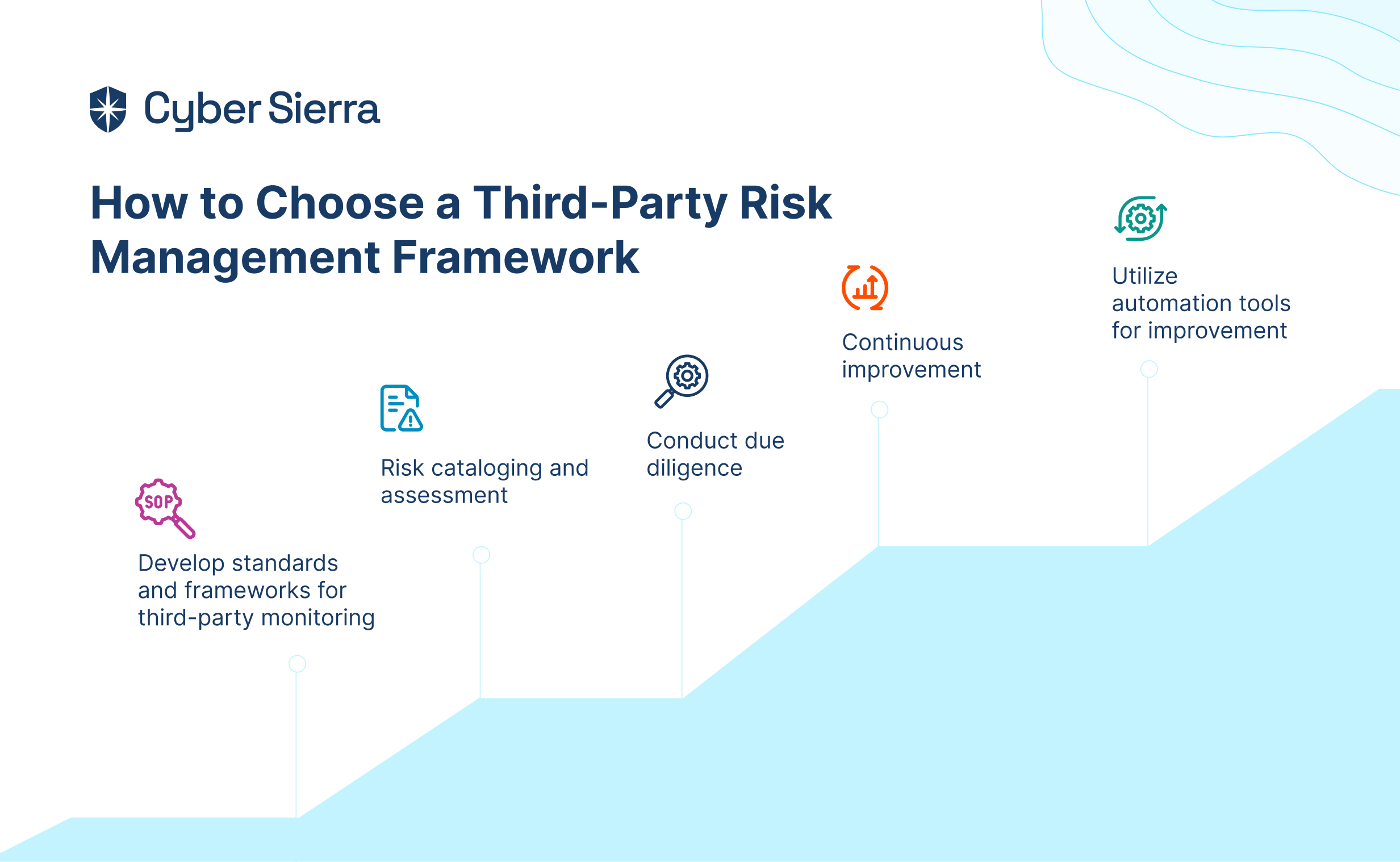
Knowing the best GRC tools is one thing but determining the right software for your business is another.While there are tons of GRC solutions on the market, there is no one-size-fits-all solution for all businesses.
Here are key considerations to help you choose the best GRC software for your specific business.
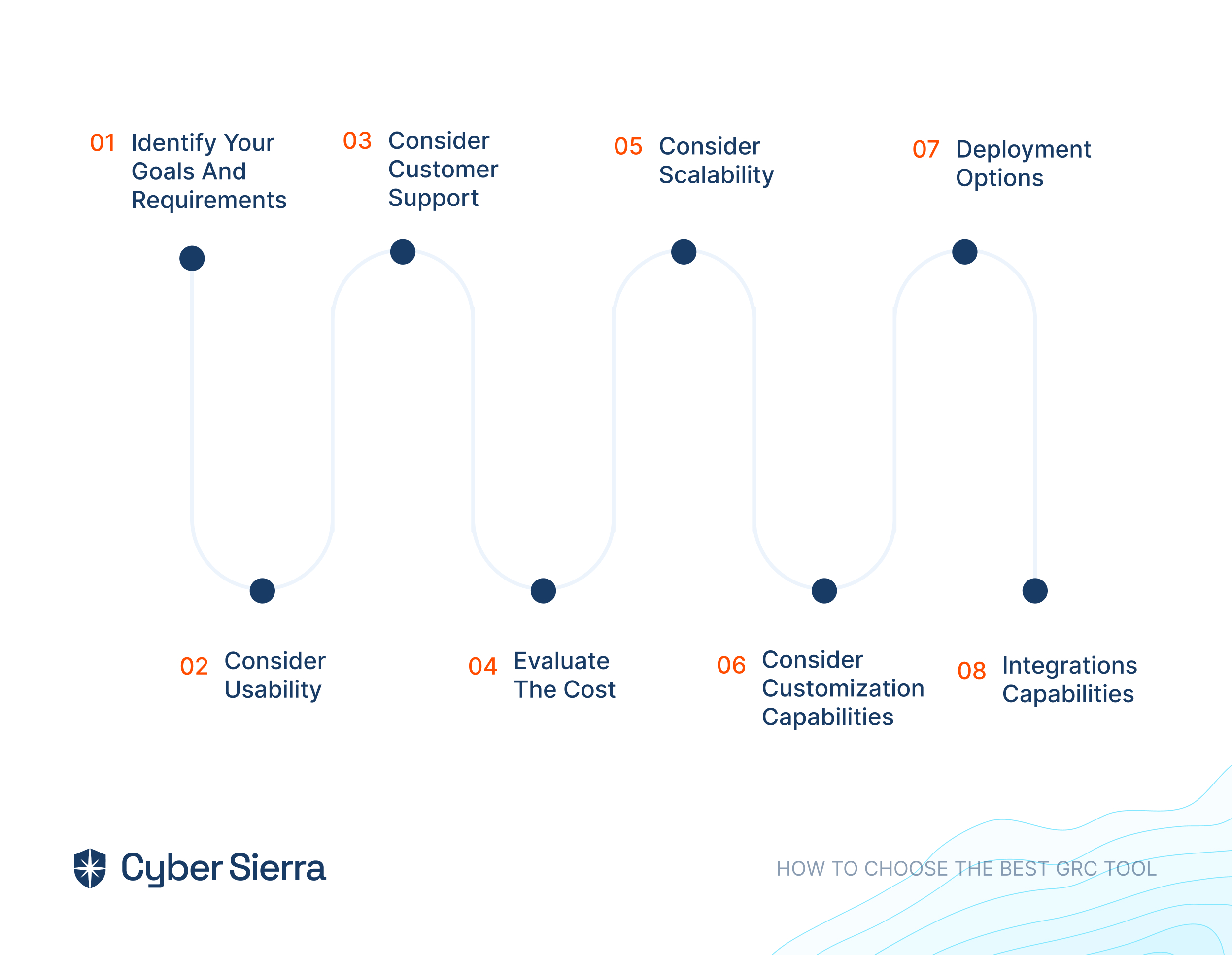
i. Identify Your Goals and Requirements
Clearly define your organization’s GRC objectives to ensure the chosen tool aligns with your specific needs and goals. Your goals may include regulatory compliance, risk management, policy enforcement, and more. This helps in selecting a solution tailored to address your unique challenges effectively.
ii. Consider Usability
Prioritize user-friendly GRC tools with intuitive interfaces and streamlined workflows to enhance adoption rates and facilitate efficient usage across your organization. Ease of navigation and accessibility features contribute to maximizing productivity and minimizing training requirements.
iii. Consider Customer Support
Assess the quality and responsiveness of the platform’s customer support services. Consider their availability, response times, and expertise levels, to ensure prompt assistance and resolution of any issues or inquiries that may arise during tool usage.
iv. Evaluate The Cost
Compare pricing models, including subscription fees, licensing options, and additional charges for features or support services. This will help you determine the overall cost-effectiveness of the GRC tool within your budget constraints while considering long-term scalability and ROI.
v. Consider Scalability
Choose a GRC tool capable of scaling alongside your organization’s growth and evolving needs. Ensure the tool can accommodate increased data volumes, user expansion, and additional functionalities without compromising performance or stability.
vi. Consider Customization Capabilities
Look for GRC solutions that offer customization options to tailor features, workflows, and reporting capabilities according to your organization’s unique requirements. This will help to ensure flexibility and alignment with specific business processes and compliance frameworks.
vii. Deployment Options
There are three types of deployment options for most GRC tools namely, cloud-based, on-premises, and hybrid. Consider how you want to access the software and assess its suitability based on factors like security, infrastructure preferences, etc.
viii. Integrations Capabilities
Prioritize GRC tools that offer seamless integration capabilities with your existing systems, applications, and data sources within your organization’s ecosystem. This will allow smooth data sharing, automation, and interoperability to streamline workflows and enhance efficiency.
How Cyber Sierra Can Help You

While most popular GRC tools manage risk and regulatory compliance, you need a robust and enterprise-wide tool that will help your organization manage all your GRC requirements in a centralized dashboard like Cyber Sierra does.
Cyber Sierra’s GRC offers unique features such as advanced risk analytics, customizable compliance frameworks, integration with emerging technologies like AI and machine learning, and more.
Additionally, the software focuses on specific industries as well as compliance standards which provide tailored solutions to meet diverse organizational needs.
Besides, it’s easy to use for both beginners and experts alike. Anyone in your team can use Cyber Sierra without prior technical knowledge.
Here is how you can automate your GRC processes with Cyber Sierra:
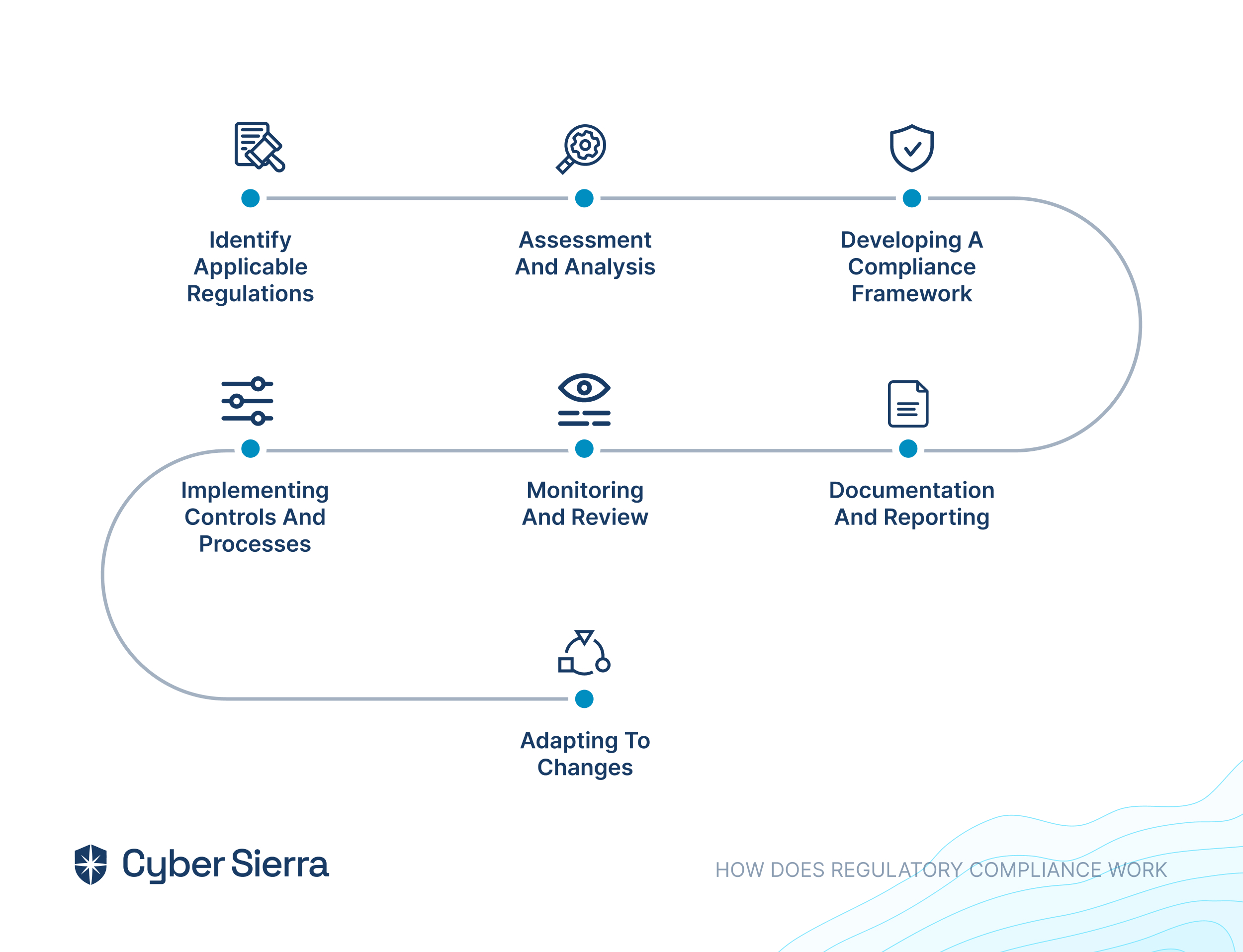
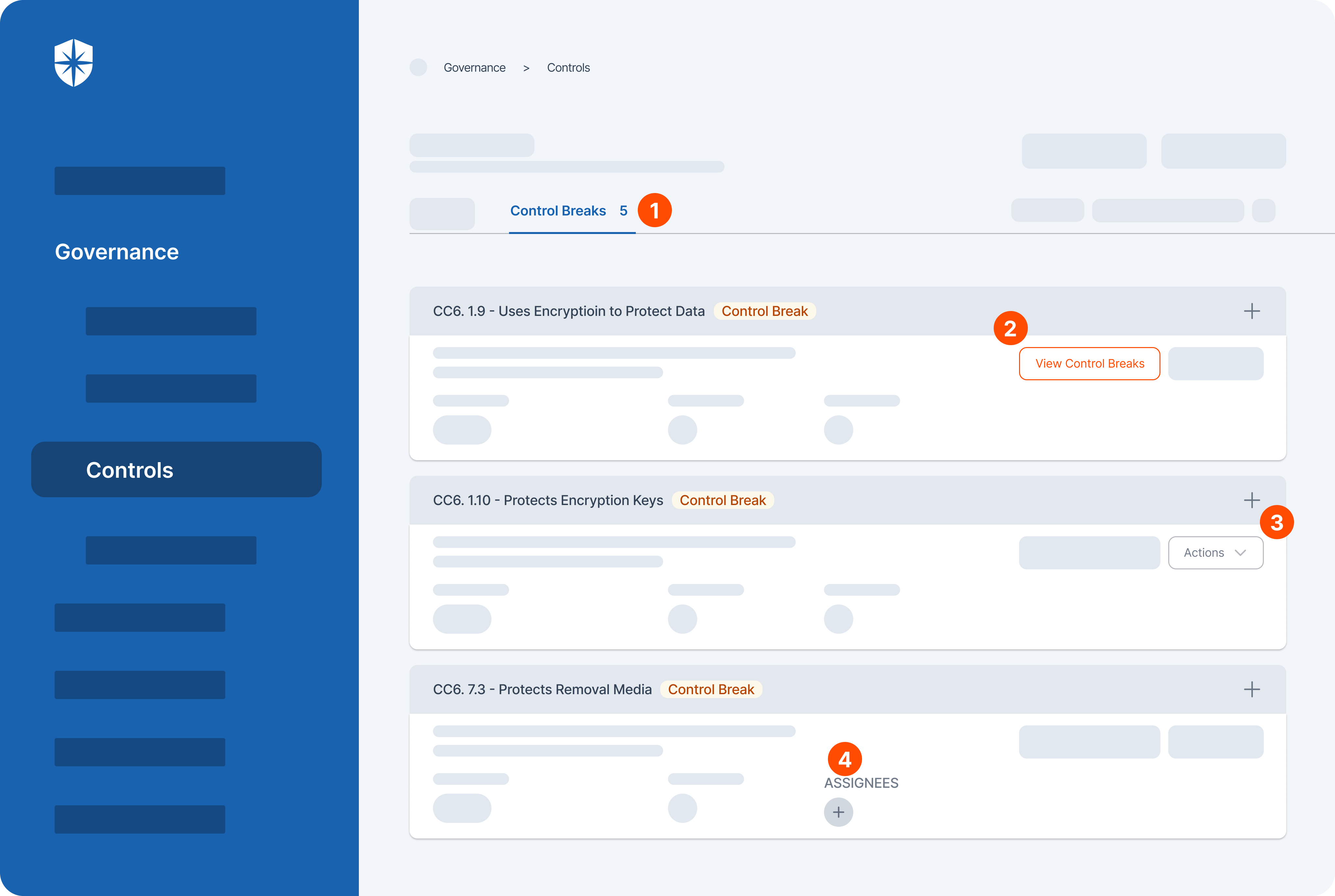
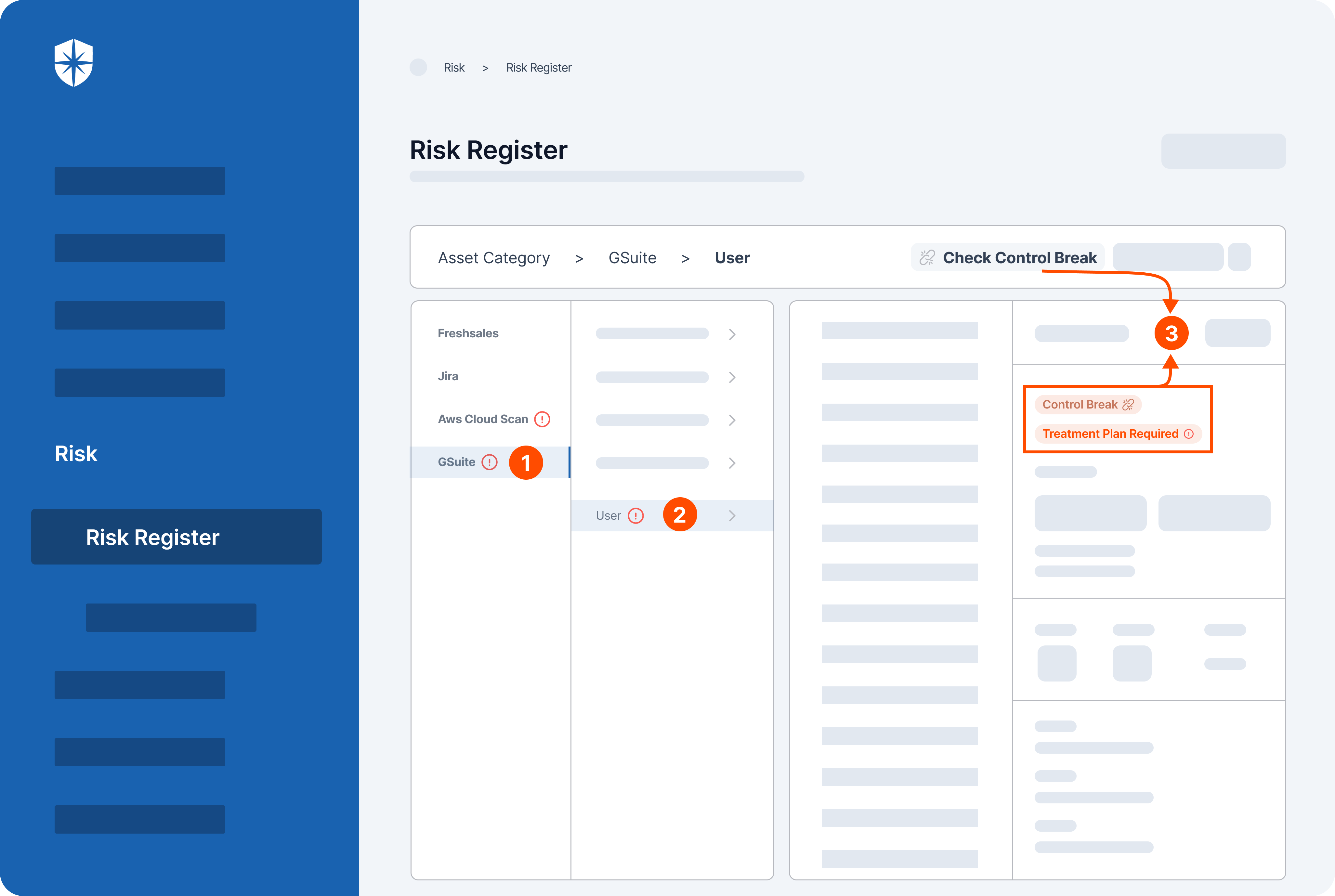
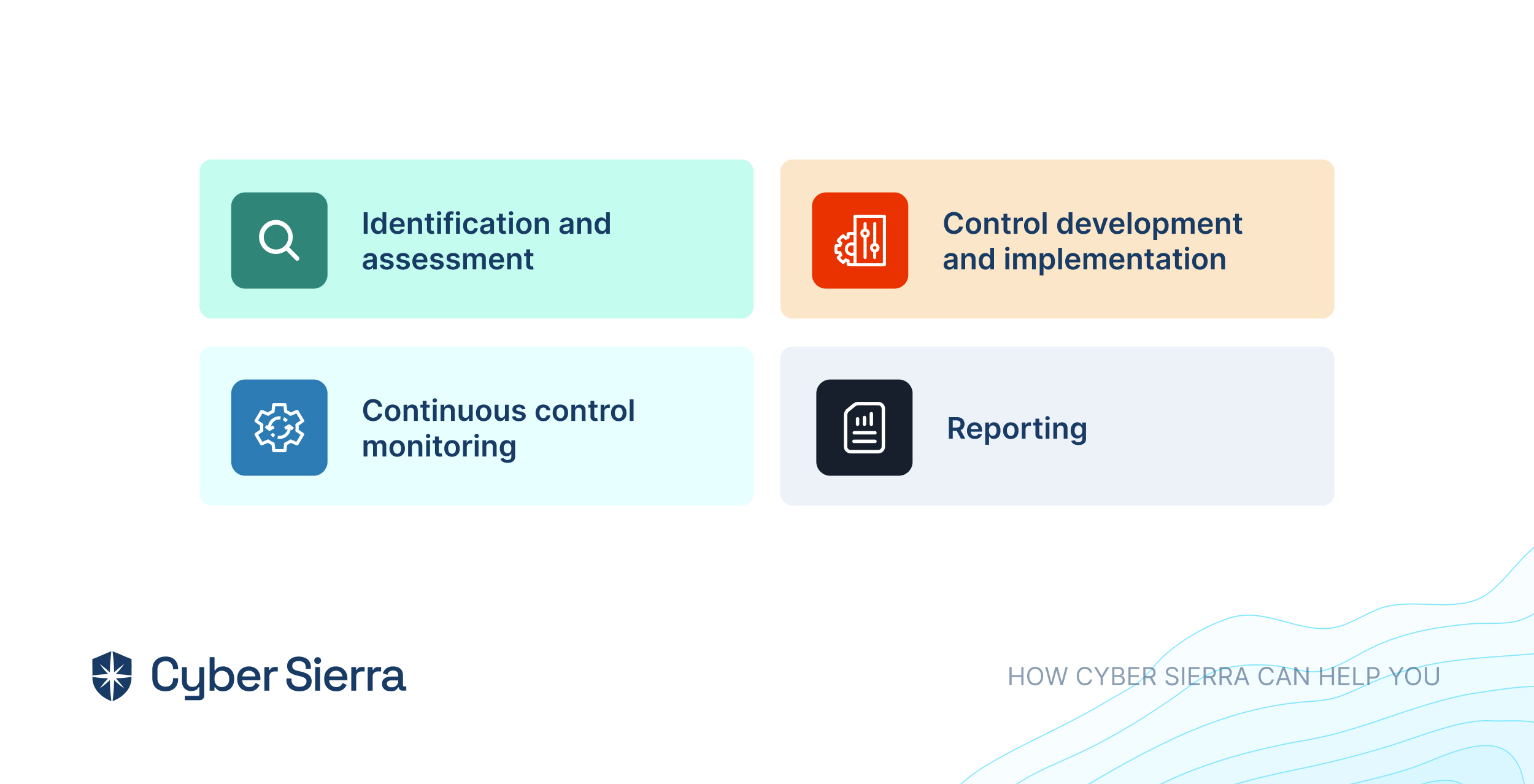
- Identification and assessment: Cyber Sierra’s GRC helps identify and assess all of your risks across all asset categories. This means you can get a comprehensive picture of your vulnerabilities from data to infrastructure.
- Control development and implementation: Once the risks are identified, the software then helps develop and implement controls to mitigate those risks. These controls can be anything from security policies to technical safeguards.
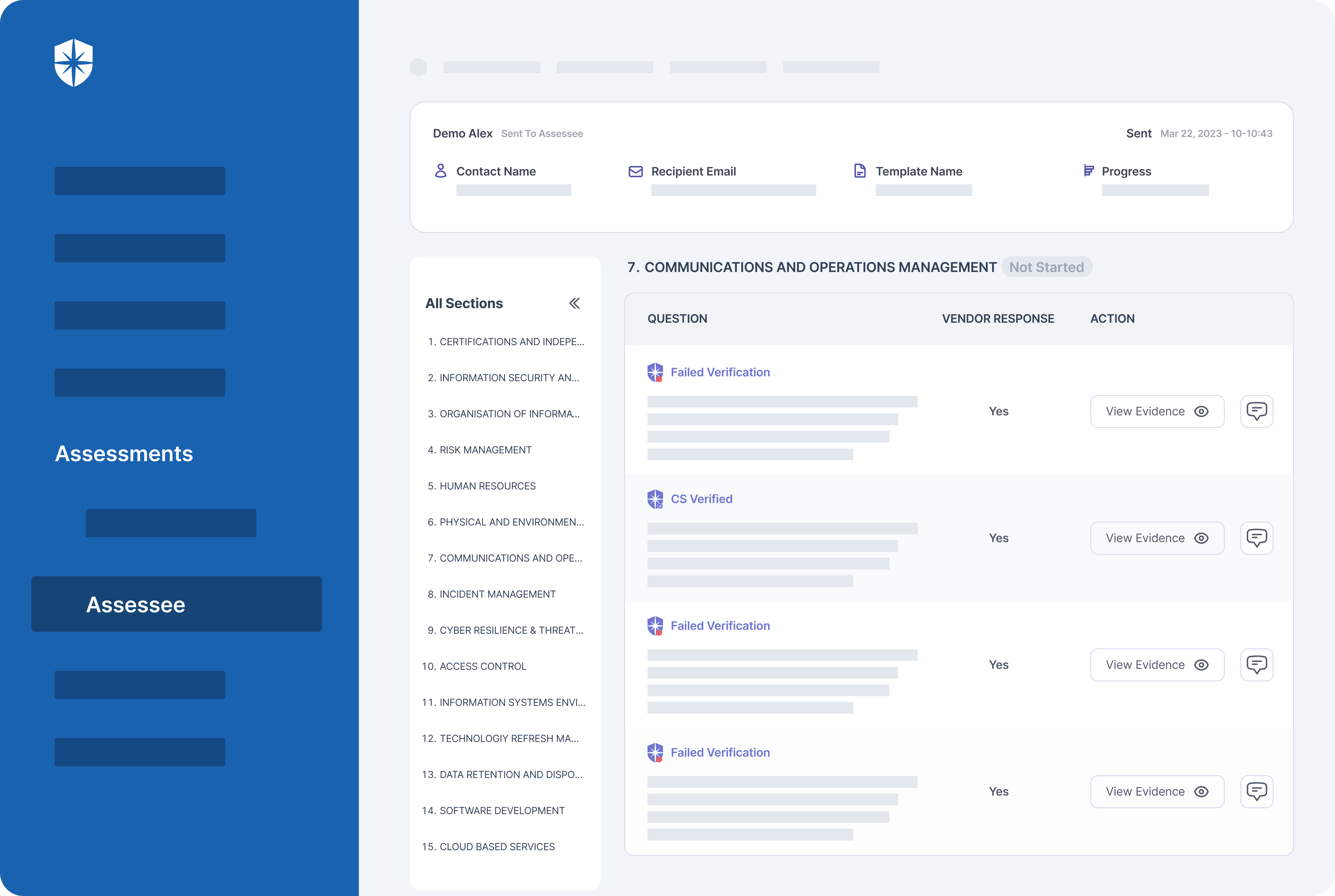
- Continuous control monitoring: Cyber Sierra’s GRC doesn’t stop at just identifying and mitigating risks. It also continuously monitors the effectiveness of those controls. This ensures that your controls are still working as intended over time.
- Reporting: Finally, Cyber Sierra’s GRC allows you to report on your GRC activities to stakeholders. This means you can easily generate reports that demonstrate your compliance posture to auditors, regulators, or other interested parties.
Automate your GRC processes and take complexity and guesswork out of compliance with Cyber Sierra today!





















A weekly newsletter sharing actionable tips for CTOs & CISOs to secure their software.
Thank you for subscribing!
Please check your email to confirm your email address.
Find out how we can assist you in
completing your compliance journey.